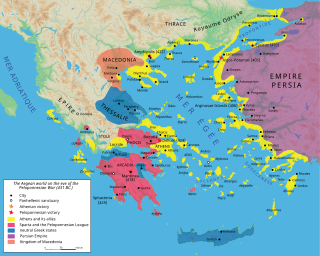
The Peloponnesian League was an alliance in the Peloponnesus from the 6th to the 4th centuries BC, dominated by Sparta. It is known mainly for being one of the two rivals in the Peloponnesian War, against the Delian League, which was dominated by Athens.

Themistocles was an Athenian politician and general. He was one of a new breed of non-aristocratic politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy. As a politician, Themistocles was a populist, having the support of lower-class Athenians, and generally being at odds with the Athenian nobility. Elected archon in 493 BC, he convinced the polis to increase the naval power of Athens, a recurring theme in his political career. During the first Persian invasion of Greece he fought at the Battle of Marathon and was possibly one of the ten Athenian strategoi (generals) in that battle.

In Greek mythology, Medea is the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, a niece of Circe and the granddaughter of the sun god Helios. Medea figures in the myth of Jason and the Argonauts, appearing in Hesiod's Theogony around 700 BC, but best known from Euripides's tragedy Medea and Apollonius of Rhodes' epic Argonautica. Medea is known in most stories as a sorceress and is often depicted as a priestess of the goddess Hecate.

The Battle of Salamis was a naval battle fought between an alliance of Greek city-states under Themistocles, and the Persian Empire under King Xerxes in 480 BC. It resulted in a decisive victory for the outnumbered Greeks. The battle was fought in the straits between the mainland and Salamis, an island in the Saronic Gulf near Athens, and marked the high point of the second Persian invasion of Greece.

Sicyon or Sikyon was an ancient Greek city state situated in the northern Peloponnesus between Corinth and Achaea on the territory of the present-day regional unit of Corinthia. An ancient monarchy at the times of the Trojan War, the city was ruled by a number of tyrants during the Archaic and Classical period and became a democracy in the 3rd century BC. Sicyon was celebrated for its contributions to ancient Greek art, producing many famous painters and sculptors. In Hellenistic times it was also the home of Aratus of Sicyon, the leader of the Achaean League.

Plataea or Plataia, also Plataeae or Plataiai, was an ancient city, located in Greece in southeastern Boeotia, south of Thebes. It was the location of the Battle of Plataea in 479 BC, in which an alliance of Greek city-states defeated the Persians.
In the modern English-language's usage of the word, a tyrant is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to oppressive means. The original Greek term meant an absolute sovereign who came to power without constitutional right, yet the word had a neutral connotation during the Archaic and early Classical periods. However, Greek philosopher Plato saw tyrannos as a negative word, and on account of the decisive influence of philosophy on politics, its negative connotations only increased, continuing into the Hellenistic period.

The Battle of Mycale was one of the two major battles that ended the second Persian invasion of Greece during the Greco-Persian Wars. It took place on or about August 27, 479 BC on the slopes of Mount Mycale, on the coast of Ionia, opposite the island of Samos. The battle was fought between an alliance of the Greek city-states, including Sparta, Athens and Corinth, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I.

The Greco-Persian Wars were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the Greeks and the enormous empire of the Persians began when Cyrus the Great conquered the Greek-inhabited region of Ionia in 547 BC. Struggling to control the independent-minded cities of Ionia, the Persians appointed tyrants to rule each of them. This would prove to be the source of much trouble for the Greeks and Persians alike.

Aristagoras, d. 497/496 BC, was the leader of the Ionian city of Miletus in the late 6th century BC and early 5th century BC and a key player during the early years of the Ionian Revolt against the Persian Achaemenid Empire. He was the son-in-law of Histiaeus, and inherited the tyranny of Miletus from him.

The Battle of Artemisium, or Battle of Artemision, was a series of naval engagements over three days during the second Persian invasion of Greece. The battle took place simultaneously with the land battle at Thermopylae, in August or September 480 BC, off the coast of Euboea and was fought between an alliance of Greek city-states, including Sparta, Athens, Corinth and others, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I.

The Battle of Plataea was the final land battle during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in 479 BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, and was fought between an alliance of the Greek city-states, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I.

Cleomenes was an Agiad King of Sparta in the late 6th and early 5th centuries BC. During his reign, which started around 519 BC, he pursued an adventurous and at times unscrupulous foreign policy aimed at crushing Argos and extending Sparta's influence both inside and outside the Peloponnese. He was a brilliant tactician. It was during his reign that the Peloponnesian League came formally into existence. During his reign, he intervened twice successfully in Athenian affairs but kept Sparta out of the Ionian Revolt. He died in prison in mysterious circumstances, with the Spartan authorities claiming his death was suicide due to insanity.

Polycrates, son of Aeaces, was the tyrant of Samos from the 540s BC to 522 BC. He had a reputation as both a fierce warrior and an enlightened tyrant.

Pheidon was an Argive ruler during the 7th century BCE and 10th in line to Temenus. He was arguably Argos's most ambitious and successful ruler during the 7th century BCE. There is a possibility that were in fact two different Pheidons who were both rulers of Argos.

Miltiades, also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Greek Athenian citizen known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He was the son of Cimon Coalemos, a renowned Olympic chariot-racer, and the father of Cimon, the noted Athenian statesman.

Corinth was a city-state (polis) on the Isthmus of Corinth, the narrow stretch of land that joins the Peloponnese to the mainland of Greece, roughly halfway between Athens and Sparta. The modern city of Corinth is located approximately 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) northeast of the ancient ruins. Since 1896, systematic archaeological investigations of the Corinth Excavations by the American School of Classical Studies at Athens have revealed large parts of the ancient city, and recent excavations conducted by the Greek Ministry of Culture have brought to light important new facets of antiquity.

The second Persian invasion of Greece occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion of Greece at the Battle of Marathon, which ended Darius I's attempts to subjugate Greece. After Darius's death, his son Xerxes spent several years planning for the second invasion, mustering an enormous army and navy. The Athenians and Spartans led the Greek resistance. About a tenth of the Greek city-states joined the 'Allied' effort; most remained neutral or submitted to Xerxes.

Korkyra was an ancient Greek city on the island of Corfu in the Ionian sea, adjacent to Epirus. It was a colony of Corinth, founded in the archaic period. According to Thucydides, the earliest recorded naval battle took place between Korkyra and Corinth, roughly 260 years before he was writing — and thus in the middle of the seventh century BC. He also writes that Korkyra was one of the three great naval powers in fifth century BC Greece, along with Athens and Corinth.
Amphicrates was an early king of Samos. He is known only from a brief reference in Herodotus and his date is much disputed.

















