Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1830. It is eponymous for the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover—George I, George II, George III, and George IV—who reigned in continuous succession from August 1714 to June 1830. The style was revived in the late 19th century in the United States as Colonial Revival architecture and in the early 20th century in Great Britain as Neo-Georgian architecture; in both it is also called Georgian Revival architecture. In the United States the term "Georgian" is generally used to describe all buildings from the period, regardless of style; in Britain it is generally restricted to buildings that are "architectural in intention", and have stylistic characteristics that are typical of the period, though that covers a wide range.

Saint George was a soldier of Cappadocian Greek origins, member of the Praetorian Guard for Roman emperor Diocletian who was sentenced to death for refusing to recant his Christian faith. He became one of the most venerated saints and megalo-martyrs in Christianity, and he was especially venerated as a military saint since the Crusades.

Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital and largest city is Tbilisi. Georgia covers a territory of 69,700 square kilometres (26,911 sq mi), and its 2017 population is about 3.718 million. Georgia is a unitary parliamentary republic, with the government elected through a representative democracy.

In heraldry, Saint George's Cross, also called the Cross of Saint George, is a red cross on a white background, which from the Late Middle Ages became associated with Saint George, the military saint, often depicted as a crusader.

Georgian Jews are one of the oldest communities in Georgia, tracing their migration into the country during the Babylonian captivity in 6th century BC. Prior to Georgia's annexation by Russia, the 2,600-year history of the Georgian Jews was marked by an almost total absence of antisemitism and a visible assimilation in the Georgian language and culture. The Georgian Jews were considered ethnically and culturally distinct from neighboring Mountain Jews. They were also traditionally a highly separate group to the Ashkenazi Jews in Georgia, who arrived following the Russian annexation of Georgia.
The culture of Georgia has evolved over the country's long history, providing it with a unique national culture and a strong literary tradition based on the Georgian language and alphabet. This has provided a strong sense of national identity that has helped to preserve Georgian distinctiveness despite repeated periods of foreign occupation.

The Georgian Apostolic Autocephalous Orthodox Church is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church in full communion with the other churches of Eastern Orthodoxy. It is Georgia's dominant religious institution, and a majority of Georgian people are members. The Georgian Orthodox Church is one of the oldest churches in the world. It asserts apostolic foundation, and its historical roots must be traced to the early and late Christianization of Iberia and Colchis by Saint Andrew in the 1st century AD and by Saint Nino in the 4th century AD, respectively.

Mtskheta is a city in Mtskheta-Mtianeti province of Georgia. One of the oldest cities of Georgia, it is located approximately 20 kilometres north of Tbilisi, at the confluence of the Mtkvari and Aragvi rivers.
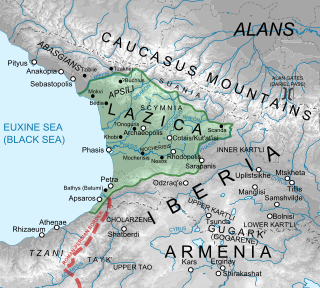
Lazica was the Latin name given to the territory of Colchis during the Roman/Byzantine period, from about the 1st century BC.

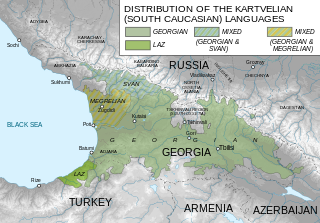
The Georgian scripts are the three writing systems used to write the Georgian language: Asomtavruli, Nuskhuri and Mkhedruli. Although the systems differ in appearance, all three are unicase, their letters share the same names and alphabetical order, and are written horizontally from left to right. Of the three scripts, Mkhedruli, once the civilian royal script of the Kingdom of Georgia and mostly used for the royal charters, is now the standard script for modern Georgian and its related Kartvelian languages, whereas Asomtavruli and Nuskhuri are used only by the Georgian Orthodox Church, in ceremonial religious texts and iconography.

David Gareja or Keshikchidagh Temple is a rock-hewn Georgian Orthodox monastery complex located in the Kakheti region of Eastern Georgia, on the half-desert slopes of Mount Gareja, some 60–70 km southeast of Georgia's capital Tbilisi. The complex includes hundreds of cells, churches, chapels, refectories and living quarters hollowed out of the rock face.

Pitsunda or Bichvinta is a resort town in the Gagra district of Abkhazia, Georgia.

The Emirs of Tbilisi ruled over the parts of today's eastern Georgia from their base in the city of Tbilisi, from 736 to 1080. Established by the Arabs during their invasions of Georgian lands, the emirate was an important outpost of the Muslim rule in the Caucasus until recaptured by the Georgians under King David IV in 1122. Since then, the city has been the capital of Georgia to this day.

The Bagrationi dynasty is a royal dynasty which reigned in Georgia from the Middle Ages until the early 19th century, being among the oldest extant Christian ruling dynasties in the world. In modern usage, the name of the dynasty is sometimes Hellenized and referred to as the Georgian Bagratids, also known in English as the Bagrations.

The Svetitskhoveli Cathedral is an Eastern Orthodox cathedral located in the historic town of Mtskheta, Georgia, to the northwest of the Georgian capital Tbilisi. A masterpiece of the Early Middle Ages, Svetitskhoveli is recognized by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. It is currently the second largest church building in Georgia, after the Holy Trinity Cathedral.

The Kingdom of Georgia, also known as the Georgian Empire, was a medieval Eurasian monarchy which emerged circa 1008 AD. It reached its Golden Age of political and economic strength during the reign of King David IV and Queen Tamar the Great from 11th to 13th centuries. Georgia became one of the pre-eminent nations of the Christian East, her pan-Caucasian empire stretching, at its largest extent, from Eastern Europe and the North Caucasus to the northern portion of Iran and Anatolia, while also maintaining religious possessions abroad, such as the Monastery of the Cross in Jerusalem and the Monastery of Iviron in Greece. It was the principal historical precursor of present-day Georgia.

The nation of Georgia was first unified as a kingdom under the Bagrationi dynasty by the King Bagrat III of Georgia in the 8th to 9th century, arising from a number of predecessor states of the ancient kingdoms of Colchis and Iberia. The Kingdom of Georgia flourished during the 10th to 12th centuries under King David IV the Builder and Queen Tamar the Great, and fell to the Mongol invasion by 1243, and after a brief reunion under George V the Brilliant to the Timurid Empire. By 1490, Georgia was fragmented into a number of petty kingdoms and principalities, which throughout the Early Modern period struggled to maintain their autonomy against Ottoman and Iranian domination until Georgia was finally annexed by the Russian Empire in the 19th century. After a brief bid for independence with the Democratic Republic of Georgia of 1918–1921, Georgia was part of the Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic from 1922 to 1936, and then formed the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic until the dissolution of the Soviet Union.