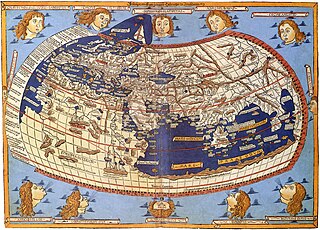
Cartography is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.
Geology is a branch of Earth science concerned with the solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Geology can also include the study of the solid features of any terrestrial planet or natural satellite such as Mars or the Moon. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology and the atmospheric sciences, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science.

A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes.
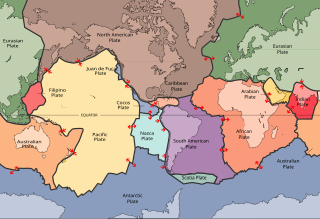
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory describing the large-scale motion of the plates making up the Earth's lithosphere since tectonic processes began on Earth between 3.3 and 3.5 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of continental drift, an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted plate-tectonic theory after seafloor spreading was validated in the late 1950s and early 1960s.

Structural geology is the study of the three-dimensional distribution of rock units with respect to their deformational histories. The primary goal of structural geology is to use measurements of present-day rock geometries to uncover information about the history of deformation (strain) in the rocks, and ultimately, to understand the stress field that resulted in the observed strain and geometries. This understanding of the dynamics of the stress field can be linked to important events in the geologic past; a common goal is to understand the structural evolution of a particular area with respect to regionally widespread patterns of rock deformation due to plate tectonics.
Paleoclimatology is the study of climates for which direct measurements were not taken. As instrumental records only span a tiny part of Earth's history, the reconstruction of ancient climate is important to understand natural variation and the evolution of the current climate. Paleoclimatology uses a variety of proxy methods from Earth and life sciences to obtain data previously preserved within rocks, sediments, boreholes, ice sheets, tree rings, corals, shells, and microfossils. Combined with techniques to date the proxies, these paleoclimate records are used to determine the past states of Earth's atmosphere.

Traditionally, the bird order Apodiformes contained three living families: the swifts (Apodidae), the treeswifts (Hemiprocnidae), and the hummingbirds (Trochilidae). In the Sibley-Ahlquist taxonomy, this order is raised to a superorder Apodimorphae in which hummingbirds are separated as a new order, Trochiliformes. With nearly 450 species identified to date, they are the most diverse order of birds after the passerines.

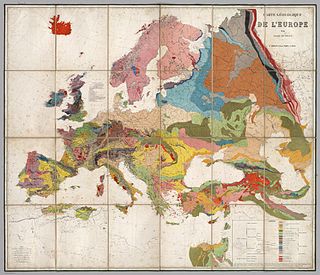
A geologic map is a special-purpose map made to show various geological features. Rock units or geologic strata are shown by color or symbols. Bedding planes and structural features such as faults, folds, are shown with strike and dip or trend and plunge symbols which give three-dimensional orientations features.

Pangaea Proxima is a possible future supercontinent configuration. Consistent with the supercontinent cycle, Pangaea Proxima could occur within the next 300 million years. This potential configuration, hypothesized by Christopher Scotese in November 1982, earned its name from its similarity to the previous Pangaea supercontinent. Scotese later changed Pangaea Ultima to Pangaea Proxima to alleviate confusion about the name Pangaea Ultima which could imply that it would be the last supercontinent. The concept was based on examination of past cycles of formation and breakup of supercontinents, not on current understanding of the mechanisms of tectonic change, which are too imprecise to project that far into the future. "It's all pretty much fantasy to start with," Scotese has said. "But it's a fun exercise to think about what might happen. And you can only do it if you have a really clear idea of why things happen in the first place."

Paleomagnetism, or palaeomagnetism, is the study of the record of the Earth's magnetic field in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials. Magnetic minerals in rocks can lock-in a record of the direction and intensity of the magnetic field when they form. This record provides information on the past behavior of Earth's magnetic field and the past location of tectonic plates. The record of geomagnetic reversals preserved in volcanic and sedimentary rock sequences (magnetostratigraphy) provides a time-scale that is used as a geochronologic tool. Geophysicists who specialize in paleomagnetism are called paleomagnetists.
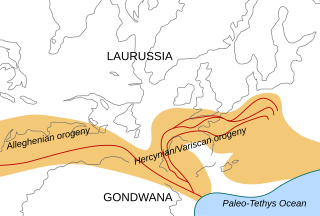
The Variscan or Hercynianorogeny was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.

Relative dating is the science of determining the relative order of past events, without necessarily determining their absolute age. In geology, rock or superficial deposits, fossils and lithologies can be used to correlate one stratigraphic column with another. Prior to the discovery of radiometric dating in the early 20th century, which provided a means of absolute dating, archaeologists and geologists used relative dating to determine ages of materials. Though relative dating can only determine the sequential order in which a series of events occurred, not when they occurred, it remains a useful technique. Relative dating by biostratigraphy is the preferred method in paleontology and is, in some respects, more accurate. The Law of Superposition, which states that older layers will be deeper in a site than more recent layers, was the summary outcome of 'relative dating' as observed in geology from the 17th century to the early 20th century.
Christopher R. Scotese is an American geologist and paleogeographer. He received his PhD from the University of Chicago in 1985. He is the creator of the Paleomap Project, which aims to map Earth over the last billion years, and is credited with predicting Pangaea Ultima, a possible future supercontinent configuration. Later Dr. Scotese changed Pangaea Ultima to Pangaea Proxima to alleviate confusion about the name Pangaea Ultima, which would imply that it would be the last supercontinent.

The history of geology is concerned with the development of the natural science of geology. Geology is the scientific study of the origin, history, and structure of the earth.

A fault trace describes the intersection of a geological fault with the Earth's surface, which leaves a visible disturbance on the surface, usually looking like a crack in the surface with jagged rock structures protruding outward. The term also applies to a line plotted on a geological map to represent a fault. These fractures tend to occur when a slip surface expands from a fault core, especially during an earthquake. This tends to occur with fault displacement, in which surfaces on both sides of a fault, known as fault blocks, separate horizontally or vertically.

Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical and chemical constitution of Earth and its atmosphere. Earth science can be considered to be a branch of planetary science, but with a much older history. Earth science encompasses four main branches of study, the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, the atmosphere, and the biosphere, each of which is further broken down into more specialized fields.

The Olympic-Wallowa lineament (OWL) – first reported by cartographer Erwin Raisz in 1945 on a relief map of the continental United States – is a physiographic feature of unknown origin in the state of Washington running approximately from the town of Port Angeles, on the Olympic Peninsula to the Wallowa Mountains of eastern Oregon.
Plate reconstruction is the process of reconstructing the positions of tectonic plates relative to each other or to other reference frames, such as the earth's magnetic field or groups of hotspots, in the geological past. This helps determine the shape and make-up of ancient supercontinents and provides a basis for paleogeographic reconstructions.

The Cliefden Caves ia heritage-listed geoheritage site in Mandurama, Cowra Shire, New South Wales, Australia. The caves comprises Ordovician fossil localities, limestone caves, a spring and tufa dams, and a site where limestone was first discovered in inland Australia.
GPlates is open-source application software offering a novel combination of interactive plate-tectonic reconstructions, geographic information system (GIS) functionality and raster data visualization.