An intelligence quotient (IQ) is a total score derived from a set of standardized tests or subtests designed to assess human intelligence. The abbreviation "IQ" was coined by the psychologist William Stern for the German term Intelligenzquotient, his term for a scoring method for intelligence tests at University of Breslau he advocated in a 1912 book.
Visual thinking, also called visual or spatial learning or picture thinking, is the phenomenon of thinking through visual processing. Visual thinking has been described as seeing words as a series of pictures. It is common in approximately 60–65% of the general population. "Real picture thinkers", those who use visual thinking almost to the exclusion of other kinds of thinking, make up a smaller percentage of the population. Research by child development theorist Linda Kreger Silverman suggests that less than 30% of the population strongly uses visual/spatial thinking, another 45% uses both visual/spatial thinking and thinking in the form of words, and 25% thinks exclusively in words. According to Kreger Silverman, of the 30% of the general population who use visual/spatial thinking, only a small percentage would use this style over and above all other forms of thinking, and can be said to be true "picture thinkers".

The Silva Method is a self-help and meditation program developed by José Silva. It claims to increase an individual's abilities through relaxation, development of higher brain functions, and psychic abilities such as clairvoyance.
An aptitude is a component of a competence to do a certain kind of work at a certain level. Outstanding aptitude can be considered "talent". Aptitude is inborn potential to perform certain kinds of activities, whether physical or mental, and whether developed or undeveloped. Aptitude is often contrasted with skills and abilities, which are developed through learning. The mass term ability refers to components of competence acquired through a combination of both aptitude and skills.
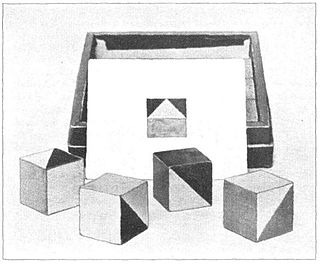
A block design test is a subtest on many IQ test batteries used as part of assessment of human intelligence. It is thought to tap spatial visualization ability and motor skill. The test-taker uses hand movements to rearrange blocks that have various color patterns on different sides to match a pattern. The items in a block design test can be scored both by accuracy in matching the pattern and by speed in completing each item.

Visual memory describes the relationship between perceptual processing and the encoding, storage and retrieval of the resulting neural representations. Visual memory occurs over a broad time range spanning from eye movements to years in order to visually navigate to a previously visited location. Visual memory is a form of memory which preserves some characteristics of our senses pertaining to visual experience. We are able to place in memory visual information which resembles objects, places, animals or people in a mental image. The experience of visual memory is also referred to as the mind's eye through which we can retrieve from our memory a mental image of original objects, places, animals or people. Visual memory is one of several cognitive systems, which are all interconnected parts that combine to form the human memory. Types of palinopsia, the persistence or recurrence of a visual image after the stimulus has been removed, is a dysfunction of visual memory.
Cognitive tests are assessments of the cognitive capabilities of humans and other animals. Tests administered to humans include various forms of IQ tests; those administered to animals include the mirror test and the T maze test. Such study is important to research concerning the philosophy of mind and psychology, as well as determination of human and animal intelligence.

Raven's Progressive Matrices or RPM is a non-verbal test typically used to measure general human intelligence and abstract reasoning and is regarded as a non-verbal estimate of fluid intelligence. It is one of the most common tests administered to both groups and individuals ranging from 5-year-olds to the elderly. It comprises 60 multiple choice questions, listed in order of increasing difficulty. This format is designed to measure the test taker's reasoning ability, the eductive ("meaning-making") component of Spearman's g.

Mental rotation is the ability to rotate mental representations of two-dimensional and three-dimensional objects as it is related to the visual representation of such rotation within the human mind. There is a relationship between areas of the brain associated with perception and mental rotation. There could also be a relationship between the cognitive rate of spatial processing, general intelligence and mental rotation.
Spatial visualization ability or visual-spatial ability is the ability to mentally manipulate 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional figures. It is typically measured with simple cognitive tests and is predictive of user performance with some kinds of user interfaces.
Creative visualization is the cognitive process of purposefully generating visual mental imagery, with eyes open or closed, simulating or recreating visual perception, in order to maintain, inspect, and transform those images, consequently modifying their associated emotions or feelings, with intent to experience a subsequent beneficial physiological, psychological, or social effect, such as expediting the healing of wounds to the body, minimizing physical pain, alleviating psychological pain including anxiety, sadness, and low mood, improving self-esteem or self-confidence, and enhancing the capacity to cope when interacting with others.
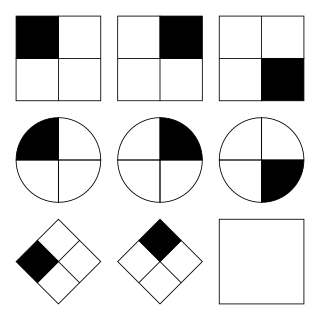
Minnesota Paper Form Board Test is said to test “imagery capacity” , “spatial visualization”,“mental visualization skills” “part–whole relationship skills” and “the ability of an individual to visualize and manipulate objects in space”. The test consists of five figures and one of the figures displayed in disarranged parts. The subject has to decide which of the figures displays the pieces joined together.
Spatial cognition is the acquisition, organization, utilization, and revision of knowledge about spatial environments. It is most about how animals including humans behave within space and the knowledge they built around it, rather than space itself. These capabilities enable individuals to manage basic and high-level cognitive tasks in everyday life. Numerous disciplines work together to understand spatial cognition in different species, especially in humans. Thereby, spatial cognition studies also have helped to link cognitive psychology and neuroscience. Scientists in both fields work together to figure out what role spatial cognition plays in the brain as well as to determine the surrounding neurobiological infrastructure.
Spatial intelligence is an area in the theory of multiple intelligences that deals with spatial judgment and the ability to visualize with the mind's eye. It is defined by Howard Gardner as a human computational capacity that provides the ability or mental skill to solve spatial problems of navigation, visualization of objects from different angles and space, faces or scenes recognition, or to notice fine details. Gardner further explains that Spatial Intelligence could be more effective to solve problems in areas related to realistic, thing-oriented, and investigative occupations. This capability is a brain skill that is also found in people with visual impairment. As researched by Gardner, a blind person can recognize shapes in a non-visual way. The spatial reasoning of the blind person allows them to translate tactile sensations into mental calculations of length and visualizations of form.

According to Paul Muchinsky in his textbook Psychology Applied to Work, "mechanical aptitude tests require a person to recognize which mechanical principle is suggested by a test item." The underlying concepts measured by these items include sounds and heat conduction, velocity, gravity, and force.
The Purdue Spatial Visualization Test-Visualization of Rotations (PSVT:R) is a test of spatial visualization ability published by Roland B. Guay in 1977. Many modifications of the test exist.
Sex differences in human intelligence have long been a topic of debate among researchers and scholars. Most psychologists now believe that there are no significant sex differences in general intelligence, although ability in particular types of intelligence does appear to vary slightly on average.
Charles Spearman developed his two-factor theory of intelligence using factor analysis. His research not only led him to develop the concept of the g factor of general intelligence, but also the s factor of specific intellectual abilities. L. L. Thurstone, Howard Gardner, and Robert Sternberg also researched the structure of intelligence, and in analyzing their data, concluded that a single underlying factor was influencing the general intelligence of individuals. However, Spearman was criticized in 1916 by Godfrey Thomson, who claimed that the evidence was not as crucial as it seemed. Modern research is still expanding this theory by investigating Spearman's law of diminishing returns, and adding connected concepts to the research.
Sex differences in cognition are widely studied in the current scientific literature. Biological and genetic differences in combination with environment and culture have resulted in the cognitive differences among men and women. Among biological factors, hormones such as testosterone and estrogen may play some role mediating these differences. Among differences of diverse mental and cognitive abilities, the largest or most well known are those relating to spatial abilities, social cognition and verbal skills and abilities.

Spatial ability or visuo-spatial ability is the capacity to understand, reason, and remember the visual and spatial relations among objects or space.








