
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits a beta particle, transforming into an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron transforms it into a proton by the emission of an electron accompanied by an antineutrino; or, conversely a proton is converted into a neutron by the emission of a positron with a neutrino in so-called positron emission. Neither the beta particle nor its associated (anti-)neutrino exist within the nucleus prior to beta decay, but are created in the decay process. By this process, unstable atoms obtain a more stable ratio of protons to neutrons. The probability of a nuclide decaying due to beta and other forms of decay is determined by its nuclear binding energy. The binding energies of all existing nuclides form what is called the nuclear band or valley of stability. For either electron or positron emission to be energetically possible, the energy release or Q value must be positive.

A muon is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 e and a spin of 1/2, but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As with other leptons, the muon is not thought to be composed of any simpler particles; that is, it is a fundamental particle.

The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol
n
or
n0
, which has a neutral charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons behave similarly within the nucleus, and each has a mass of approximately one dalton, they are both referred to as nucleons. Their properties and interactions are described by nuclear physics. Protons and neutrons are not elementary particles; each is composed of three quarks.

A neutrino is a fermion that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small (-ino) that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles. The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the electromagnetic interaction or the strong interaction. Thus, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and undetected.

In particle physics, quantum electrodynamics (QED) is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved. QED mathematically describes all phenomena involving electrically charged particles interacting by means of exchange of photons and represents the quantum counterpart of classical electromagnetism giving a complete account of matter and light interaction.

In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:

In particle physics, a lepton is an elementary particle of half-integer spin that does not undergo strong interactions. Two main classes of leptons exist: charged leptons, and neutral leptons. Charged leptons can combine with other particles to form various composite particles such as atoms and positronium, while neutrinos rarely interact with anything, and are consequently rarely observed. The best known of all leptons is the electron.
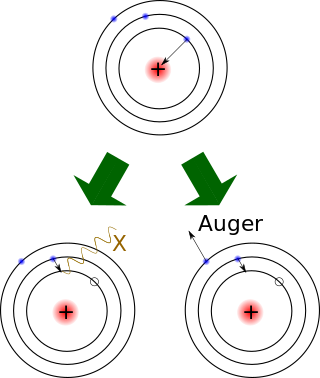
Electron capture is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. This process thereby changes a nuclear proton to a neutron and simultaneously causes the emission of an electron neutrino.

Neutron radiation is a form of ionizing radiation that presents as free neutrons. Typical phenomena are nuclear fission or nuclear fusion causing the release of free neutrons, which then react with nuclei of other atoms to form new nuclides—which, in turn, may trigger further neutron radiation. Free neutrons are unstable, decaying into a proton, an electron, plus an electron antineutrino. Free neutrons have a mean lifetime of 887 seconds.
A subcritical reactor is a nuclear fission reactor concept that produces fission without achieving criticality. Instead of sustaining a chain reaction, a subcritical reactor uses additional neutrons from an outside source. There are two general classes of such devices. One uses neutrons provided by a nuclear fusion machine, a concept known as a fusion–fission hybrid. The other uses neutrons created through spallation of heavy nuclei by charged particles such as protons accelerated by a particle accelerator, a concept known as an accelerator-driven system (ADS) or accelerator-driven sub-critical reactor.
The synthesis of precious metals involves the use of either nuclear reactors or particle accelerators to produce these elements.

Neutrinoless double beta decay (0νββ) is a commonly proposed and experimentally pursued theoretical radioactive decay process that would prove a Majorana nature of the neutrino particle. To this day, it has not been found.

Muon spin spectroscopy, also known as µSR, is an experimental technique based on the implantation of spin-polarized muons in matter and on the detection of the influence of the atomic, molecular or crystalline surroundings on their spin motion. The motion of the muon spin is due to the magnetic field experienced by the particle and may provide information on its local environment in a very similar way to other magnetic resonance techniques, such as electron spin resonance and, more closely, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).
The Delta baryons are a family of subatomic particle made of three up or down quarks, the same constituent quarks that make up the more familiar protons and neutrons.
T2K is a particle physics experiment studying the oscillations of the accelerator neutrinos. The experiment is conducted in Japan by the international cooperation of about 500 physicists and engineers with over 60 research institutions from several countries from Europe, Asia and North America and it is a recognized CERN experiment (RE13). T2K collected data within its first phase of operation from 2010 till 2021. The second phase of data taking (T2K-II) is expected to start in 2023 and last until commencement of the successor of T2K – the Hyper-Kamiokande experiment in 2027.
In particle physics, the Peskin–Takeuchi parameters are a set of three measurable quantities, called S, T, and U, that parameterize potential new physics contributions to electroweak radiative corrections. They are named after physicists Michael Peskin and Tatsu Takeuchi, who proposed the parameterization in 1990; proposals from two other groups came almost simultaneously.

Cargo scanning or non-intrusive inspection (NII) refers to non-destructive methods of inspecting and identifying goods in transportation systems. It is often used for scanning of intermodal freight shipping containers. In the US it is spearheaded by the Department of Homeland Security and its Container Security Initiative (CSI) trying to achieve one hundred percent cargo scanning by 2012 as required by the US Congress and recommended by the 9/11 Commission. In the US the main purpose of scanning is to detect special nuclear materials (SNMs), with the added bonus of detecting other types of suspicious cargo. In other countries the emphasis is on manifest verification, tariff collection and the identification of contraband. In February 2009, approximately 80% of US incoming containers were scanned. To bring that number to 100% researchers are evaluating numerous technologies, described in the following sections.

Nuclear transmutation is the conversion of one chemical element or an isotope into another chemical element. Nuclear transmutation occurs in any process where the number of protons or neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is changed.

The Accelerator Neutrino Neutron Interaction Experiment (ANNIE) is a proposed water Cherenkov detector experiment designed to examine the nature of neutrino interactions. This experiment will study phenomena like proton decay, and neutrino oscillations, by analyzing neutrino interactions in gadolinium-loaded water and measuring their neutron yield. Neutron Tagging plays an important role in background rejection from atmospheric neutrinos. By implementing early prototypes of LAPPDs, high precision timing is possible. The suggested location for ANNIE is the SciBooNE hall on the Booster Neutrino Beam associated with the MiniBooNE experiment. The neutrino beam originates in Fermilab where The Booster delivers 8 GeV protons to a beryllium target producing secondary pions and kaons. These secondary mesons decay to produce a neutrino beam with an average energy of around 800 MeV. ANNIE will begin installation in the summer of 2015. Phase I of ANNIE, mapping the neutron background, completed in 2017. The detector is being upgraded for full science operation which is expected to begin late 2018.

When embedded in an atomic nucleus, neutrons are (usually) stable particles. Outside the nucleus, free neutrons are unstable and have a mean lifetime of 877.75+0.50
−0.44 s or 879.6±0.8 s. Therefore, the half-life for this process is 611±1 s.













