A trade union, often simply called a union, is an organization of workers who have come together to achieve many common goals, such as protecting the integrity of their trade, improving safety standards, and attaining better wages, benefits, and working conditions through the increased bargaining power wielded by the creation of a monopoly of the workers. Trade unions typically fund the formal organization, head office, and legal team functions of the trade union through regular fees or union dues. The delegate staff of the trade union representation in the workforce are made up of workplace volunteers who are appointed by members in democratic elections.

The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), members of which are commonly termed "Wobblies", is an international labor union that was founded in 1905 in Chicago, Illinois, in the United States. The union combines general unionism with industrial unionism, as it is a general union, subdivided between the various industries which employ its members. The philosophy and tactics of the IWW are described as "revolutionary industrial unionism", with ties to socialist, syndicalist, and anarchist labor movements.

The National Labor Relations Act of 1935 is a foundational statute of United States labor law that guarantees the right of private sector employees to organize into trade unions, engage in collective bargaining, and take collective action such as strikes. Central to the act was a ban on company unions. The act was written by Senator Robert F. Wagner, passed by the 74th United States Congress, and signed into law by President Franklin D. Roosevelt.

Strike action, also called labor strike, labour strike, or simply strike, is a work stoppage, caused by the mass refusal of employees to work. A strike usually takes place in response to employee grievances. Strikes became common during the Industrial Revolution, when mass labor became important in factories and mines. In most countries, strike actions were quickly made illegal, as factory owners had far more power than workers. Most Western countries partially legalized striking in the late 19th or early 20th centuries.

The United Mine Workers of America is a North American labor union best known for representing coal miners. Today, the Union also represents health care workers, truck drivers, manufacturing workers and public employees in the United States and Canada. Although its main focus has always been on workers and their rights, the UMW of today also advocates for better roads, schools, and universal health care. By 2014, coal mining had largely shifted to open pit mines in Wyoming, and there were only 60,000 active coal miners. The UMW was left with 35,000 members, of whom 20,000 were coal miners, chiefly in underground mines in Kentucky and West Virginia. However it was responsible for pensions and medical benefits for 40,000 retired miners, and for 50,000 spouses and dependents.

The Western Federation of Miners (WFM) was a labor union that gained a reputation for militancy in the mines of the western United States and British Columbia. Its efforts to organize both hard rock miners and smelter workers brought it into sharp conflicts – and often pitched battles – with both employers and governmental authorities. One of the most dramatic of these struggles occurred in the Cripple Creek district of Colorado in 1903–04; the conflicts were thus dubbed the Colorado Labor Wars. The WFM also played a key role in the founding of the Industrial Workers of the World in 1905, but left that organization several years later.

The United Farm Workers of America, or more commonly just United Farm Workers (UFW), is a labor union for farmworkers in the United States. It originated from the merger of two workers' rights organizations, the Agricultural Workers Organizing Committee (AWOC) led by organizer Larry Itliong, and the National Farm Workers Association (NFWA) led by César Chávez and Dolores Huerta. They became allied and transformed from workers' rights organizations into a union as a result of a series of strikes in 1965, when the mostly Filipino farmworkers of the AWOC in Delano, California, initiated a grape strike, and the NFWA went on strike in support. As a result of the commonality in goals and methods, the NFWA and the AWOC formed the United Farm Workers Organizing Committee on August 22, 1966. This organization was accepted into the AFL-CIO in 1972 and changed its name to the United Farm Workers Union.
The labor history of the United States describes the history of organized labor, US labor law, and more general history of working people, in the United States. Beginning in the 1930s, unions became important allies of the Democratic Party. Some historians question why a Labor Party did not emerge in the United States, in contrast to Western Europe.

The International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers (IAM) is an AFL-CIO/CLC trade union representing approx. 646,933 workers as of 2006 in more than 200 industries with most of its membership in the United States and Canada.

The International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW) is a labor union that represents nearly 750,000 workers and retirees in the electrical industry in the United States, Canada, Panama, Guam, and several Caribbean island states; particularly electricians, or inside wiremen, in the construction industry and lineworkers and other employees of public utilities. The union also represents some workers in the computer, telecommunications, broadcasting, and other fields related to electrical work.

The Women's Trade Union League (WTUL) (1903–1950) was a U.S. organization of both working class and more well-off women to support the efforts of women to organize labor unions and to eliminate sweatshop conditions. The WTUL played an important role in supporting the massive strikes in the first two decades of the twentieth century that established the International Ladies' Garment Workers' Union and Amalgamated Clothing Workers of America and in campaigning for women's suffrage among men and women workers.

Labor unions in the United States are organizations that represent workers in many industries recognized under US labor law since the 1935 enactment of the National Labor Relations Act. Their activity today centers on collective bargaining over wages, benefits, and working conditions for their membership, and on representing their members in disputes with management over violations of contract provisions. Larger trade unions also typically engage in lobbying activities and electioneering at the state and federal level.

The National Labor Secretariat was a trade union federation in the Netherlands from 1893 to 1940.
A wildcat strike action, often referred to as a wildcat strike, is a strike action undertaken by unionized workers without union leadership's authorization, support, or approval; this is sometimes termed an unofficial industrial action. The legality of wildcat strikes varies between countries and over time, although they are not typically criminal offenses.
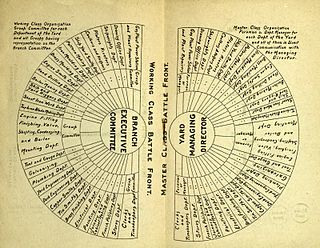
The Industrial Workers of Great Britain was a group which promoted industrial unionism in the early 20th century.

The Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) was a federation of unions that organized workers in industrial unions in the United States and Canada from 1935 to 1955. Created in 1935 by John L. Lewis, who was a part of the United Mine Workers (UMW), it was originally called the Committee for Industrial Organization but changed its name in 1938 when it broke away from the American Federation of Labor (AFL). It also changed names because it was not successful with organizing unskilled workers with the AFL.
The Carbon County Strikes took place in Carbon County, Utah from 1903–1904. The strikes primarily consisted of Slavic and Italian immigrant mine workers who partnered with the United Mine Workers of America strikes in Colorado to protest the dangerous working conditions of the Utah coal mines. The Carbon County strikes were considered the most important labor confrontation in the United States at the time. The Utah Fuel Company strongly opposed initiatives to unionize coal workers in Utah and were the primary opposition to the UMWA at the time. The Carbon County Strikes would ultimately fail in its attempt to unionize the coal workers of Utah simply because it "did not have enough support, either internally or externally, to win against a powerful and influential company that effectively played on radical, anti-foreign sentiments in defending its position" but it demonstrated a significant nationwide effort in strengthening unionization in the west.
The Scottish Operative Tailors' and Tailoresses' Association was a trade union representing clothing workers in Scotland.
This article discusses the history and present status of labor unions in Sudan.
The Trade Union Commission was a national trade union federation in Belgium.












