Related Research Articles

In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part of biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential.

A nuclease is an enzyme capable of cleaving the phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides of nucleic acids. Nucleases variously effect single and double stranded breaks in their target molecules. In living organisms, they are essential machinery for many aspects of DNA repair. Defects in certain nucleases can cause genetic instability or immunodeficiency. Nucleases are also extensively used in molecular cloning.

Exodeoxyribonuclease V is an enzyme of E. coli that initiates recombinational repair from potentially lethal double strand breaks in DNA which may result from ionizing radiation, replication errors, endonucleases, oxidative damage, and a host of other factors. The RecBCD enzyme is both a helicase that unwinds, or separates the strands of DNA, and a nuclease that makes single-stranded nicks in DNA. It catalyses exonucleolytic cleavage in either 5′- to 3′- or 3′- to 5′-direction to yield 5′-phosphooligonucleotides.
RecQ helicase is a family of helicase enzymes initially found in Escherichia coli that has been shown to be important in genome maintenance. They function through catalyzing the reaction ATP + H2O → ADP + P and thus driving the unwinding of paired DNA and translocating in the 3' to 5' direction. These enzymes can also drive the reaction NTP + H2O → NDP + P to drive the unwinding of either DNA or RNA.
In molecular biology, endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain. Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically, while many, typically called restriction endonucleases or restriction enzymes, cleave only at very specific nucleotide sequences. Endonucleases differ from exonucleases, which cleave the ends of recognition sequences instead of the middle (endo) portion. Some enzymes known as "exo-endonucleases", however, are not limited to either nuclease function, displaying qualities that are both endo- and exo-like. Evidence suggests that endonuclease activity experiences a lag compared to exonuclease activity.

Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) is a pathway that repairs double-strand breaks in DNA. NHEJ is referred to as "non-homologous" because the break ends are directly ligated without the need for a homologous template, in contrast to homology directed repair(HDR), which requires a homologous sequence to guide repair. NHEJ is active in both non-dividing and proliferating cells, while HDR is not readily accessible in non-dividing cells. The term "non-homologous end joining" was coined in 1996 by Moore and Haber.

RecA is a 38 kilodalton protein essential for the repair and maintenance of DNA. A RecA structural and functional homolog has been found in every species in which one has been seriously sought and serves as an archetype for this class of homologous DNA repair proteins. The homologous protein is called RAD51 in eukaryotes and RadA in archaea.

Triple-stranded DNA is a DNA structure in which three oligonucleotides wind around each other and form a triple helix. In triple-stranded DNA, the third strand binds to a B-form DNA double helix by forming Hoogsteen base pairs or reversed Hoogsteen hydrogen bonds.
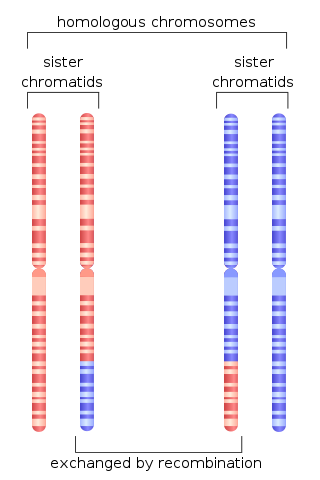
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids.
A nick is a discontinuity in a double stranded DNA molecule where there is no phosphodiester bond between adjacent nucleotides of one strand typically through damage or enzyme action. Nicks allow DNA strands to untwist during replication, and are also thought to play a role in the DNA mismatch repair mechanisms that fix errors on both the leading and lagging daughter strands.

In microbiology, genetics, cell biology, and molecular biology, competence is the ability of a cell to alter its genetics by taking up extracellular ("naked") DNA from its environment in the process called transformation. Competence may be differentiated between natural competence, a genetically specified ability of bacteria which is thought to occur under natural conditions as well as in the laboratory, and induced or artificial competence, which arises when cells in laboratory cultures are treated to make them transiently permeable to DNA. Competence allows for rapid adaptation and DNA repair of the cell. This article primarily deals with natural competence in bacteria, although information about artificial competence is also provided.
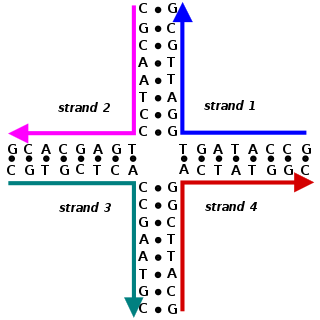
A Holliday junction is a branched nucleic acid structure that contains four double-stranded arms joined. These arms may adopt one of several conformations depending on buffer salt concentrations and the sequence of nucleobases closest to the junction. The structure is named after Robin Holliday, the molecular biologist who proposed its existence in 1964.

Slipped strand mispairing (SSM),, is a mutation process which occurs during DNA replication. It involves denaturation and displacement of the DNA strands, resulting in mispairing of the complementary bases. Slipped strand mispairing is one explanation for the origin and evolution of repetitive DNA sequences.
Recombinases are genetic recombination enzymes.
In molecular biology, a displacement loop or D-loop is a DNA structure where the two strands of a double-stranded DNA molecule are separated for a stretch and held apart by a third strand of DNA. An R-loop is similar to a D-loop, but in this case the third strand is RNA rather than DNA. The third strand has a base sequence which is complementary to one of the main strands and pairs with it, thus displacing the other complementary main strand in the region. Within that region the structure is thus a form of triple-stranded DNA. A diagram in the paper introducing the term illustrated the D-loop with a shape resembling a capital "D", where the displaced strand formed the loop of the "D".
The RecF pathway, also called the RecFOR pathway, is a pathway of homologous recombination that repairs DNA in bacteria. It repairs breaks that occur on only one of DNA's two strands, known as single-strand gaps. The RecF pathway can also repair double-strand breaks in DNA when the RecBCD pathway, another pathway of homologous recombination in bacteria, is inactivated by mutations. Like the RecBCD pathway, the RecF pathway requires RecA for strand invasion. The two pathways are also similar in their phases of branch migration, in which the Holliday junction slides in one direction, and resolution, in which the Holliday junctions are cleaved apart by enzymes.

Synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA) is a major mechanism of homology-directed repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Although many of the features of SDSA were first suggested in 1976, the double-Holliday junction model proposed in 1983 was favored by many researchers. In 1994, studies of double-strand gap repair in Drosophila were found to be incompatible with the double-Holliday junction model, leading researchers to propose a model they called synthesis-dependent strand annealing. Subsequent studies of meiotic recombination in S. cerevisiae found that non-crossover products appear earlier than double-Holliday junctions or crossover products, challenging the previous notion that both crossover and non-crossover products are produced by double-Holliday junctions and leading the authors to propose that non-crossover products are generated through SDSA.
Crossover junction endodeoxyribonuclease, also known as Holliday junction resolvase, Holliday junction endonuclease, Holliday junction-cleaving endonuclease, Holliday junction-resolving endoribonuclease, crossover junction endoribonuclease, and cruciform-cutting endonuclease, is an enzyme involved in DNA repair and homologous recombination. Specifically, it performs endonucleolytic cleavage that results in single-stranded crossover between two homologous DNA molecules at the Holliday junction to produce recombinant DNA products for chromosomal segregation. This process is known as Holliday junction resolution.
No-SCAR genome editing is an editing method that is able to manipulate the Escherichia coli genome. The system relies on recombineering whereby DNA sequences are combined and manipulated through homologous recombination. No-SCAR is able to manipulate the E. coli genome without the use of the chromosomal markers detailed in previous recombineering methods. Instead, the λ-Red recombination system facilitates donor DNA integration while Cas9 cleaves double-stranded DNA to counter-select against wild-type cells. Although λ-Red and Cas9 genome editing are widely used technologies, the no-SCAR method is novel in combining the two functions; this technique is able to establish point mutations, gene deletions, and short sequence insertions in several genomic loci with increased efficiency and time sensitivity.
Bacterial recombination is a type of genetic recombination in bacteria characterized by DNA transfer from one organism called donor to another organism as recipient. This process occurs in three main ways:
References
- Amundsen SK, Sharp JW, Smith GR (2016) RecBCD Enzyme "Chi Recognition" Mutants Recognize Chi Recombination Hotspots in the Right DNA Context. Genetics 204(1):139-52. PMID 27401752
- Taylor AF, Amundsen SK, Smith GR (2016) Unexpected DNA context-dependence identifies a new determinant of Chi recombination hotspots. Nucleic Acids Res. 44(17):8216-28. PMID 27330137
- Smith GR. (2012). How RecBCD Enzyme and Chi Promote DNA Break Repair and Recombination: a Molecular Biologist's View. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 76(2): 217-28. PMID 22688812
- Dillingham MS, Kowalczykowski SC. (2008). RecBCD enzyme and the repair of double-stranded DNA breaks. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 72(4): 642-671. PMID 19052323
- Amundsen SK, Taylor AF, Reddy M, Smith GR. (2007). Intersubunit signaling in RecBCD enzyme, a complex protein machine regulated by Chi hot spots. Genes Dev 21(24): 3296-3307. PMID 18079176
- Stahl FW. (2005). Chi: A little sequence controls a big enzyme. Genetics 170(2): 487–493. PMID 15980270