
A descriptive statistic is a summary statistic that quantitatively describes or summarizes features from a collection of information, while descriptive statistics is the process of using and analysing those statistics. Descriptive statistics is distinguished from inferential statistics by its aim to summarize a sample, rather than use the data to learn about the population that the sample of data is thought to represent. This generally means that descriptive statistics, unlike inferential statistics, is not developed on the basis of probability theory, and are frequently non-parametric statistics. Even when a data analysis draws its main conclusions using inferential statistics, descriptive statistics are generally also presented. For example, in papers reporting on human subjects, typically a table is included giving the overall sample size, sample sizes in important subgroups, and demographic or clinical characteristics such as the average age, the proportion of subjects of each sex, the proportion of subjects with related co-morbidities, etc.

Statistics is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.

Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to deduce properties of an underlying distribution of probability. Inferential statistical analysis infers properties of a population, for example by testing hypotheses and deriving estimates. It is assumed that the observed data set is sampled from a larger population.
The theory of statistics provides a basis for the whole range of techniques, in both study design and data analysis, that are used within applications of statistics. The theory covers approaches to statistical-decision problems and to statistical inference, and the actions and deductions that satisfy the basic principles stated for these different approaches. Within a given approach, statistical theory gives ways of comparing statistical procedures; it can find a best possible procedure within a given context for given statistical problems, or can provide guidance on the choice between alternative procedures.

SPSS Statistics is a software package used for interactive, or batched, statistical analysis. Long produced by SPSS Inc., it was acquired by IBM in 2009. Current versions have the brand name: IBM SPSS Statistics.
The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the UK Parliament.
Economic statistics is a topic in applied statistics that concerns the collection, processing, compilation, dissemination, and analysis of economic data. It is also common to call the data themselves 'economic statistics', but for this usage see economic data. The data of concern to economic statistics may include those of an economy within a region, country, or group of countries. Economic statistics may also refer to a subtopic of official statistics for data produced by official organizations. Analyses within economic statistics both make use of and provide the empirical data needed in economic research, whether descriptive or econometric. They are a key input for decision making as to economic policy. The subject includes statistical analysis of topics and problems in microeconomics, macroeconomics, business, finance, forecasting, data quality, and policy evaluation. It also includes such considerations as what data to collect in order to quantify some particular aspect of an economy and of how best to collect in any given instance.

Eurostat is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Its main responsibilities are to provide statistical information to the institutions of the European Union (EU) and to promote the harmonisation of statistical methods across its member states and candidates for accession as well as EFTA countries. The organisations in the different countries that cooperate with Eurostat are summarised under the concept of the European Statistical System.

Mathematical statistics is the application of probability theory, a branch of mathematics, to statistics, as opposed to techniques for collecting statistical data. Specific mathematical techniques which are used for this include mathematical analysis, linear algebra, stochastic analysis, differential equations, and measure theory.

The Philippine Statistics Authority, abbreviated as PSA, is the central statistical authority of the Philippine government that collects, compiles, analyzes and publishes statistical information on economic, social, demographic, political affairs and general affairs of the people of the Philippines and enforces the civil registration functions in the country.
Statistics Denmark is a Danish governmental organization under the Ministry for Economic and Interior Affairs. The organization is responsible for creating statistics on the Danish society, for example employment statistics, trade balance, and demographics.
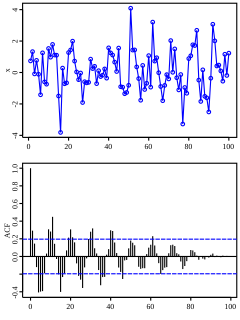
In the analysis of data, a correlogram is a chart of correlation statistics. For example, in time series analysis, a plot of the sample autocorrelations versus is an autocorrelogram. If cross-correlation is plotted, the result is called a cross-correlogram.
SDMX, which stands for Statistical Data and Metadata eXchange is an international initiative that aims at standardising and modernising (“industrialising”) the mechanisms and processes for the exchange of statistical data and metadata among international organisations and their member countries.
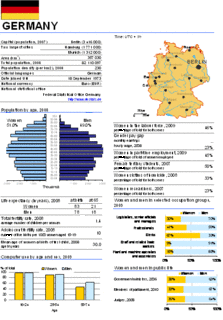
Official statistics are statistics published by government agencies or other public bodies such as international organizations as a public good. They provide quantitative or qualitative information on all major areas of citizens' lives, such as economic and social development, living conditions, health, education, and the environment.

A census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for the census in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) is responsible for the census in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) is responsible for the census in Northern Ireland.

The Hungarian Central Statistical Office is a quango responsible for collecting, processing and publishing statistics about Hungary, its economy, and its inhabitants. The office provides details for parliamentary and administrative offices, local councils and academia, financial institutions, the public at large and the media.

Data science is an inter-disciplinary field that uses scientific methods, processes, algorithms and systems to extract knowledge and insights from many structural and unstructured data. Data science is related to data mining, machine learning and big data.










