An embedded system is a controller programmed and controlled by a real-time operating system (RTOS) with a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electrical system, often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. Embedded systems control many devices in common use today. Ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured are used in embedded systems.

A secure cryptoprocessor is a dedicated computer on a chip or microprocessor for carrying out cryptographic operations, embedded in a packaging with multiple physical security measures, which give it a degree of tamper resistance. Unlike cryptographic processors that output decrypted data onto a bus in a secure environment, a secure cryptoprocessor does not output decrypted data or decrypted program instructions in an environment where security cannot always be maintained.

A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC) is a physical electronic authorization device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card sized card with an embedded integrated circuit. Many smart cards include a pattern of metal contacts to electrically connect to the internal chip. Others are contactless, and some are both. Smart cards can provide personal identification, authentication, data storage, and application processing. Applications include identification, financial, mobile phones (SIM), public transit, computer security, schools, and healthcare. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within organizations. Several nations have deployed smart cards throughout their populations.

Tokenization, when applied to data security, is the process of substituting a sensitive data element with a non-sensitive equivalent, referred to as a token, that has no extrinsic or exploitable meaning or value. The token is a reference that maps back to the sensitive data through a tokenization system. The mapping from original data to a token uses methods which render tokens infeasible to reverse in the absence of the tokenization system, for example using tokens created from random numbers. The tokenization system must be secured and validated using security best practices applicable to sensitive data protection, secure storage, audit, authentication and authorization. The tokenization system provides data processing applications with the authority and interfaces to request tokens, or detokenize back to sensitive data.
A backdoor is a method, often secret, of bypassing normal authentication or encryption in a computer system, a product, or an embedded device, or its embodiment, e.g. as part of a cryptosystem, an algorithm, a chipset, or a "homunculus computer" —a tiny computer-within-a-computer. Backdoors are often used for securing remote access to a computer, or obtaining access to plaintext in cryptographic systems. The backdoor may be used to gain access to passwords, delete data on hard drives, or transfer information within the cloud.
Pirate decryption most often refers to the decryption, or decoding, of pay TV or pay radio signals without permission from the original broadcaster. The term "pirate" in this case is used in the sense of copyright infringement and has little or nothing to do with sea piracy, nor with pirate radio, which involved the operation of a small broadcast radio station without lawfully obtaining a license to transmit. The MPAA and other groups which lobby in favour of intellectual property regulations have labelled such decryption as "signal theft" even though there is no direct tangible loss on the part of the original broadcaster, arguing that losing out on a potential chance to profit from a consumer's subscription fees counts as a loss of actual profit.
Data security means protecting digital data, such as those in a database, from destructive forces and from the unwanted actions of unauthorized users, such as a cyberattack or a data breach.
Secure communication is when two entities are communicating and do not want a third party to listen in. For that they need to communicate in a way not susceptible to eavesdropping or interception. Secure communication includes means by which people can share information with varying degrees of certainty that third parties cannot intercept what was said. Other than spoken face-to-face communication with no possible eavesdropper, it is probably safe to say that no communication is guaranteed secure in this sense, although practical obstacles such as legislation, resources, technical issues, and the sheer volume of communication serve to limit surveillance.
VideoGuard, produced by NDS, is a digital encryption system for use with conditional access television broadcasting. It is used on digital satellite television systems - some of which are operated by News Corporation, which owned about half (49%) of NDS until its sale to Cisco in 2012. Its two most widely used implementations are BSkyB's Sky in the United Kingdom and Ireland and DirecTV in the United States, the former of which launched the digital version of the system in 1998. Several other broadcasters around the world use the VideoGuard system, including DirecTV (Colombia), DirecTV (LatinAmerica), Hot (Israel), Yes (Israel), Viasat (Scandinavia), SKY Italia (Italy), Sky Brazil (Brazil), Sky Network Television, Foxtel (Australia), Airtel DigitalTV (India), Tata Sky & Hathway (DVB-C) (India), Astro (Malaysia), TrueVisions (Thailand), D-Smart (Turkey), TotalTV (Balkan), ONO (Spain), Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (Canada), China Central Television (China), SBB (Serbia), KabelBW (Germany), Vivacom (Bulgaria), Dolce (Romania), STAR TV/Fox International Channels (Asia), Cignal Digital TV (Philippines), Indovision (Indonesia), Telecom Italia (Italy), OTAU TV (Kazakhstan), OTE TV (Greece), Oi TV (Brazil).

VideoCipher is a brand name of analog scrambling and de-scrambling equipment for cable and satellite television invented primarily to enforce Television receive-only (TVRO) satellite equipment to only receive TV programming on a subscription basis.
Conditional access or conditional access system is the protection of content by requiring certain criteria to be met before granting access to the content. The term is commonly used in relation to digital television systems.
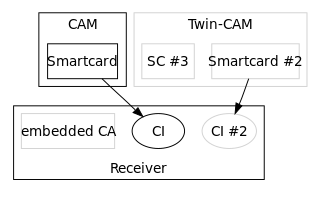
In Digital Video Broadcasting, the Common Interface is a technology which allows decryption of pay TV channels. Pay TV stations want to choose which encryption method to use. The Common Interface allows TV manufacturers to support many different pay TV stations, by allowing to plug in exchangeable conditional-access modules (CAM) for various encryption schemes.

A Secure Access Module is based on SmartCard Integrated circuits and is used to enhance the security and cryptography performance in devices, commonly in devices needing to perform secure transactions, such as payment terminals. It can be used for cryptographic computation and secure authentication against smart cards or contactless EMV cards.
KeyFly is a conditional access (CA) system developed by SIDSA which is compatible with the DVB-CSA platform. The system is based on SIDSA MACtsp processors, and conditional-access modules for it can integrate the card directly into the CAM.
Multi-Choice TV (MCTV) is a television service provider in Barbados. It is a Multichannel Multipoint Distribution Service (MMDS) or DVB-C wireless microwave-based broadcast subscription television provider. They offer a variety of packages which can be considered as comparatively priced to similar providers throughout the world.

A free-to-air or FTA Receiver is a satellite television receiver designed to receive unencrypted broadcasts. Modern decoders are typically compliant with the MPEG-2/DVB-S and more recently the MPEG-4/DVB-S2 standard for digital television, while older FTA receivers relied on analog satellite transmissions which have declined rapidly in recent years.
Cable television piracy, a form of copyright infringement, is the act of obtaining unauthorized access to cable television services. In older analog cable systems, most cable channels were not encrypted and cable theft was often as easy as plugging a coaxial cable attached to the user's television into an apartment house cable distribution box. In some rural areas nonsubscribers would even run long cables to distribution boxes on nearby utility poles. Set-top boxes were required with some systems, but these were generic, and often in an unknowing violation of contract, former customers would donate them to thrift stores for sale or retain them indefinitely in storage when they ended their subscription to the service rather than return them to the provider.
Mobile security, or more specifically mobile device security, has become increasingly important in mobile computing. Of particular concern is the security of personal and business information now stored on smartphones.