
The foreign relations of Finland are the responsibility of the president of Finland, who leads foreign policy in cooperation with the government. Implicitly the government is responsible for internal policy and decision making in the European Union. Within the government, preparative discussions are conducted in the government committee of foreign and security policy, which includes the Prime Minister and at least the Minister of Foreign Affairs and the Minister of Defence, and at most four other ministers as necessary. The committee meets with the President as necessary. Laws concerning foreign relations are discussed in the parliamentary committee of foreign relations. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs implements the foreign policy.

Though the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA) is the government agency responsible for the conduct of foreign relations of Nepal, historically, it is the Office of Prime Minister (PMO) that has exercised the authority to formulate and conduct policies related to Nepal's foreign affairs. As a landlocked country wedged between two larger and far stronger powers, Nepal has tried to maintain good relations with both of its neighbors, People's Republic of China and Republic of India. Nepal's relationship with China, India, and the United States has remained utmost priority for successive Nepali governments. The relationship between Nepal and India however was significantly hampered during the 2015 Nepal blockade by pro-Indian anti-Nepal protestors, where the Government of Nepal accused India of using "Russia-Ukraine" tactics to cause unrest along Nepal's southern border using ethnically Indian residents of Nepal. India strictly denied the allegation and said the unrest were solely due to Madheshi protesters. For the most part though, Nepal has traditionally maintained a non-aligned policy and enjoys friendly relations with its neighboring countries and almost all the major countries of the world.

Ethiopian-Greek relations are the international relations between Ethiopia and Greece. In general, bilateral relations between the two countries have been limited, though they have maintained a formal relationship for over a century, including via the signature of several bilateral trade deals.

Ethiopian–Turkish relations are foreign relations between Ethiopia and Turkey. Ethiopia has an embassy in Ankara and Turkey has an embassy in Addis Ababa.

Finland–Mozambique relations refers to the bilateral relationship of Finland and Mozambique. Finland recognised Mozambique on July 4, 1975. Both countries established diplomatic relations on July 18, 1975. Mozambique is represented in Finland through its embassy in Stockholm, Sweden. Finland has an embassy in Maputo. In November 2008, Finland's President Tarja Halonen called her country's relationship with Mozambique "excellent".

Kenyan–Finnish relations are bilateral relations between Kenya and Finland.

Ethiopia–Ireland relations are foreign relations between Ethiopia and Ireland. Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1994, the same year Ireland opened an embassy in Addis Ababa. Ethiopia had an embassy in Dublin before its closure in 2021. But was reopened before this was finished.

Norway–Romania relations are foreign relations between Norway and Romania. Both countries established diplomatic relations on April 3, 1917. Norway has an embassy in Bucharest and an honorary consulate in Constanţa. Romania has an embassy in Oslo and 4 honorary consulates.

Canada–Ethiopia relations are foreign relations between Canada and Ethiopia. Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1956. Canada opened an embassy in Addis Ababa in 1957; although Ethiopia opened an embassy in Ottawa in 1962, it was closed the next year due to financial constraints and not re-opened until 1989. In 2021, Ethiopia closed its embassy in Ottawa again due to reshuffling and reorganization. In 2022, Ethiopia reopened its embassy in Ottawa.

Luxembourg and Vietnam established diplomatic relations in 1973. Luxembourg's representation in Vietnam is through its embassy in Bangkok, Thailand. Vietnam is represented through its embassy in Brussels, Belgium.

Bilateral and diplomatic relations exist between these two countries. Bahrain does not have an embassy in Spain, it relates its diplomatic activities in this country through its embassy in Paris. Spain also has no embassy in Bahrain, but its embassy in Kuwait is accredited to this country, Spain has an Honorary Consulate in Manama (Bahrain).

Singapore–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Singapore is accredited to Spain through its embassy in Paris, France and has two honorary consulates in Barcelona and Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Singapore.

Cape Verde–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Cape Verde has an embassy in Madrid, a consulate-general in Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and two consulates in Alicante and La Coruña. Spain has an embassy in Praia.

Ethiopia–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Ethiopia has no embassy in Spain, but the Ethiopian embassy in Paris is accredited to Spain. Ethiopia has an honorary consulate in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Addis Ababa.
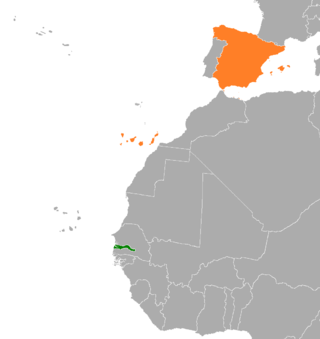
Gambia–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Gambia has an embassy in Madrid and honorary consulates in Almería, Barcelona, Gerona, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Madrid and Zaragoza. Spain has an embassy office in Banjul.

Guinea-Bissau–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries.
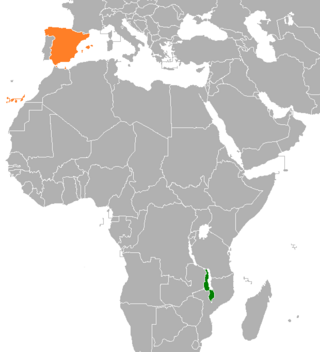
Malawi–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Malawi has an embassy in Madrid and a consulate in Barcelona. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Spain does not have representation in Lilongwe. The Spanish Embassy in Harare (Zimbabwe) is accredited to Malawi.

Namibia–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Namibia is accredited to Spain from its embassy in Paris, France. Spain has an embassy in Windhoek.

Niger–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Niger has an embassy in Madrid and Spain has an embassy in Niamey. Also, Niger has a consulate in Madrid.

Rwanda–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Rwanda does not have an embassy in Spain, however its embassy in Paris, France, is accredited to Spain and maintains an honorary consulate in Madrid. Spain does not have an embassy in Rwanda, however, its embassy in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, is accredited to Rwanda and maintains an honorary consulate in Kigali.






















