
Benoit B.Mandelbrot was a Polish-born French-American mathematician and polymath with broad interests in the practical sciences, especially regarding what he labeled as "the art of roughness" of physical phenomena and "the uncontrolled element in life". He referred to himself as a "fractalist" and is recognized for his contribution to the field of fractal geometry, which included coining the word "fractal", as well as developing a theory of "roughness and self-similarity" in nature.
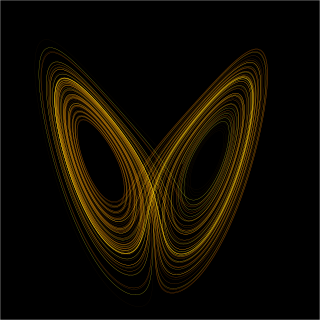
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of scientific study and branch of mathematics focused on underlying patterns and deterministic laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, and were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals, and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state. A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can cause a tornado in Texas.
A complex system is a system composed of many components which may interact with each other. Examples of complex systems are Earth's global climate, organisms, the human brain, infrastructure such as power grid, transportation or communication systems, complex software and electronic systems, social and economic organizations, an ecosystem, a living cell, and ultimately the entire universe.
Econophysics is a heterodox interdisciplinary research field, applying theories and methods originally developed by physicists in order to solve problems in economics, usually those including uncertainty or stochastic processes and nonlinear dynamics. Some of its application to the study of financial markets has also been termed statistical finance referring to its roots in statistical physics. Econophysics is closely related to social physics.
Stephen Alan "Steve" Ross was the inaugural Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics at the MIT Sloan School of Management after a long career as the Sterling Professor of Economics and Finance at the Yale School of Management. He is known for initiating several important theories and models in financial economics. He was a widely published author in finance and economics, and was a coauthor of a best-selling Corporate Finance textbook.
Philip Mirowski is a historian and philosopher of economic thought at the University of Notre Dame. He received a PhD in Economics from the University of Michigan in 1979.

J. Doyne Farmer is an American complex systems scientist and entrepreneur with interests in chaos theory, complexity and econophysics. He is Baillie Gifford Professor of Mathematics at Oxford University, where he is also Director of the Complexity Economics at the Institute for New Economic Thinking at the Oxford Martin School. Additionally he is an external professor at the Santa Fe Institute. His current research is on complexity economics, focusing on systemic risk in financial markets and technological progress. During his career he has made important contributions to complex systems, chaos, artificial life, theoretical biology, time series forecasting and econophysics. He co-founded Prediction Company, one of the first companies to do fully automated quantitative trading. While a graduate student he led a group that called itself Eudaemonic Enterprises and built the first wearable digital computer, which was used to beat the game of roulette.

Social studies of finance is an interdisciplinary research area that combines perspectives from anthropology, economic sociology, science and technology studies, international political economy, behavioral finance, and cultural studies in the study of financial markets and financial instruments. Work in social studies of finance emphasizes the social and cultural dimensions of financial activities, but focuses also on technical and economic dimensions such as pricing and trading.
Statistical finance, is the application of econophysics to financial markets. Instead of the normative roots of finance, it uses a positivist framework. It includes exemplars from statistical physics with an emphasis on emergent or collective properties of financial markets. Empirically observed stylized facts are the starting point for this approach to understanding financial markets.
Complexity economics is the application of complexity science to the problems of economics. It sees the economy not as a system in equilibrium, but as one in motion, perpetually constructing itself anew. It uses computational and mathematical analysis to explore how economic structure is formed and reformed, in continuous interaction with the adaptive behavior of the 'agents' in the economy.

David John Orrell is a Canadian writer and mathematician. He received his doctorate in mathematics from the University of Oxford. His work in the prediction of complex systems such as the weather, genetics and the economy has been featured in New Scientist, the Financial Times, The Economist, Adbusters, BBC Radio, Russia-1, and CBC TV. He now conducts research and writes in the areas of systems biology and economics, and runs a mathematical consultancy Systems Forecasting. He is the son of theatre historian and English professor John Orrell.

Robert James Shiller is an American economist, academic, and author. As of 2022, he served as a Sterling Professor of Economics at Yale University and is a fellow at the Yale School of Management's International Center for Finance. Shiller has been a research associate of the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) since 1980, was vice president of the American Economic Association in 2005, its president-elect for 2016, and president of the Eastern Economic Association for 2006–2007. He is also the co‑founder and chief economist of the investment management firm MacroMarkets LLC.
John Barkley Rosser Jr. is a mathematical economist and Professor of Economics at James Madison University in Harrisonburg, Virginia since 1988. He is known for work in nonlinear economic dynamics, including applications in economics of catastrophe theory, chaos theory, and complexity theory. With Marina V. Rosser he invented the concept of the "new traditional economy". He introduced into economic discourse the concepts of chaotic bubbles, chaotic hysteresis, and econochemistry. He also invented the concepts of the megacorpstate and hypercyclic morphogenesis. He was the first to provide a mathematical model of the period of financial distress in a speculative bubble. With Marina V. Rosser and Ehsan Ahmed, he was the first to argue for a two-way positive link between income inequality and the size of an underground economy in a nation. Rosser's equation has been used to forecast ratios of future Social Security benefits to current ones in real terms.
Neil Fraser Johnson is an English physicist who is notable for his work in complexity theory and complex systems, spanning quantum information, econophysics, and condensed matter physics. He is currently Professor of Physics at George Washington University in Washington D.C. where he heads up a new initiative in Complexity and Data Science which combines cross-disciplinary fundamental research with data science, with a view to resolving complex real-world problems.

George M. Zaslavsky was a Soviet mathematical physicist and one of the founders of the physics of dynamical chaos.
Jean-Philippe Bouchaud is a French physicist. He is co-founder and chairman of Capital Fund Management (CFM), adjunct professor at École Normale Supérieure and co-director of the CFM-Imperial Institute of Quantitative Finance at Imperial College London. He is a member of the French Academy of Sciences, and held the Bettencourt Innovation Chair at Collège de France in 2020.
Quantum finance is an interdisciplinary research field, applying theories and methods developed by quantum physicists and economists in order to solve problems in finance. It is a branch of econophysics.

Nicola Acocella is an Italian economist and academic, Emeritus Professor of Economic Policy since 2014.
Muthusamy Lakshmanan is an Indian theoretical physicist currently working as Professor of Eminence at the Department of Nonlinear Dynamics of Bharathidasan University. Presently he is the DST-SERB National Science Chair awarded by Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology. He has held several research fellowships which included Raja Rammanna fellowship of Department of Atomic Energy, Alexander von Humboldt fellowship, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science fellowship, Royal Society Nuffield Foundation fellowship, and NASI-Senior Scientist Platinum Jubilee Fellowship. In the year 2021, on August 15, he was conferred with Dr. A. P. J Abdul Kalam Award by the Government of Tamil Nadu.
Quantum economics is an emerging research field which applies mathematical methods and ideas from quantum physics to the field of economics. It is motivated by the belief that economic processes such as financial transactions have much in common with quantum processes, and can be appropriately modeled using the quantum formalism. It draws on techniques from the related areas of quantum finance and quantum cognition, and is a sub-field of quantum social science.







