Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulation to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. It is essential because, apart from relatively recent results concerning the hydrogen molecular ion, the quantum many-body problem cannot be solved analytically, much less in closed form. While computational results normally complement the information obtained by chemical experiments, it can in some cases predict hitherto unobserved chemical phenomena. It is widely used in the design of new drugs and materials.
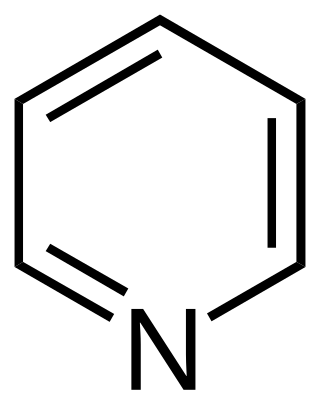
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of these heterocycles.

The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a rows and columns arrangement of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of chemistry. It is a graphic formulation of the periodic law, which states that the properties of the chemical elements exhibit an approximate periodic dependence on their atomic numbers. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. The rows of the table are called periods, and the columns are called groups. Elements from the same group of the periodic table show similar chemical characteristics. Trends run through the periodic table, with nonmetallic character increasing from left to right across a period, and from down to up across a group, and metallic character increasing in the opposite direction. The underlying reason for these trends is electron configurations of atoms. The periodic table exclusively lists electrically neutral atoms that have an equal number of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons and puts isotopes at the same place. Other atoms, like nuclides and isotopes, are graphically collected in other tables like the tables of nuclides.

Physical chemistry is the study of macroscopic and microscopic phenomena in chemical systems in terms of the principles, practices, and concepts of physics such as motion, energy, force, time, thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, statistical mechanics, analytical dynamics and chemical equilibria.

The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all degree levels and in all fields of chemistry, chemical engineering, and related fields. It is one of the world's largest scientific societies by membership. The ACS is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization and holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Its headquarters are located in Washington, D.C., and it has a large concentration of staff in Columbus, Ohio.

The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 34,000 in the UK and a further 8,000 abroad. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge where RSC Publishing is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing and Shanghai, China and in Bangalore, India.
Chemical physics is a subdiscipline of chemistry and physics that investigates physicochemical phenomena using techniques from atomic and molecular physics and condensed matter physics; it is the branch of physics that studies chemical processes from the point of view of physics. While at the interface of physics and chemistry, chemical physics is distinct from physical chemistry in that it focuses more on the characteristic elements and theories of physics. Meanwhile, physical chemistry studies the physical nature of chemistry. Nonetheless, the distinction between the two fields is vague, and scientists often practice in both fields during the course of their research.
The philosophy of chemistry considers the methodology and underlying assumptions of the science of chemistry. It is explored by philosophers, chemists, and philosopher-chemist teams. For much of its history, philosophy of science has been dominated by the philosophy of physics, but the philosophical questions that arise from chemistry have received increasing attention since the latter part of the 20th century.

ChemComm, formerly known as Journal of the Chemical Society D: Chemical Communications (1969–1971), Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications (1972–1995), is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. It covers all aspects of chemistry. In January 2012, the journal moved to publishing 100 issues per year. The current chair of the editorial board is Douglas Stephan, while the executive editor is Richard Kelly.

The Journal of Organic Chemistry, colloquially known as JOC, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal for original contributions of fundamental research in all branches of theory and practice in organic and bioorganic chemistry. It is published by the publishing arm of the American Chemical Society, with 24 issues per year. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal had a 2017 impact factor of 4.805 and it is the journal that received the most cites in the field of organic chemistry. According to Web of Knowledge, eleven papers from the journal have received more than 1,000 citations, with the most cited paper having received 7,967 citations. The current editor-in-chief is Scott J. Miller from Yale University.
Chemische Berichte was a German-language scientific journal of all disciplines of chemistry founded in 1868. It was one of the oldest scientific journals in chemistry, until it merged with Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas to form Chemische Berichte/Recueil in 1997. Chemische Berichte/Recueil was then merged with other European journals in 1998 to form European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry.
The Journal of the Chemical Society was a scientific journal established by the Chemical Society in 1849 as the Quarterly Journal of the Chemical Society. The first editor was Edmund Ronalds. The journal underwent several renamings, splits, and mergers throughout its history. In 1980, the Chemical Society merged with several other organizations into the Royal Society of Chemistry. The journal's continuity is found in Chemical Communications, Dalton Transactions, Faraday Transactions, and Perkin Transactions, all of which are published by the Royal Society of Chemistry.

The Journal of Physical Chemistry A is a scientific journal which reports research on the chemistry of molecules - including their dynamics, spectroscopy, kinetics, structure, bonding, and quantum chemistry. It is published weekly by the American Chemical Society.

Chemistry education is the study of teaching and learning chemistry. It is one subset of STEM education or discipline-based education research (DBER). Topics in chemistry education include understanding how students learn chemistry and determining the most efficient methods to teach chemistry. There is a constant need to improve chemistry curricula and learning outcomes based on findings of chemistry education research (CER). Chemistry education can be improved by changing teaching methods and providing appropriate training to chemistry instructors, within many modes, including classroom lectures, demonstrations, and laboratory activities.

Chemistry World is a monthly chemistry news magazine published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. The magazine addresses current events in world of chemistry including research, international business news and government policy as it affects the chemical science community, plus the best product applications. It features regular columns by Philip Ball, Derek Lowe, Andrea Sella, Raychelle Burks, Alice Motion and Vanessa Seifert. The magazine is sent to all members of the Royal Society of Chemistry and is included in the cost of membership. In August 2016, the magazine began offering a "soft" paywall option, where a limited amount of content is made available free to all unregistered readers.

The Journal of Biological Chemistry (JBC) is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1905. Since 1925, it is published by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. It covers research in areas of biochemistry and molecular biology. The editor is Alex Toker. As of January 2021, the journal is fully open access. In press articles are available free on its website immediately after acceptance.
The Science Citation Index Expanded – previously titled Science Citation Index – is a citation index originally produced by the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) and created by Eugene Garfield.

ChemSpider is a database of chemicals. ChemSpider is owned by the Royal Society of Chemistry.
Science Publishing Group (SPG) is an open-access publisher of academic journals and books established in 2012. It has an address in New York City but is actually based in Pakistan. The company has been criticized for predatory publishing practices. As of 2019, it publishes 430 journals in various fields.











