
Braille is a tactile writing system used by people who are visually impaired. It is traditionally written with embossed paper. Braille users can read computer screens and other electronic supports using refreshable braille displays. They can write braille with the original slate and stylus or type it on a braille writer, such as a portable braille notetaker or computer that prints with a braille embosser.
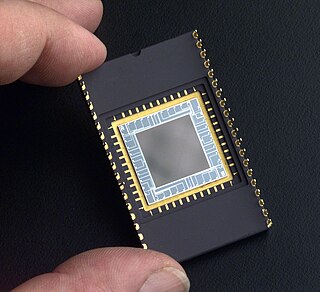
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time. CCDs move charge between capacitive bins in the device, with the shift allowing for the transfer of charge between bins.

Design by contract (DbC), also known as contract programming, programming by contract and design-by-contract programming, is an approach for designing software. It prescribes that software designers should define formal, precise and verifiable interface specifications for software components, which extend the ordinary definition of abstract data types with preconditions, postconditions and invariants. These specifications are referred to as "contracts", in accordance with a conceptual metaphor with the conditions and obligations of business contracts.
In law and government, de facto describes practices that exist in reality, even if not officially recognized by laws. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with de jure, which refers to things that happen according to law. Unofficial customs that are widely accepted are sometimes called de facto standards.
In proprietary software, an end-user license agreement (EULA) or software license agreement is the contract between the licensor and purchaser, establishing the purchaser's right to use the software. The license may define ways under which the copy can be used, in addition to the automatic rights of the buyer including the first sale doctrine and 17 U.S.C. § 117.

Quid pro quo is a Latin phrase used in English to mean an exchange of goods or services, in which one transfer is contingent upon the other; "a favour for a favour". Phrases with similar meanings include: "give and take", "tit for tat", and "you scratch my back, and I'll scratch yours" and "one hand washes the other".
A quasi-contract is a fictional contract recognised by a court. The notion of a quasi-contract can be traced to Roman law and is still a concept used in some modern legal systems.
A memorandum of understanding (MoU) is a type of agreement between two (bilateral) or more (multilateral) parties. It expresses a convergence of will between the parties, indicating an intended common line of action. It is often used either in cases where parties do not imply a legal commitment or in situations where the parties cannot create a legally enforceable agreement. It is a more formal alternative to a gentlemen's agreement.
Hahn Air is a German airline headquartered in Dreieich, offering scheduled and charter flights within Europe from its base at Düsseldorf Airport.
A choice of law clause or proper law clause is a term of a contract in which the parties specify that any dispute arising under the contract shall be determined in accordance with the law of a particular jurisdiction.

Demotic is the ancient Egyptian script derived from northern forms of hieratic used in the Nile Delta, and the stage of the Egyptian language written in this script, following Late Egyptian and preceding Coptic. The term was first used by the Greek historian Herodotus to distinguish it from hieratic and hieroglyphic scripts. By convention, the word "Demotic" is capitalized in order to distinguish it from demotic Greek.

An arbitration clause is a clause in a contract that requires the parties to resolve their disputes through an arbitration process. Although such a clause may or may not specify that arbitration occur within a specific jurisdiction, it always binds the parties to a type of resolution outside the courts, and is therefore considered a kind of forum selection clause.

Legal writing involves the analysis of fact patterns and presentation of arguments in documents such as legal memoranda and briefs. One form of legal writing involves drafting a balanced analysis of a legal problem or issue. Another form of legal writing is persuasive, and advocates in favor of a legal position. Another form legal writing involves drafting legal instruments, such as contracts and wills.

Interline Bus Services is an Australian bus company operating services in South West Sydney.
Legal English is the type of English as used in legal writing. In general, a legal language is a formalized language based on logic rules which differs from the ordinary natural language in vocabulary, morphology, syntax, and semantics, as well as other linguistic features, aimed to achieve consistency, validity, completeness and soundness, while keeping the benefits of a human-like language such as intuitive execution, complete meaning and open upgrade. However, Legal English has been referred to as a "sublanguage", as legal English differs from ordinary English. A specialized use of certain terms and linguistic patterns governs the teaching of legal language. Thus, "we study legal language as a kind of second language, a specialized use of vocabulary, phrases, and syntax that helps us to communicate more easily with each other".
Interlining, also known as interline ticketing and interline booking, is a voluntary commercial agreement between individual airlines to handle passengers traveling on itineraries that require multiple flights on multiple airlines. Such agreements allow passengers to change from one flight on one airline to another flight on another airline without having to gather their bags or check-in again.

Interline Brands, Inc., headquartered in Jacksonville, Florida, is one of the largest wholesale distributors and direct marketers of maintenance, repair and operations (MRO) products for non-industrial businesses in the United States. Interline Brands distributes a broad range of products such as HVAC, janitorial supplies, plumbing supplies and security supplies.
Servicio Aéreo Ejecutivo (SAE) was a small Air Taxi operator in Peru that later on expanded operations to include charter passenger and cargo flights.

The title-transfer theory of contract (TTToC) is a legal interpretation of contracts developed by economist Murray Rothbard and jurist Williamson Evers. The theory interprets all contractual obligations in terms of property rights, viewing a contract as a bundle of title transfers. The TTToC stands in oppositions to most mainstream contract theories which view contractual obligations as the result of a binding promise. Proponents of the approach often claim it is superior on grounds of both consistency and ethical considerations. The TTToC is often supported by libertarians.








