
Copra is the dried meat or kernel of the coconut, which is the fruit of the coconut palm. Coconut oil is extracted from copra, making it an important agricultural commodity for many coconut-producing countries. It also yields de-fatted coconut cake after oil extraction, which is mainly used as feed for livestock.

Coconut oil, or copra oil, is an edible oil extracted from the kernel or meat of mature coconuts harvested from the coconut palm. It has various applications. Because of its high saturated fat content, it is slow to oxidize and, thus, resistant to rancidification, lasting up to six months at 24 °C (75 °F) without spoiling.

A cash crop or profit crop is an agricultural crop which is grown to sell for profit. It is typically purchased by parties separate from a farm. The term is used to differentiate marketed crops from subsistence crops, which are those fed to the producer's own livestock or grown as food for the producer's family. In earlier times cash crops were usually only a small part of a farm's total yield, while today, especially in developed countries, almost all crops are mainly grown for revenue. In the least developed countries, cash crops are usually crops which attract demand in more developed nations, and hence have some export value.

Coconut milk is an opaque, milky-white liquid extracted from the grated pulp of mature coconuts. The opacity and rich taste of coconut milk is due to its high oil content, most of which is saturated fat. Coconut milk is a traditional food ingredient used in Southeast Asia, Oceania, South Asia, and East Africa. It is also used for cooking in the Caribbean, tropical Latin America, and West Africa, where coconuts were introduced during the colonial era.

Agriculture in the Philippines employs 27.7% of the Filipino workforce as of 2017, according to the World Bank

Coconut production plays an important role in the national economy of the Philippines. According to figures published in December 2009 by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, it is the world's largest producer of coconuts, producing 19,500,000 tonnes in 2009. Production in the Philippines is generally concentrated in medium-sized farms.
Coconut production plays an important role in the national economy of Indonesia. According to figures published in December 2009 by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, it is the world's second largest producer of coconuts, producing 15,319,500 tonnes in 2009.
Coconut production plays an important role in the national economy of India. According to figures published in December 2009 by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, India is the world's third largest producer of coconuts, producing 10,894,000 tonnes in 2009.
Coconut production contributes to the national economy of Brazil. According to figures published in December 2009 by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, it is the world's fourth-largest producer of coconuts, producing 2,759,044 tonnes in 2009.
Coconut production contributes to the national economy of Sri Lanka. According to figures published in December 2009 by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, it is the world's fifth largest producer of coconuts, producing 2,200,000 tonnes in 2009.

Coconut production contributes to the national economy of Thailand. According to figures published in December 2009 by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, it is the world's sixth largest producer of coconuts, producing 1,721,640 tonnes in 2009. In 2012 it was reported that Thailand had 216,000 hectares of coconut palm plantations and produced 845 million whole coconuts.
Coconut production contributes to the national economy of Mexico. According to figures published in December 2009 by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, it is the world's seventh largest producer of coconuts, producing 1,246,400 tonnes in 2009.

There were 795 million undernourished people in the world in 2014, a decrease of 216 million since 1990, despite the fact that the world already produces enough food to feed everyone—7 billion people—and could feed more than that—12 billion people.
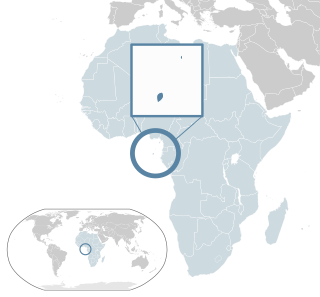
Santomean cuisine comprises the cuisine, dishes and foods of São Tomé and Príncipe, a Portuguese-speaking island nation in the Gulf of Guinea, off the western equatorial coast of Central Africa. The country consists of two archipelagos around the two main islands: São Tomé and Príncipe, located about 140 kilometres (87 mi) apart and about 250 and 225 kilometres, respectively, off the northwestern coast of Gabon.

In 2013, the island country Niue produced 3,200 tonnes of coconuts valued at INT$385,830. Coconut is a cash crop on the island, which is converted to derivatives such as copra and coconut cream in tinned form, and also exported. Originally, the island had a profusion of coconut trees reflected in the country's name, Niue, in the local language. The Niue Development Board is responsible for planning and execution of schemes of agricultural produce, including coconut and related products.

A staple food, food staple, or simply a staple, is a food that is eaten routinely and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for a given people, supplying a large fraction of energy needs and generally forming a significant proportion of the intake of other nutrients as well. A staple food of a specific society may be eaten as often as every day or every meal, and most people live on a diet based on just a small number of food staples. Specific staples vary from place to place, but typically are inexpensive or readily available foods that supply one or more of the macronutrients needed for survival and health: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Typical examples include tubers and roots, grains, legumes, and seeds.














