Laminar flow is the property of fluid particles in fluid dynamics to follow smooth paths in layers, with each layer moving smoothly past the adjacent layers with little or no mixing. At low velocities, the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing, and adjacent layers slide past one another smoothly. There are no cross-currents perpendicular to the direction of flow, nor eddies or swirls of fluids. In laminar flow, the motion of the particles of the fluid is very orderly with particles close to a solid surface moving in straight lines parallel to that surface. Laminar flow is a flow regime characterized by high momentum diffusion and low momentum convection.
In thermal fluid dynamics, the Nusselt number is the ratio of convective to conductive heat transfer at a boundary in a fluid. Convection includes both advection and diffusion (conduction). The conductive component is measured under the same conditions as the convective but for a hypothetically motionless fluid. It is a dimensionless number, closely related to the fluid's Rayleigh number.

A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant.
In thermodynamics, the heat transfer coefficient or film coefficient, or film effectiveness, is the proportionality constant between the heat flux and the thermodynamic driving force for the flow of heat. It is used in calculating the heat transfer, typically by convection or phase transition between a fluid and a solid. The heat transfer coefficient has SI units in watts per square meter per kelvin (W/m²K).
There are two different Bejan numbers (Be) used in the scientific domains of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics. Bejan numbers are named after Adrian Bejan.

A falling film evaporator is an industrial device to concentrate solutions, especially with heat sensitive components. The evaporator is a special type of heat exchanger.
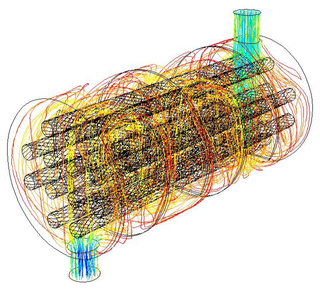
A shell-and-tube heat exchanger is a class of heat exchanger designs. It is the most common type of heat exchanger in oil refineries and other large chemical processes, and is suited for higher-pressure applications. As its name implies, this type of heat exchanger consists of a shell with a bundle of tubes inside it. One fluid runs through the tubes, and another fluid flows over the tubes to transfer heat between the two fluids. The set of tubes is called a tube bundle, and may be composed of several types of tubes: plain, longitudinally finned, etc.

Fouling is the accumulation of unwanted material on solid surfaces. The fouling materials can consist of either living organisms (biofouling) or a non-living substance. Fouling is usually distinguished from other surface-growth phenomena in that it occurs on a surface of a component, system, or plant performing a defined and useful function and that the fouling process impedes or interferes with this function.
A plate heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger that uses metal plates to transfer heat between two fluids. This has a major advantage over a conventional heat exchanger in that the fluids are exposed to a much larger surface area because the fluids are spread out over the plates. This facilitates the transfer of heat, and greatly increases the speed of the temperature change. Plate heat exchangers are now common and very small brazed versions are used in the hot-water sections of millions of combination boilers. The high heat transfer efficiency for such a small physical size has increased the domestic hot water (DHW) flowrate of combination boilers. The small plate heat exchanger has made a great impact in domestic heating and hot-water. Larger commercial versions use gaskets between the plates, whereas smaller versions tend to be brazed.

Slurry ice is a phase changing refrigerant made up of millions of ice "micro-crystals" formed and suspended within a solution of water and a freezing point depressant. Some compounds used in the field are salt, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, alcohols like isobutyl and ethanol, and sugars like sucrose and glucose. Slurry ice has greater heat absorption compared to single phase refrigerants like brine, because the melting enthalpy of the ice is also used.
Concentric Tube Heat Exchangers are used in a variety of industries for purposes such as material processing, food preparation, and air-conditioning. They create a temperature driving force by passing fluid streams of different temperatures parallel to each other, separated by a physical boundary in the form of a pipe. This induces forced convection, transferring heat to/from the product.

In chemical engineering, a jacketed vessel is a container that is designed for controlling temperature of its contents, by using a cooling or heating "jacket" around the vessel through which a cooling or heating fluid is circulated.

In fluid dynamics, the Reynolds number is a dimensionless quantity that helps predict fluid flow patterns in different situations by measuring the ratio between inertial and viscous forces. At low Reynolds numbers, flows tend to be dominated by laminar (sheet-like) flow, while at high Reynolds numbers, flows tend to be turbulent. The turbulence results from differences in the fluid's speed and direction, which may sometimes intersect or even move counter to the overall direction of the flow. These eddy currents begin to churn the flow, using up energy in the process, which for liquids increases the chances of cavitation.

Pumpable icetechnology (PIT) uses thin liquids, with the cooling capacity of ice. Pumpable ice is typically a slurry of ice crystals or particles ranging from 5 micrometers to 1 cm in diameter and transported in brine, seawater, food liquid, or gas bubbles of air, ozone, or carbon dioxide.
In engineering, physics, and chemistry, the study of transport phenomena concerns the exchange of mass, energy, charge, momentum and angular momentum between observed and studied systems. While it draws from fields as diverse as continuum mechanics and thermodynamics, it places a heavy emphasis on the commonalities between the topics covered. Mass, momentum, and heat transport all share a very similar mathematical framework, and the parallels between them are exploited in the study of transport phenomena to draw deep mathematical connections that often provide very useful tools in the analysis of one field that are directly derived from the others.
A climbing/falling film plate evaporator is a specialized type of evaporator in which a thin film of liquid is passed over a rising and falling plate to allow the evaporation process to occur. It is an extension of the falling film evaporator, and has application in any field where the liquid to be evaporated cannot withstand extended exposure to high temperatures, such as the concentration of fruit juices.
Circulation evaporators are a type of evaporating unit designed to separate mixtures unable to be evaporated by a conventional evaporating unit. Circulation evaporation incorporates the use of both heat exchangers and flash separation units in conjunction with circulation of the solvent in order to remove liquid mixtures without conventional boiling. There are two types of Circulation Evaporation; Natural Circulation Evaporators and Forced Circulation Evaporators, both of which are still currently used in industry today, although forced Circulation systems, which have a circulation pump as opposed to natural systems with no driving force, have a much wider range of appropriate uses.
A rising film or vertical long tube evaporator is a type of evaporator that is essentially a vertical shell and tube heat exchanger. The liquid being evaporated is fed from the bottom into long tubes and heated with steam condensing on the outside of the tube from the shell side. This is to produce steam and vapour within the tube bringing the liquid inside to a boil. The vapour produced then presses the liquid against the walls of the tubes and causes the ascending force of this liquid. As more vapour is formed, the centre of the tube will have a higher velocity which forces the remaining liquid against the tube wall forming a thin film which moves upwards. This phenomenon of the rising film gives the evaporator its name.
Heat transfer enhancement is the process of increasing the effectiveness of heat exchangers. This can be achieved when the heat transfer power of a given device is increased or when the pressure losses generated by the device are reduced. A variety of techniques can be applied to this effect, including generating strong secondary flows or increasing boundary layer turbulence.








