Related Research Articles

Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis which allows biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living cells and between cells, in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissues and organs as well as organism structure and function. Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms of biological phenomena.
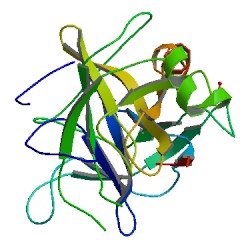
Chymotrypsin (EC 3.4.21.1, chymotrypsins A and B, alpha-chymar ophth, avazyme, chymar, chymotest, enzeon, quimar, quimotrase, alpha-chymar, alpha-chymotrypsin A, alpha-chymotrypsin) is a digestive enzyme component of pancreatic juice acting in the duodenum, where it performs proteolysis, the breakdown of proteins and polypeptides. Chymotrypsin preferentially cleaves peptide amide bonds where the side chain of the amino acid N-terminal to the scissile amide bond (the P1 position) is a large hydrophobic amino acid (tyrosine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine). These amino acids contain an aromatic ring in their side chain that fits into a hydrophobic pocket (the S1 position) of the enzyme. It is activated in the presence of trypsin. The hydrophobic and shape complementarity between the peptide substrate P1 side chain and the enzyme S1 binding cavity accounts for the substrate specificity of this enzyme. Chymotrypsin also hydrolyzes other amide bonds in peptides at slower rates, particularly those containing leucine at the P1 position.

In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions.
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group -NH
2 but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the protonated form (NH2+) under biological conditions, while the carboxyl group is in the deprotonated −COO− form. The "side chain" from the α carbon connects to the nitrogen forming a pyrrolidine loop, classifying it as a aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L-glutamate. It is encoded by all the codons starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG).

Clinical chemistry is a division in medical laboratory sciences focusing on qualitative tests of important compounds, referred to as analytes or markers, in bodily fluids and tissues using analytical techniques and specialized instruments. This interdisciplinary field includes knowledge from medicine, biology, chemistry, biomedical engineering, informatics, and an applied form of biochemistry.
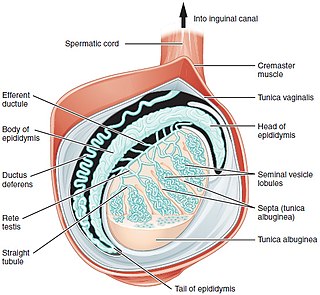
A testicle or testis is the male gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testicles are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone, whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone.
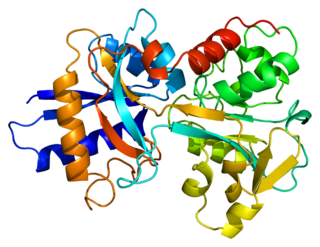
Transferrins are glycoproteins found in vertebrates which bind and consequently mediate the transport of iron (Fe) through blood plasma. They are produced in the liver and contain binding sites for two Fe3+ ions. Human transferrin is encoded by the TF gene and produced as a 76 kDa glycoprotein.

Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words urine and analysis, is a panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and microscopic examination. Macroscopic examination targets parameters such as color, clarity, odor, and specific gravity; urine test strips measure chemical properties such as pH, glucose concentration, and protein levels; and microscopy is performed to identify elements such as cells, urinary casts, crystals, and organisms.

The enzyme alkaline phosphatase is a phosphatase with the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryotes alike, with the same general function, but in different structural forms suitable to the environment they function in. Alkaline phosphatase is found in the periplasmic space of E. coli bacteria. This enzyme is heat stable and has its maximum activity at high pH. In humans, it is found in many forms depending on its origin within the body – it plays an integral role in metabolism within the liver and development within the skeleton. Due to its widespread prevalence in these areas, its concentration in the bloodstream is used by diagnosticians as a biomarker in helping determine diagnoses such as hepatitis or osteomalacia.
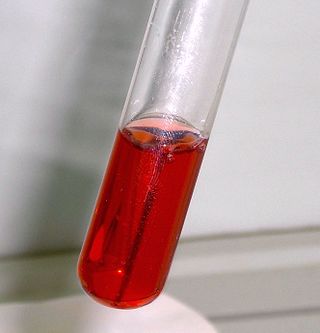
Seliwanoff’s test is a chemical test which distinguishes between aldose and ketose sugars. If the sugar contains a ketone group, it is a ketose. If a sugar contains an aldehyde group, it is an aldose. This test relies on the principle that, when heated, ketoses are more rapidly dehydrated than aldoses. It is named after Theodor Seliwanoff, the chemist who devised the test. When added to a solution containing ketoses, a red color is formed rapidly indicating a positive test. When added to a solution containing aldoses, a slower forming light pink is observed instead.

The Sakaguchi test is a chemical test used to detect presence of arginine in proteins. It is named after the Japanese food scientist and organic chemist, Shoyo Sakaguchi (1900–1995) who described the test in 1925. The Sakaguchi reagent used in the test consists of 1-Naphthol and a drop of sodium hypobromite. The guanidino (–C group in arginine reacts with the Sakaguchi reagent to form a red-coloured complex.
The Hopkins-Cole reaction, also known as the glyoxylic acid reaction, is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of tryptophan in proteins. A protein solution is mixed with Hopkins Cole reagent, which consists of glyoxylic acid. Concentrated sulfuric acid is slowly added to form two layers. A purple ring appears between the two layers if the test is positive for tryptophan. Nitrites, chlorates, nitrates and excess chlorides prevent the reaction from occurring.
The Acree-Rosenheim reaction is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of tryptophan in proteins. A protein mixture is mixed with formaldehyde. Concentrated sulfuric acid is added to form two layers. A purple ring appears between the two layers if the test is positive for tryptophan.
The rapid furfural test is a chemical test used to distinguish between glucose and fructose. The rapid furfural test is similar to Molisch's test but uses concentrated hydrochloric acid instead of concentrated sulfuric acid and the solution is boiled. Dilute sugar solution is added to ethanolic 1-naphthol and concentrated hydrochloric acid. The solution is then boiled and if a purple colour forms within thirty seconds, fructose is present. If a purple colour does not appear before thirty seconds, glucose is present.
Gunzberg's test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of hydrochloric acid. Gunzberg's reagent is made by dissolving two grams of phloroglucinol and one gram of vanillin in 100 millilitres of 95% ethanol. Hydrochloric acid catalyses Gunzberg's reagent to form a red complex.
Kelling's test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of lactic acid in gastric juice.
Gmelin's test is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of bile pigments in urine. It is named after Leopold Gmelin, who introduced the test. Five millilitres of urine is slowly added to five millilitres of concentrated nitric acid in a test-tube. Different coloured rings between the two layers are visible if bile pigments are present as they are oxidised to various chemical products. Nitric acid is used as the oxidising agent. Blue, green and violet rings are seen if bilirubin is present. Gmelin's test is not sensitive, so a positive result always indicates the presence of bile pigments, but a negative result does not exclude the presence of small quantities of bile pigments.
Hay's test, also known as Hay's sulphur powder test, is a chemical test used for detecting the presence of bile salts in urine.
Salkowski's test, also known simply as Salkowski test, is a qualitative chemical test, that is used in chemistry and biochemistry for detecting a presence of cholesterol and other sterols. This biochemical method got its name after German biochemist Ernst Leopold Salkowski, who is known for development of multiple new chemical tests, that are used for detection of different kinds of molecules. A solution that has tested positive on the Salkowski's test becomes red and gets yellow glow.
References
- ↑ Dandekar (1 January 2004). Practicals And Viva In Medical Biochemistry. Elsevier India. p. 26. ISBN 978-81-8147-025-6.
- Nigam (1 April 2007). Lab Manual in Biochemistry: Immunology and Biotechnology. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. p. 152. ISBN 978-0-07-061767-4.
- Chawla (1 January 2003). Practical Clinical Biochemistry: Methods and Interpretations. Jaypee Brothers Publishers. p. 59. ISBN 978-81-8061-108-7.
- A.C. Croftan. Clinical Urinology. Рипол Классик. p. 115. ISBN 978-1-275-01265-3. - ↑ Elizabeth A. Martin, ed. (25 February 2010). Concise Colour Medical Dictionary. Oxford University Press. p. 335. ISBN 978-0-19-955715-8.