Laconia or Lakonia is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word laconic—to speak in a blunt, concise way—is derived from the name of this region, a reference to the ancient Spartans who were renowned for their verbal austerity and blunt, often pithy remarks.
Messenia or Messinia is a regional unit in the southwestern part of the Peloponnese region, in Greece. Until the implementation of the Kallikratis plan on 1 January 2011, Messenia was a prefecture (nomos) covering the same territory. The capital and largest city of Messenia is Kalamata.
Neochori may refer to the following places:
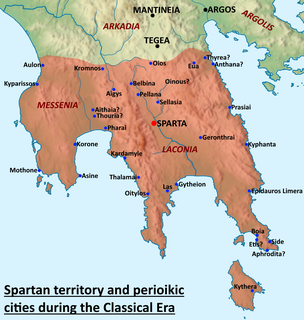
The Perioeci or Perioikoi were the second-tier citizens of the polis of Sparta until c. 200 BC. They lived in several dozen cities within Spartan territories, which were dependent on Sparta. The perioeci only had political rights in their own city, while the course of the Spartan state exclusively belonged to Spartan citizens, or Spartiates.

Asine was an ancient Greek city of ancient Argolis, located on the coast. It is mentioned by Homer in the Catalogue of Ships in the Iliad as one of the places subject to Diomedes, king of Argos. It is said to have been founded by the Dryopes, who originally dwelt on Mount Parnassus. In one of the early wars (740 BCE) between the Lacedaemonians and the Argives, the Asinaeans joined the former when they invaded the Argive territory under their king Nicander; but as soon as the Lacedaemonians returned home, the Argives laid siege to Asine and razed it to the ground, sparing only the temple of the Pythaëus Apollo. The Asinaeans escaped by sea; and the Lacedaemonians gave to them, after the end of the First Messenian War, a portion of the Messenian territory, where they built a new town. Nearly ten centuries after the destruction of the city its ruins were visited by Pausanias, who found the temple of Apollo still standing.

Asini is a village and a former municipality in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece, named after the ancient city of Asine. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Nafplio, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 136.873 km2. Population 5,340 (2011). The seat of the municipality was in Drepano.
Pigadia may refer to several locations in Greece:
Asine was a town of ancient Laconia. According to Strabo, it was situated between Amathus and Gythium. It was often under Spartan control. Polybius relates that Philip V of Macedon, in his invasion of Laconia, suffered a repulse before Asine (218 BCE), which appears from his narrative to have been near Gythium. Pausanias, in describing the same event as Polybius, says that Philip was repulsed before "Las", which originally stood on the summit of "Mount Asia". There can therefore be no doubt that the "Las" of Pausanias and the "Asine" of Polybius are the same place; and the resemblance between the names "Asia" and "Asine" probably led Polybius into the error of calling Las by the latter name; an error which was the more likely to arise, because Herodotus and Thucydides speak of the Messenian Asine as a town in Laconia, since Messenia formed a part of Laconia at the time when they wrote. The error of Polybius was perpetuated by Strabo and Stephanus of Byzantium. During the Roman period Asine belonged to Sparta although most of the other towns in the area were part of the Union of Free Laconians.
Kyparissia may refer to several places and jurisdictions in Greece :

The Swedish Institute at Athens was founded in 1946 and is one of 19 foreign archaeological institutes operating in Athens, Greece. The Institute is one of three Swedish research institutes in the Mediterranean, along with the Swedish Institute of Classical Studies in Rome and the Swedish Research Institute in Istanbul. Besides the premises in Athens the institute has an office in Stockholm and a guesthouse in Kavala. It also owns the Nordic Library along with the Danish Institute at Athens, the Finnish Institute at Athens and the Norwegian Institute at Athens.

The First Messenian War was a war between Messenia and Sparta. It began in 743 BC and ended in 724 BC, according to the dates given by Pausanias.

The regions of ancient Greece were areas identified by the ancient Greeks as geographical sub-divisions of the Hellenic world. These regions are described in the works of ancient historians and geographers, and in the legends and myths of the ancient Greeks.
Limnae or Limnai may refer to:
Pharae is an ancient city of Achaea.
Antheia was a figure in Greek mythology.
Hermione or Hermium or Hermion was a town at the southern extremity of Argolis, in the wider use of this term, but an independent city during the Classical period of Greek history, and possessing a territory named Hermionis (Ἑρμιονίς). The sea between the southern coast of Argolis and the island of Hydra was called after it the Hermionitic Gulf, which was regarded as distinct from the Argolic and Saronic Gulfs.
Polichna is a village in Poland.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.







