
A financial market is a market in which people trade financial securities and derivatives at low transaction costs. Some of the securities include stocks and bonds, raw materials and precious metals, which are known in the financial markets as commodities.

In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset with the hope that it will become more valuable shortly. It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline in value.

Nostalgia is a sentimentality for the past, typically for a period or place with happy personal associations. The word nostalgia is a learned formation of a Greek compound, consisting of νόστος (nóstos), meaning "homecoming", a Homeric word, and ἄλγος (álgos), meaning "sorrow" or "despair", and was coined by a 17th-century medical student to describe the anxieties displayed by Swiss mercenaries fighting away from home. Described as a medical condition—a form of melancholy—in the early modern period, it became an important trope in Romanticism.

Media manipulation refers to orchestrated campaigns in which actors exploit the distinctive features of broadcasting mass communications or digital media platforms to mislead, misinform, or create a narrative that advance their interests and agendas.

Retro style is imitative or consciously derivative of lifestyles, trends, or art forms from history, including in music, modes, fashions, or attitudes. In popular culture, the "nostalgia cycle" is typically for the two decades that begin 20–30 years ago.

Lateral thinking is a manner of solving problems using an indirect and creative approach via reasoning that is not immediately obvious. It involves ideas that may not be obtainable using only traditional step-by-step logic.

New Coke was the unofficial name of a reformulation of the soft drink Coca-Cola, introduced by The Coca-Cola Company in April, 1985. It was renamed Coke II in 1990, and discontinued in July 2002.
Creative problem-solving (CPS) is the mental process of searching for an original and previously unknown solution to a problem. To qualify, the solution must be novel and reached independently. The creative problem-solving process was originally developed by Alex Osborn and Sid Parnes. Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of using creativity to develop new ideas and solutions to problems. The process is based on separating divergent and convergent thinking styles, so that one can focus their mind on creating at the first stage, and then evaluating at the second stage.

Edward Charles Francis Publius de Bono was a Maltese physician and commentator. He originated the term lateral thinking, wrote many books on thinking including Six Thinking Hats.

A flea market is a type of street market that provides space for vendors to sell previously owned (second-hand) goods. This type of market is often seasonal. However, in recent years there has been the development of 'formal' and 'casual' markets which divides a fixed-style market (formal) with long-term leases and a seasonal-style market with short-term leases. Consistently, there tends to be an emphasis on sustainable consumption whereby items such as used goods, collectibles, antiques and vintage clothing can be purchased, in an effort to combat climate change and fast fashion.

In economics, a luxury good is a good for which demand increases more than what is proportional as income rises, so that expenditures on the good become a more significant proportion of overall spending. Luxury goods are in contrast to necessity goods, where demand increases proportionally less than income. Luxury goods is often used synonymously with superior goods.
Creativity techniques are methods that encourage creative actions, whether in the arts or sciences. They focus on a variety of aspects of creativity, including techniques for idea generation and divergent thinking, methods of re-framing problems, changes in the affective environment and so on. They can be used as part of problem solving, artistic expression, or therapy.
Bryan Edward Nesbitt is an automobile designer and currently head of General Motors Corporation International Operations Design, based in Shanghai, China. Nesbitt is also brand chairman for Wuling and Baojun, two automakers with which GM has joint ventures.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to thought (thinking):

Six Thinking Hats was written by Dr. Edward de Bono. "Six Thinking Hats" and the associated idea parallel thinking provide a means for groups to plan thinking processes in a detailed and cohesive way, and in doing so to think together more effectively.
Organizational memory (OM), sometimes called institutional memory or corporate memory, is the accumulated body of data, information, and knowledge created in the course of an organization's existence. The concept of organizational memory includes the ideas of components knowledge acquisition, knowledge processing or maintenance, and knowledge usage like search and retrieval. Falling under the wider disciplinary umbrella of knowledge management, it has two repositories: an organization's archives, including its electronic data bases; and individuals' memories.
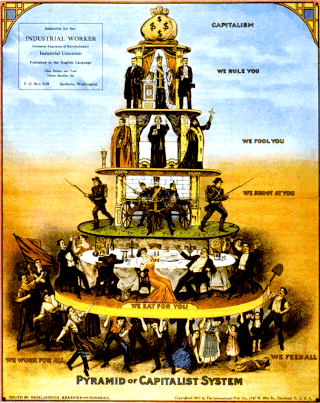
Propaganda techniques are methods used in propaganda to convince an audience to believe what the propagandist wants them to believe. Many propaganda techniques are based on socio-psychological research. Many of these same techniques can be classified as logical fallacies or abusive power and control tactics.
Parallel thinking is a term coined by Edward de Bono.
Lateral computing is a lateral thinking approach to solving computing problems. Lateral thinking has been made popular by Edward de Bono. This thinking technique is applied to generate creative ideas and solve problems. Similarly, by applying lateral-computing techniques to a problem, it can become much easier to arrive at a computationally inexpensive, easy to implement, efficient, innovative or unconventional solution.
Emotional branding is a term used within marketing communication that refers to the practice of building brands that appeal directly to a consumer's emotional state, needs and aspirations. Emotional branding is successful when it triggers an emotional response in the consumer, that is, a desire for the advertised brand that cannot fully be rationalized. Emotional brands have a significant impact when the consumer experiences a strong and lasting attachment to the brand comparable to a feeling of bonding, companionship or love. Examples of emotional branding include the nostalgic attachment to the Kodak brand of film, bonding with the Jim Beam bourbon brand, and love for the McDonald's brand.












