
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries.
Handloading, or reloading, is the practice of making firearm cartridges by assembling the individual components, rather than purchasing mass-assembled, factory-loaded ammunition.

A cartridge, also known as a round, is a type of pre-assembled firearm ammunition packaging a projectile, a propellant substance and an ignition device (primer) within a metallic, paper, or plastic case that is precisely made to fit within the barrel chamber of a breechloading gun, for convenient transportation and handling during shooting. Although in popular usage the term "bullet" is often used to refer to a complete cartridge, the correct usage only refers to the projectile.

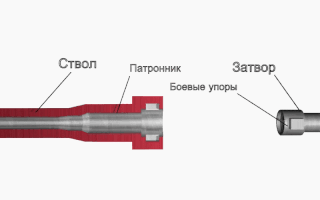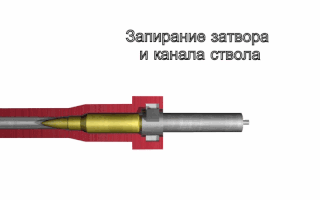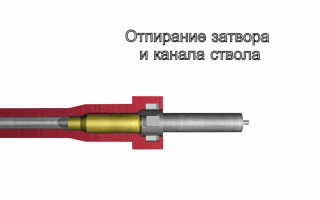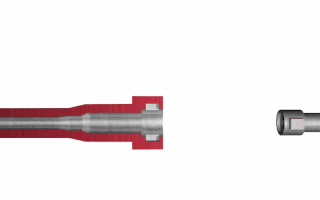
The slide on the majority of fully/semi-automatic pistols is the upper part that reciprocates ("slides") with recoil during the gun's operating cycle. It serves as the bolt carrier group (BCG) and partly as the receiver, and generally houses the firing pin/striker, the extractor and frequently also the barrel, and provides a mounting platform for iron and optical sights.

A breechloader is a firearm, in which the user loads the ammunition from the breech end of the barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, in which the user loads the ammunition from the (muzzle) end of the barrel.

A gun barrel is a crucial part of gun-type weapons such as small firearms, artillery pieces, and air guns. It is the straight shooting tube, usually made of rigid high-strength metal, through which a contained rapid expansion of high-pressure gas(es) is used to propel a projectile out of the front end (muzzle) at a high velocity. The hollow interior of the barrel is called the bore, and the diameter of the bore is called its caliber, usually measured in inches or millimetres.

The .22 Long Rifle or simply .22 LR or 22 is a long-established variety of .22 caliber rimfire ammunition originating from the United States. It is used in a wide range of rifles, pistols, revolvers, and submachine guns.
Internal ballistics, a subfield of ballistics, is the study of the propulsion of a projectile.

A blank is a firearm cartridge that, when fired, does not shoot a projectile like a bullet or pellet, but generates a muzzle flash and an explosive sound like a normal gunshot would. Firearms may need to be modified to allow a blank to cycle the action, and the shooter experiences less recoil with a blank than with a live round. Blanks are often used in prop guns for shooting simulations that have no need for ballistic results, but still demand light and sound effects, such as in historical reenactments, special effects for theatre, movie and television productions, combat training, for signaling, and cowboy mounted shooting. Specialised blank cartridges are also used for their propellant force in fields as varied as construction, shooting sports, and fishing and general recreation.

Hang fire is an unexpected delay between the triggering of a firearm and the ignition of the propellant. This failure was common in firearm actions that relied on open primer pans, due to the poor or inconsistent quality of the powder, although modern firearms are also susceptible. The delay is usually too brief to be noticed, but can be several seconds. A hangfire should be suspected whenever a firearm fails to fire, but has not clearly malfunctioned.
Blowback is a system of operation for self-loading firearms that obtains energy from the motion of the cartridge case as it is pushed to the rear by expanding gas created by the ignition of the propellant charge.

In breechloading firearms, an extractor is an action component that serves to remove spent casings of previously fired cartridges from the chamber, in order to vacate the chamber for loading a fresh round of ammunition.

Locked breech is the design of a breech-reloading firearm's action. This is important in understanding how a self-reloading firearm works. In the simplest terms, the locked breech is one way to slow down the opening of the breech of a self-reloading firearm when fired. The source of power for the movement is recoil.
A slamfire is a discharge of a firearm occurring as a cartridge is being loaded into the chamber. Some firearms are designed to slamfire, but the term also describes a malfunction of self-loading firearms. Shooters accustomed to firearms requiring trigger activation for discharge may be unprepared for a slamfire discharge.
Limp wristing is a phenomenon commonly encountered by semi-automatic pistol shooters, where the shooter's grip is not firm enough and the wrist is not held firm/straight enough to keep the frame of the firearm from traveling rearward while the bolt or slide of the firearm cycles. This condition often results in a failure to complete the operating cycle, properly termed a malfunction, but commonly termed a "jam". Both semi-automatic rifles and semi-automatic shotguns, if fired without the stock held against the shoulder correctly, may also be prone to limp wristing. Of the important variables involved in this type of malfunction, bullet and gas momentum, slide and barrel mass, recoil spring pre-load and spring rate, and shooting hand and arm mass are much more important than the compliance (limpness) of the wrist.
The following are terms related to firearms and ammunition topics.

A paper cartridge is one of various types of small arms ammunition used before the advent of the metallic cartridge. These cartridges consisted of a paper cylinder or cone containing the bullet, gunpowder, and in some cases, a primer or a lubricating and anti-fouling agent. Combustible cartridges are paper cartridges that use paper treated with oxidizers to allow them to burn completely upon ignition.
A firearm malfunction is the failure of a firearm to operate as intended for causes other than user error. Malfunctions range from temporary and relatively safe situations, such as a casing that did not eject, to potentially dangerous occurrences that may permanently damage the gun and cause injury or death. Improper handling of certain types of malfunctions can be very dangerous. Following gun safety rules can prevent firearm malfunctions, and limit the damage inflicted by them if they do occur. Proper cleaning and maintenance of a firearm play a big role in preventing malfunctions.
Recoil operation is an operating mechanism used to implement locked-breech autoloading firearms. Recoil operated firearms use the energy of recoil to cycle the action, as opposed to gas operation or blowback operation using the pressure of the propellant gas.
In firearms and artillery, the primer is the chemical and/or device responsible for initiating the propellant combustion that will propel the projectiles out of the gun barrel.












