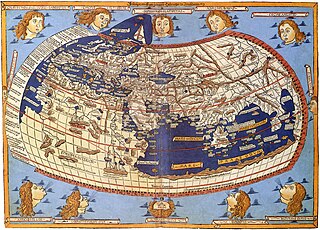
Cartography is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.

A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes.

Rococo, less commonly Roccoco, also known as Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and dramatic style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, and trompe-l'œil frescoes to create surprise and the illusion of motion and drama. It is often described as the final expression of the Baroque movement.

Guillaume Delisle, also spelled Guillaume de l'Isle, was a French cartographer known for his popular and accurate maps of Europe and the newly explored Americas.

Rose window is often used as a generic term applied to a circular window, but is especially used for those found in Gothic cathedrals and churches. The windows are divided into segments by stone mullions and tracery. The term rose window was not used before the 17th century and comes from the English flower name rose.

The Adam style is an 18th-century neoclassical style of interior design and architecture, as practised by Scottish architect William Adam and his sons, of whom Robert (1728–1792) and James (1732–1794) were the most widely known.

The applied arts are all the arts that apply design and decoration to everyday and essentially practical objects in order to make them aesthetically pleasing. The term is used in distinction to the fine arts, which are those that produce objects with no practical use, whose only purpose is to be beautiful or stimulate the intellect in some way. In practice, the two often overlap. Applied arts largely overlap with decorative arts, and the modern making of applied art is usually called design.
A cartouche is a rounded oblong frame for royal names in Egyptian hieroglyphs.

An Ex Libris from ex-librīs, also known as a bookplate, is a printed or decorative label pasted into a book, often on the front endpaper, to indicate ownership. Simple typographical bookplates are termed "book labels".

Pictorial maps depict a given territory with a more artistic rather than technical style. It is a type of map in contrast to road map, atlas, or topographic map. The cartography can be a sophisticated 3-D perspective landscape or a simple map graphic enlivened with illustrations of buildings, people and animals. They can feature all sorts of varied topics like historical events, legendary figures or local agricultural products and cover anything from an entire continent to a college campus. Drawn by specialized artists and illustrators, pictorial maps are a rich, centuries-old tradition and a diverse art form that ranges from cartoon maps on restaurant placemats to treasured art prints in museums.

Rigobert Bonne was a French cartographer, widely considered to be one of the most important cartographers of the late 18th century.

A cartouche is an oval or oblong design with a slightly convex surface, typically edged with ornamental scrollwork. It is used to hold a painted or low-relief design. Since the early 16th century, the cartouche is a scrolling frame device, derived originally from Italian cartuccia. Such cartouches are characteristically stretched, pierced and scrolling.
Borden D. Dent (1938–2000) was an American geographer and cartographer who served as professor emeritus and chairman of the Department of Geography and Anthropology at Georgia State University. His textbook, Cartography: Thematic Map Design, is one of the seminal texts in the field, and its sixth edition was reissued in 2009.
Italian Neoclassical interior design refers to furnishing and interior decorating trends in Italy which occurred during the Neoclassical period
Karl Johann Felsko was an architect and son of chief architect of Riga Johann Daniel Felsko. He was one of the leading architects during the building boom in Riga in the late 19th and early 20th century. There were more than 115 multi-story apartment and public buildings, factories and other buildings built following his designs. He was a master of Eclecticism style. His work, primarily seen in apartment buildings in Riga, included carefully placed filigree elements of order, cornices, pediments, garlands, cartouches, herms and more. His productivity decreased a great deal at the beginning of the 20th century with the introduction of Art Nouveau.

Cartography throughout the 14th-16th centuries played a significant role in the expansion of the kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula for a multitude of reasons. Primarily, the maps developed during this period served as navigational tools for maritime folk such as explorers, sailors and navigators. Mostly the expansion of the Crown of Aragon (which included the Kingdom of Aragon, Kingdom of Valencia and Kingdom of Majorca, together with the Principality of Catalonia, all its territories with seashore on the Mediterranean Sea. The Crown of Aragon controlled the routes across the Mediterranean Sea from the Kingdom of Jerusalem to Europe, as part of the commercial-trade route known as the Silk Road.

Cambriae Typus, the "model image of Wales", is the earliest published map of Wales as a separate country from the rest of Great Britain. Made by Elizabethan polymath Humphrey Llwyd in 1573, the map shows Wales stretching to the River Severn, including large areas of what is now England.

The Rococo Revival style emerged in Second Empire France and then was adapted in England. Revival of the rococo style was seen all throughout Europe during the 19th century within a variety of artistic modes and expression including decorative objects of art, paintings, art prints, furniture, and interior design. In much of Europe and particularly in France, the original rococo was regarded as a national style, and to many, its reemergence recalled national tradition. Rococo revival epitomized grandeur and luxury in European style and was another expression of 19th century romanticism and the growing interest and fascination with natural landscape.

The Army Headquarters Building, also known as the Stone Palace and the Baumgarten's Palace, is located in Serbia, in Belgrade at 33 Kneza Miloša street. It was built in the period from 1924 to 1928 after the design of the architect, Russian immigrant, Vasily Wilhelm Baumgarten. This monumental and decorative building represents one of the best examples of public buildings erected in Belgrade in the period between two World Wars in the style of academism. After the Second World War in the time of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, it was the used as the headquarters of the Yugoslav People's Army. Since 1984 the building has been under the protection of the country and has the status of cultural monument.

J. R. R. Tolkien's maps, depicting his fictional Middle-earth and other places in his legendarium, helped him with plot development, guided the reader through his often complex stories, and contributed to the impression of depth and worldbuilding in his writings.
















