The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is an Internet standard communication protocol for electronic mail transmission. Mail servers and other message transfer agents use SMTP to send and receive mail messages. User-level email clients typically use SMTP only for sending messages to a mail server for relaying, and typically submit outgoing email to the mail server on port 587 or 465 per RFC 8314. For retrieving messages, IMAP is standard, but proprietary servers also often implement proprietary protocols, e.g., Exchange ActiveSync.
A Domain Name System blocklist, Domain Name System-based blackhole list, Domain Name System blacklist (DNSBL) or real-time blackhole list (RBL) is a service for operation of mail servers to perform a check via a Domain Name System (DNS) query whether a sending host's IP address is blacklisted for email spam. Most mail server software can be configured to check such lists, typically rejecting or flagging messages from such sites.
Various anti-spam techniques are used to prevent email spam.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is an email authentication method which ensures the sending mail server is authorized to originate mail from the email sender's domain. This authentication only applies to the email sender listed in the "envelope from" field during the initial SMTP connection. If the email is bounced, a message is sent to this address, and for downstream transmission it typically appears in the "Return-Path" header. To authenticate the email address which is actually visible to recipients on the "From:" line, other technologies such as DMARC must be used. Forgery of this address is known as email spoofing, and is often used in phishing and email spam.
Greylisting is a method of defending e-mail users against spam. A mail transfer agent (MTA) using greylisting will "temporarily reject" any email from a sender it does not recognize. If the mail is legitimate, the originating server will try again after a delay, and if sufficient time has elapsed, the email will be accepted.
A bounce message or just "bounce" is an automated message from an email system, informing the sender of a previous message that the message has not been delivered. The original message is said to have "bounced".
Sender ID is an historic anti-spoofing proposal from the former MARID IETF working group that tried to join Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and Caller ID. Sender ID is defined primarily in Experimental RFC 4406, but there are additional parts in RFC 4405, RFC 4407 and RFC 4408.
qpsmtpd is an SMTP daemon written in Perl. It was originally designed to be a drop-in replacement for qmail-smtpd, the SMTP component of qmail, and it is now also compatible with Postfix, Exim, sendmail and virtually any software that "speaks SMTP". It has a flexible plugin system, making it easy to interoperate with other pieces in a mail system.
Email authentication, or validation, is a collection of techniques aimed at providing verifiable information about the origin of email messages by validating the domain ownership of any message transfer agents (MTA) who participated in transferring and possibly modifying a message.
Forward-confirmed reverse DNS (FCrDNS), also known as full-circle reverse DNS, double-reverse DNS, or iprev, is a networking parameter configuration in which a given IP address has both forward (name-to-address) and reverse (address-to-name) Domain Name System (DNS) entries that match each other. This is the standard configuration expected by the Internet standards supporting many DNS-reliant protocols. David Barr published an opinion in RFC 1912 (Informational) recommending it as best practice for DNS administrators, but there are no formal requirements for it codified within the DNS standard itself.
The Sender Rewriting Scheme (SRS) is a scheme for bypassing the Sender Policy Framework's (SPF) methods of preventing forged sender addresses. Forging a sender address is also known as email spoofing.
Context filtering is an anti-spam / mail policy method that does not deal with the contents of the mail but rather uses the context of the SMTP connection to decide whether a mail will be accepted or not.
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication method designed to detect forged sender addresses in email, a technique often used in phishing and email spam.
In networking, a black hole refers to a place in the network where incoming or outgoing traffic is silently discarded, without informing the source that the data did not reach its intended recipient.
SURBL is a collection of URI DNSBL lists of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) hosts, typically web site domains, that appear in unsolicited messages. SURBL can be used to search incoming e-mail message bodies for spam payload links to help evaluate whether the messages are unsolicited. For example, if http://www.example.com is listed, then e-mail messages with a message body containing this URI may be classified as unsolicited. URI DNSBLs differ from prior DNSBLs, which commonly list mail sending IP addresses. SURBL is a specific instance of the general URI DNSBL list type.
The Anti-Spam SMTP Proxy (ASSP) is an open-source, Perl based, platform-independent transparent SMTP proxy server.
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) is an email authentication protocol. It is designed to give email domain owners the ability to protect their domain from unauthorized use, commonly known as email spoofing. The purpose and primary outcome of implementing DMARC is to protect a domain from being used in business email compromise attacks, phishing email, email scams and other cyber threat activities.
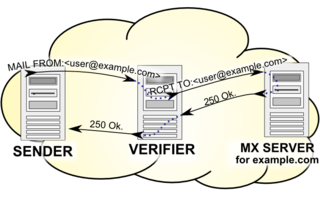
Callback verification, also known as callout verification or Sender Address Verification, is a technique used by SMTP software in order to validate e-mail addresses. The most common target of verification is the sender address from the message envelope. It is mostly used as an anti-spam measure.
Backscatter is incorrectly automated bounce messages sent by mail servers, typically as a side effect of incoming spam.
Haraka is an open source SMTP server. Its architecture is plugin-oriented and event-driven. The server and its plugins are written in JavaScript using the Node.js framework.
