Lists of events in the history of rail transport are organised into the yearly lists below.
| 1427 | 1513 | 1571 | 1604 | 1645 |
| 1700s | Cat:1700s |
| 1710s | Cat:1710s |
| 1720s | Cat:1720s |
| 1730s | Cat:1730s |
| 1740s | Cat:1740s |
| 1750s | Cat:1750s |
| 1760s | Cat:1760s |
| 1770s | Cat:1770s |
| 1780s | Cat:1780s |
| 1790s | Cat:1790s |
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board.

Rail transport is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails.

A train is a series of connected vehicles that run along a railway track and transport people or freight. Trains are typically pulled or pushed by locomotives, though some are self-propelled, such as multiple units. Passengers and cargo are carried in railroad cars, also known as wagons. Trains are designed to a certain gauge, or distance between rails. Most trains operate on steel tracks with steel wheels, the low friction of which makes them more efficient than other forms of transport.
Rail or rails may refer to:
This is a series of lists by country. The lists generally cover topics related to sovereign countries; however, states with limited recognition are also included.
This page provides an index of articles on rail transport by country.
In the history of rail transport, dating back to the 19th century, there have been hundreds of named passenger trains. Lists of these have been organized into geographical regions. Trains with numeric names are spelled out. For example, the 20th Century Limited is listed under "Twentieth Century Limited".
Rail transport – means of conveyance of passengers and goods by way of wheeled vehicles running on rail tracks consisting of steel rails installed on sleepers/ties and ballast.
Ottoman railways may refer to:
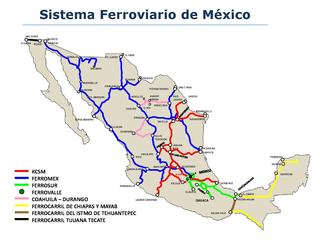
Mexico has a freight railway system owned by the national government and operated by various entities under concessions (charters) granted by the national government. The railway system provides freight and passenger service throughout the country, connecting major industrial centers with ports and with rail connections at the United States border. Passenger rail services were limited to a number of tourist trains between 1997, when Ferrocarriles Nacionales de México suspended service, and 2008, when Ferrocarril Suburbano de la Zona Metropolitana de México inaugurated Mexico's first commuter rail service between Mexico City and the State of Mexico. This is not including the Mexico City Metro, which started service in 1969.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to transport:
This is the list of rail accident lists.
These lists of urban rail transit systems are sorted by the type of system:

Urban rail transit in India plays an important role in intracity transportation in the major cities which are highly populated. It consists of rapid transit, suburban rail, monorail and tram systems. According to a report published in 2021, a total of 2.63 billion people travelled annually in metro systems across India's fifteen major cities, placing the country as one of the busiest urban rapid transit hubs in the world in terms of ridership. The combined length of 871 kilometres of metro systems in India makes it the fourth longest in operation in the world.

Public transport is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typically managed on a schedule, operated on established routes, and that charge a posted fee for each trip. There is no rigid definition of which kinds of transport are included, and air travel is often not thought of when discussing public transport—dictionaries use wording like "buses, trains, etc." Examples of public transport include city buses, trolleybuses, trams and passenger trains, rapid transit and ferries. Public transport between cities is dominated by airlines, coaches, and intercity rail. High-speed rail networks are being developed in many parts of the world.
The 2,520 railway stations on the National Rail network in Great Britain are classified into six categories by the Department for Transport. The scheme was devised in 1996 and there was a review in 2009 when 106 stations changed categories. The categorisation scheme is owned by Network Rail, the site landlord of most of the stations.

Sydney Trains is the operator and brand name of the commuter rail network serving the city of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The network is a commuter rail system with a central underground core that covers 369 km (229 mi) of route length over 813 km (505 mi) of track, with 170 stations on eight lines.

Transport for Wales is a not-for-profit company owned by the Welsh Government and managed at arms length by its appointed board. TfW oversees the Transport for Wales Group consisting of itself and its subsidiaries: Transport for Wales Rail, the train operator of the Wales & Borders railway franchise; Pullman Rail Limited; and TfW Innovation Services Limited, a joint venture between TfW (51%) and former operator KeolisAmey Wales (49%).