
Caterina di Jacopo di Benincasa, known as Catherine of Siena, was an Italian mystic and pious laywoman who engaged in papal and Italian politics through extensive letter-writing and advocacy. Canonized in 1461, she is revered as a saint and as a Doctor of the Church due to her extensive theological authorship. She is also considered to have influenced Italian literature.

Lorenzo Monaco was an Italian painter and miniaturist of the late Gothic to early Renaissance age. He was born Piero di Giovanni. Little is known about his youth, apart from the fact that he was apprenticed in Florence. He has been considered the last important exponent of the Giotto style, before the Renaissance revolution that came with Fra Angelico and Masaccio.

The Donner Party, sometimes called the Donner–Reed Party, were a group of American pioneers who migrated to California in a wagon train from the Midwest. Delayed by a multitude of mishaps, they spent the winter of 1846–1847 snowbound in the Sierra Nevada mountain range. Some of the migrants resorted to cannibalism to survive, primarily eating the bodies of those who had succumbed to starvation, sickness or extreme cold, but in one case two Native American guides were deliberately killed for this purpose.

Dangerfield F. Newby, was the oldest of John Brown's raiders, and one of the five black raiders. He died during Brown's raid on the federal armory in Harpers Ferry, Virginia.

The Loggia dei Lanzi, also called the Loggia della Signoria, is a building on a corner of the Piazza della Signoria in Florence, Italy, adjoining the Uffizi Gallery. It consists of wide arches open to the street. The arches rest on clustered pilasters with Corinthian capitals. The wide arches appealed so much to the Florentines that Michelangelo proposed that they should be continued all around the Piazza della Signoria.

Eleanor of Toledo, born Doña Leonor Álvarez de Toledo y Pimentel-Osorio, was a Spanish noblewoman and Duchess of Florence as the first wife of Cosimo I de' Medici. A keen businesswoman, she financed many of her husband's political campaigns and important buildings like the Pitti Palace. She ruled as regent of Florence during his frequent absences: Eleanor ruled during Cosimo's military campaigns in Genoa in 1541 and 1543, his illness from 1544 to 1545, and again at times when the war for the conquest of Siena (1551–1554). She founded many Jesuit churches. She is credited with being the first modern first lady or consort.

Cosmê Tura, also known as Il Cosmè or Cosimo Tura, was an Italian early-Renaissance painter and considered one of the founders of the School of Ferrara.

The Lovers of Teruel is a romance story that is alleged to have taken place in 1217 in the city of Teruel (Aragón).

The Black Death peaked in Europe between 1348 and 1350, with an estimated third of the continent's population ultimately succumbing to the disease. Often simply referred to as "The Plague", the Black Death had both immediate and long-term effects on human population across the world as one of the most devastating pandemics in human history, including a series of biological, social, economic, political and religious upheavals that had profound effects on the course of world history, especially European history. Symptoms of the Bubonic Plague included painful and enlarged or swollen lymph nodes, headaches, chills, fatigue, vomiting, and fevers, and within 3 to 5 days, 80% of the victims would be dead. Historians estimate that it reduced the total world population from 475 million to between 350 and 375 million. In most parts of Europe, it took nearly 80 years for population sizes to recover, and in some areas, it took more than 150 years.
Roderick Alleyn is a fictional character who first appeared in 1934. He is the policeman hero of the 32 detective novels of Ngaio Marsh. Marsh and her gentleman detective belong firmly in the Golden Age of Detective Fiction, although the last Alleyn novel, Light Thickens, was published in 1982.

The pyramid complex of Userkaf was built c. 2490 BC for the pharaoh Userkaf, founder of the 5th Dynasty of Egypt. It is located in the pyramid field at Saqqara, on the north-east of the step pyramid of Djoser. Constructed in dressed stone with a core of rubble, the pyramid is now ruined and resembles a conical hill in the sands of Saqqara. For this reason, it is known locally as El-Haram el-Maharbish, the "Heap of Stone", and was recognized as a royal pyramid by western archaeologists in the 19th century.

Maria Josepha of Bavaria was Holy Roman Empress, Queen of the Romans, Archduchess of Austria, Grand Duchess of Tuscany, among other titles, by her marriage to Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor. By birth, she was a Princess and Duchess of Bavaria as the daughter of Charles VII, Holy Roman Emperor, elector of Bavaria, and Archduchess Maria Amalia of Austria.

Pocong is a Javanese ghost that is said to be the soul of a dead person trapped in their shroud. Known in Indonesian as kain kafan, the shroud is the prescribed length of cloth used in Muslim burials to wrap the body of the dead person. The dead body is covered in white fabric tied over the head, under the feet, and on the neck.

The Black Death was one of the most devastating pandemics in human history, resulting in the deaths of an estimated 75 to 200 million people in Eurasia, and peaking in Eurasia from 1321 to 1353. Its migration followed the sea and land trading routes of the medieval world. This migration has been studied for centuries as an example of how the spread of contagious diseases is impacted by human society and economics.

The Black Death (1346–1353) had great effects on the art and literature of medieval societies that experienced it.

Mary "Mamie" Dickens was the eldest daughter of the English novelist Charles Dickens and his wife Catherine. She wrote a book of reminiscences about her father, and in conjunction with her aunt, Georgina Hogarth, she edited the first collection of his letters.

The Cronaca fiorentina di Marchionne di Coppo Stefani written by Baldassarre Bonaiuti is considered one of the best works written on the Black Death in Florence in the year 1348. It is the only known literary work by Bonaiuti. It was written in vulgar Latin. There is no information as to when he may have started his work, but he devoted much time on it in his retirement from about 1378 until his death, a period of seven years.
Laudomia Forteguerri was an accomplished Italian poet and a member of one of the most powerful families in the sixteenth-century Republic of Siena. She is considered by some historians to be Italy's earliest lesbian writer, and she was famous for her beauty, wit, and intelligence. In January 1553, Forteguerri led a group of women in helping with the construction of a defensive bastion to protect her city against an anticipated attack from Imperial Spanish forces. The attack and siege that followed in 1554–55 ultimately lead to the fall of the independent Republic. Forteguerri became a legendary figure in Sienese history and her legacy has lived on long after her death.
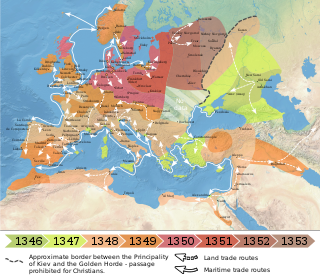
The Black Death was present in Italy between 1347-1348. Sicily and the Italian Peninsula was the first area in then Catholic Western Europe to be reached by the bubonic plague pandemic known as the Black Death, which reached the region by an Italian ship from the Crimea which landed in Messina in Sicily in October 1347.

The Coinage of the Republic of Siena are the coins minted by the Republic of Siena from the second half of the 12th century until the fall of the Republic of Siena exiled in Montalcino (Italy) in 1559, following the Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis.

















