
A stock market, equity market, or share market is the aggregation of buyers and sellers of stocks, which represent ownership claims on businesses; these may include securities listed on a public stock exchange, as well as stock that is only traded privately, such as shares of private companies which are sold to investors through equity crowdfunding platforms. Investment is usually made with an investment strategy in mind.
In finance, technical analysis is an analysis methodology for analysing and forecasting the direction of prices through the study of past market data, primarily price and volume. Behavioral economics and quantitative analysis use many of the same tools of technical analysis, which, being an aspect of active management, stands in contradiction to much of modern portfolio theory. The efficacy of both technical and fundamental analysis is disputed by the efficient-market hypothesis, which states that stock market prices are essentially unpredictable, and research on whether technical analysis offers any benefit has produced mixed results.

In finance, being short in an asset means investing in such a way that the investor will profit if the value of the asset falls. This is the opposite of a more conventional "long" position, where the investor will profit if the value of the asset rises.

Day trading is a form of speculation in securities in which a trader buys and sells a financial instrument within the same trading day, so that all positions are closed before the market closes for the trading day to avoid unmanageable risks and negative price gaps between one day's close and the next day's price at the open. Traders who trade in this capacity are generally classified as speculators. Day trading contrasts with the long-term trades underlying buy-and-hold and value investing strategies. Day trading may require fast trade execution, sometimes as fast as milli-seconds in scalping, therefore a direct-access day trading software is often needed.

In finance, a futures contract is a standardized legal contract to buy or sell something at a predetermined price for delivery at a specified time in the future, between parties not yet known to each other. The asset transacted is usually a commodity or financial instrument. The predetermined price of the contract is known as the forward price. The specified time in the future when delivery and payment occur is known as the delivery date. Because it derives its value from the value of the underlying asset, a futures contract is a derivative.

A futures exchange or futures market is a central financial exchange where people can trade standardized futures contracts defined by the exchange. Futures contracts are derivatives contracts to buy or sell specific quantities of a commodity or financial instrument at a specified price with delivery set at a specified time in the future. Futures exchanges provide physical or electronic trading venues, details of standardized contracts, market and price data, clearing houses, exchange self-regulations, margin mechanisms, settlement procedures, delivery times, delivery procedures and other services to foster trading in futures contracts. Futures exchanges can be organized as non-profit member-owned organizations or as for-profit organizations. Futures exchanges can be integrated under the same brand name or organization with other types of exchanges, such as stock markets, options markets, and bond markets. Non-profit member-owned futures exchanges benefit their members, who earn commissions and revenue acting as brokers or market makers. For-profit futures exchanges earn most of their revenue from trading and clearing fees.
Prediction markets are open markets where specific outcomes can be predicted using financial incentives. Essentially, they are exchange-traded markets created for the purpose of trading the outcome of events. The market prices can indicate what the crowd thinks the probability of the event is. A prediction market contract trades between 0 and 100%. The most common form of a prediction market is a binary option market, which will expire at the price of 0 or 100%. Prediction markets can be thought of as belonging to the more general concept of crowdsourcing which is specially designed to aggregate information on particular topics of interest. The main purposes of prediction markets are eliciting aggregating beliefs over an unknown future outcome. Traders with different beliefs trade on contracts whose payoffs are related to the unknown future outcome and the market prices of the contracts are considered as the aggregated belief.

A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.
An equity swap is a financial derivative contract where a set of future cash flows are agreed to be exchanged between two counterparties at set dates in the future. The two cash flows are usually referred to as "legs" of the swap; one of these "legs" is usually pegged to a floating rate such as LIBOR. This leg is also commonly referred to as the "floating leg". The other leg of the swap is based on the performance of either a share of stock or a stock market index. This leg is commonly referred to as the "equity leg". Most equity swaps involve a floating leg vs. an equity leg, although some exist with two equity legs.

The 2005 British Columbia general election was held on May 17, 2005, to elect members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs) of the Province of British Columbia (BC), Canada. The British Columbia Liberal Party formed the government of the province prior to this general election under the leadership of Premier Gordon Campbell. The main opposition was the British Columbia New Democratic Party, whose electoral representation was reduced to two MLAs in the previous provincial election in 2001.
Stock dilution, also known as equity dilution, is the decrease in existing shareholders' ownership percentage of a company as a result of the company issuing new equity. New equity increases the total shares outstanding which has a dilutive effect on the ownership percentage of existing shareholders. This increase in the number of shares outstanding can result from a primary market offering, employees exercising stock options, or by issuance or conversion of convertible bonds, preferred shares or warrants into stock. This dilution can shift fundamental positions of the stock such as ownership percentage, voting control, earnings per share, and the value of individual shares.
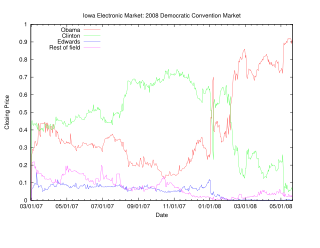
The Iowa Electronic Markets (IEM) are a group of real-money prediction markets/futures markets operated by the University of Iowa Tippie College of Business. Unlike normal futures markets, the IEM is not-for-profit; the markets are run for educational and research purposes.

In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the holder, the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option. Options are typically acquired by purchase, as a form of compensation, or as part of a complex financial transaction. Thus, they are also a form of asset and have a valuation that may depend on a complex relationship between underlying asset price, time until expiration, market volatility, the risk-free rate of interest, and the strike price of the option. Options may be traded between private parties in over-the-counter (OTC) transactions, or they may be exchange-traded in live, public markets in the form of standardized contracts.
Popular Science Predictions Exchange (PPX) was an online virtual prediction market run as part of the Popular Science website. The application was designed by the same group behind the Hollywood Stock Exchange using their virtual specialist application. Users traded virtual currency, known as POP$, based on the likelihood of a certain event being realized by a given date. Stock prices would range between POP$0 and POP$100 and were intended to reflect the general confidence of the users about that event. A stock at price POP$95 would mean roughly that users believed there to be a 95% chance of the event happening. If an event was realized by the given date, the stock will pay out POP$100 per share. A stock that did not occur by the closing date was worth POP$0 per share.
Intrade.com was a web-based trading exchange whose members "traded" contracts between each other on the probabilities of various events occurring. After having been forced to exclude US traders in 2012, on 10 March 2013 Intrade suspended all trading, citing possible "financial irregularities". For a time after the suspension, the intrade.com website stated that they were working on a relaunch of the site, called "Intrade 2.0", but as of August 2014 it states that "It appears very unlikely now that Intrade will resume trading services in the way it had operated previously", and announced plans to close all accounts and refund monies by 31 December 2014.
The PollyVote project uses the high-profile application of predicting U.S. presidential election results to demonstrate advances in forecasting research. The project is run by political science professors and forecasting experts, one of which is J. Scott Armstrong. All procedures, data, and results are fully disclosed and freely available online.
Political forecasting aims at forecasting the outcomes of political events. Political events can be a number of events such as diplomatic decisions, actions by political leaders and other areas relating to politicians and political institutions. The area of political forecasting concerning elections is highly popular, especially amongst mass market audiences. Political forecasting methodology makes frequent use of mathematics, statistics and data science. Political forecasting as it pertains to elections is related to psephology.

In finance, stock consists of all the shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided. A single share of the stock means fractional ownership of the corporation in proportion to the total number of shares. This typically entitles the shareholder (stockholder) to that fraction of the company's earnings, proceeds from liquidation of assets, or voting power, often dividing these up in proportion to the amount of money each stockholder has invested. Not all stock is necessarily equal, as certain classes of stock may be issued for example without voting rights, with enhanced voting rights, or with a certain priority to receive profits or liquidation proceeds before or after other classes of shareholders.
iPredict was a New Zealand prediction market that offered prediction exchanges on current events, political issues and economic issues. iPredict was jointly owned by the New Zealand Institute for the Study of Competition and Regulation and Victoria University of Wellington. The site launched on 9 September 2008 and closed 1 December 2016.
PredictIt is a New Zealand-based online prediction market that offers exchanges on political and financial events. PredictIt is owned and operated by Victoria University of Wellington with support from Aristotle, Inc. The company's office is located in Washington, D.C.




