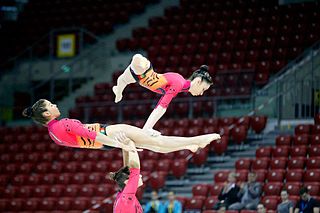Diving is the sport of jumping or falling into water from a platform or springboard, usually while performing acrobatics. Diving is an internationally recognized sport that is part of the Olympic Games. In addition, unstructured and non-competitive diving is a recreational pastime.

Gymnastics is a sport that includes physical exercises requiring balance, strength, flexibility, agility, coordination,dedication and endurance. The movements involved in gymnastics contribute to the development of the arms, legs, shoulders, back, chest, and abdominal muscle groups. Gymnastics evolved from exercises used by the ancient Greeks that included skills for mounting and dismounting a horse, and from circus performance skills.

In gymnastics, the floor is a specially prepared exercise surface, which is considered an apparatus. It is used by both male and female gymnasts. The gymnastics event performed on the floor is called floor exercise. The English abbreviation for the event in gymnastics scoring is FX.

Rhythmic gymnastics is a sport in which gymnasts perform on a floor with an apparatus: hoop, ball, clubs, ribbon or rope. The sport combines elements of gymnastics, dance and calisthenics; gymnasts must be strong, flexible, agile, dexterous and coordinated. Rhythmic gymnastics is governed by the International Gymnastics Federation (FIG), which first recognized it as a sport in 1963. It became an Olympic sport in 1984, with an individual all-around event. The group all-around competition was added to the Olympics in 1996. At the international level, rhythmic gymnastics is a women-only sport. The most prestigious competitions, besides the Olympic Games, are the World Championships, World Games, European Championships, European Games, the World Cup Series and the Grand Prix Series. Gymnasts are judged on their artistry, execution of skills, and difficulty of skills, for which they gain points. They perform leaps, balances, and rotations along with handling the apparatus.

Trampolining or trampoline gymnastics is a recreational activity, acrobatic training tool as well as a competitive Olympic sport in which athletes perform acrobatics while bouncing on a trampoline. In competition, these can include simple jumps in the straight, pike, tuck, or straddle position to more complex combinations of forward and/or backward somersaults and twists. Scoring is based on the difficulty and on the total seconds spent in the air. Points are deducted for bad form and horizontal displacement from the center of the bed.
Artistic gymnastics is a discipline of gymnastics in which athletes perform short routines on different apparatuses. The sport is governed by the Fédération Internationale de Gymnastique (FIG), which designs the Code of Points and regulates all aspects of elite international competition. Within individual countries, gymnastics is regulated by national federations like British Gymnastics and USA Gymnastics. Artistic gymnastics is a popular spectator sport at many competitions, including the Summer Olympic Games.

The International English Language Testing System (IELTS), is an international standardized test of English language proficiency for non-native English language speakers. It is jointly managed by the British Council, IDP: IELTS Australia and Cambridge Assessment English, and was established in 1989. IELTS is one of the major English-language tests in the world.

The Code of Points is a rulebook that defines the scoring system for each level of competition in gymnastics. There is not a universal international Code of Points, and every oversight organization — such as the FIG, NCAA Gymnastics, and most national gymnastics federations — designs and employs its own unique Code of Points.

Equestrian vaulting, or simply vaulting, is most often described as gymnastics and dance on horseback, which can be practiced both competitively or non-competitively. Vaulting has a history as an equestrian act at circuses, but its origins stretch back at least two-thousand years. It is open to both men and women and is one of ten equestrian disciplines recognized by the International Federation for Equestrian Sports. Therapeutic or interactive vaulting is also used as an activity for children and adults who may have balance, attention, gross motor skill or social deficits.
The Defense Language Proficiency Test (DLPT) is a battery of foreign language tests produced by the Defense Language Institute and used by the United States Department of Defense (DoD). They are intended to assess the general language proficiency of native English speakers in a specific foreign language, in the skills of reading and listening. An Oral Proficiency Interview (OPI) is sometimes administered to Defense Language Institute students to establish the graduate's proficiency in speaking following training there, but it is not part of the DLPT.

United States of America Gymnastics is the national governing body for gymnastics in the United States. Established in 1963 as the U.S. Gymnastics Federation (USGF), USA Gymnastics is responsible for selecting and training national teams for the Olympic Games and World Championships. The mission of USA Gymnastics is to encourage participation and the pursuit of excellence in all aspects of gymnastics.
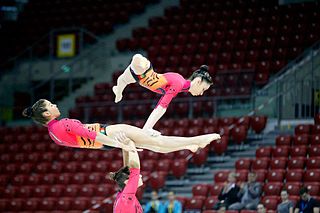
Acrobatic gymnastics is a competitive gymnastic discipline where partnerships of gymnasts work together and perform figures consisting of acrobatic moves, dance and tumbling, set to music. There are three types of routines; a 'balance' routine where the focus is on strength, poise and flexibility; a 'dynamic' routine which includes throws, somersaults and catches, and a 'combined' routine which includes elements from both balance and dynamic.

Tumbling, sometimes referred to as power tumbling, is a gymnastics discipline in which participants perform a series of acrobatic skills down a 25 metres (82 ft) long sprung track. Each series, known as a pass, comprises eight elements in which the athlete jumps, twists and flips placing only their hands and feet on the track. Tumblers are judged on the difficulty and form of their routine. There are both individual and team competitions in the sport.
Aleksandr Sergeyevich Balandin is a retired Russian gymnast. He is known for his work on the rings and has three skills named after him on this apparatus. He placed fourth in the rings at the 2012 Olympics.
In cricket, a player's batting average is the total number of runs they have scored divided by the number of times they have been out, usually given to two decimal places. Since the number of runs a player scores and how often they get out are primarily measures of their own playing ability, and largely independent of their teammates, batting average is a good metric for an individual player's skill as a batter. The number is also simple to interpret intuitively. If all the batter's innings were completed, this is the average number of runs they score per innings. If they did not complete all their innings, this number is an estimate of the unknown average number of runs they score per innings.

T20 is a disability sport classification for disability athletics in track and jump events. It broadly covers athletes with intellectual disabilities.
Stunt is competitive cheerleading in a different format. In spring 2011, USA Cheer announced that 21 universities are now committed to this sport. STUNT requires high athletic skills and its competition format and scoring systems are unique. The maximum number of players on each team can reach 30 athletes. STUNT is being considered for NCAA Emerging Sports for Women status and has been designed to meet Title IX's requirements for intercollegiate sports. As of June 2020, the NCAA Division I Strategic Vision and Planning Committee did not recommend introducing a STUNT proposal into the next legislative cycle.

Andreas Bretschneider is a German artistic gymnast and member of the national team. He participated at the 2015 World Artistic Gymnastics Championships in Glasgow, and eventually competed for the German squad at the 2016 Summer Olympics, finishing seventh in the artistic team all-around tournament, and twentieth in the individual all-around.
Intellectual disability sport classification is a classification system used for disability sport that allows people with intellectual disabilities to fairly compete with and against other people with intellectual disabilities. Separate classification systems exist for the elite athlete with a disability side affiliated with the Paralympic movement and Virtus, and the sports for all model affiliated with Special Olympics. People with intellectual disabilities have issues with conceptual skills, social skills and practical skills. They have IQs of 75 points or lower, limitations in adaptive behaviour and their disability manifested and was documented prior to turning 18 years of age.
Degree of difficulty is a concept used in several sports and other competitions to indicate the technical difficulty of a skill, performance, or course, often as a factor in scoring. Sports which incorporate a degree of difficulty in scoring include bouldering, cross-country skiing, diving, equestrianism, figure skating, freestyle skiing, gymnastics, rhythmic gymnastics, surfing, synchronized swimming and trampoline. Degree of difficulty is typically intended to be an objective measure, in sports whose scoring may also rely on subjective judgments of performance.