
Altaic is a controversial proposed language family that would include the Turkic, Mongolic and Tungusic language families and possibly also the Japonic and Koreanic languages. The hypothetical language family has long been rejected by most comparative linguists, although it continues to be supported by a small but stable scholarly minority. Speakers of the constituent languages are currently scattered over most of Asia north of 35° N and in some eastern parts of Europe, extending in longitude from Turkey to Japan. The group is named after the Altai mountain range in the center of Asia.
Siberia is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its various predecessor states since the centuries-long conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in the late 16th century and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over 13.1 million square kilometres (5,100,000 sq mi), but home to only one-fifth of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Omsk, and Chelyabinsk are the largest cities in the area.

The Ural Mountains, or simply the Urals, is a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north-south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan. The mountain range forms part of the conventional boundary between the continents of Europe and Asia. Vaygach Island and the islands of Novaya Zemlya form a further continuation of the chain to the north into the Arctic Ocean. The average altitudes of the Urals are around 1,000–1,300 metres (3,300–4,300 ft), the highest point being Mount Narodnaya, which reaches a height of 1,894 metres (6,214 ft).

Ural-Altaic, Uralo-Altaic or Uraltaic is a linguistic convergence zone and former language-family proposal uniting the Uralic and the Altaic languages. It is generally now agreed that even the Altaic languages do not share a common descent: the similarities among Turkic, Mongolic and Tungusic are better explained by diffusion and borrowing. Just as Altaic, internal structure of the Uralic family also has been debated since the family was first proposed. Doubts about the validity of most or all of the proposed higher-order Uralic branchings are becoming more common. The term continues to be used for the central Eurasian typological, grammatical and lexical convergence zone.

The Bashkirs or Bashkurts are a Kipchak Turkic ethnic group indigenous to Russia. They are concentrated in Bashkortostan, a republic of the Russian Federation and in the broader historical region of Badzhgard, which spans both sides of the Ural Mountains, where Eastern Europe meets North Asia. Smaller communities of Bashkirs also live in the Republic of Tatarstan, the oblasts of Perm Krai, Chelyabinsk, Orenburg, Tyumen, Sverdlovsk and Kurgan and other regions in Russia; sizable minorities exist in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan.

North Asia or Northern Asia, also referred to as Siberia, is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geographical terms and is coextensive with the Asian part of Russia, and consists of three federal districts of Russia: Ural, Siberian, and the Far Eastern. North Asia is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to its north; by Eastern Europe to its west; by Central and East Asia to its south; and by the Pacific Ocean and North America to its east. It covers an area of 13,100,000 square kilometres (5,100,000 sq mi), or 8.8% of Earth's total land area; and is the largest subregion of Asia by area, but is also the least populated, with a population of around 33 million, accounting for merely 0.74% of Asia's population.

The Ural, known before 1775 as Yaik, is a river flowing through Russia and Kazakhstan in the continental border between Europe and Asia. It originates in the southern Ural Mountains and discharges into the Caspian Sea. At 2,428 kilometres (1,509 mi), it is the third-longest river in Europe after the Volga and the Danube, and the 18th-longest river in Asia. The Ural is conventionally considered part of the boundary between the continents of Europe and Asia.

A dissected plateau is a plateau area that has been severely eroded such that the relief is sharp. Such an area may be referred to as mountainous, but dissected plateaus are distinguishable from orogenic mountain belts by the lack of folding, metamorphism, extensive faulting, or magmatic activity that accompanies orogeny.
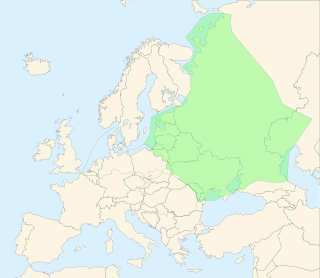
The East European Plain is a vast interior plain extending east of the North European Plain, and comprising several plateaus stretching roughly from 25 degrees longitude eastward. It includes Volhynian-Podolian Upland on its westernmost fringe, the Central Russian Upland, and, on the eastern border, encompasses the Volga Upland. The plain includes also a series of major river basins such as the Dnepr Basin, the Oka–Don Lowland, and the Volga Basin. At the southeastern point of the East European Plain are the Caucasus and Crimean mountain ranges. Together with the North European Plain, and covering the Baltic states, European Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Moldova, southeastern Romania, and, at its southernmost point, the Danubian Plain in Northern Bulgaria, it constitutes the majority of the Great European Plain, the greatest mountain-free part of the European landscape. The plain spans approximately 4,000,000 km2 (2,000,000 sq mi) and averages about 170 m (560 ft) in elevation. The highest point of the plain, located in the Valdai Hills, is 346.9 metres (1,138.1 ft).

Turanism, also known as pan-Turanianism, pan-Turanism, or simply Turan, is a pseudoscientific pan-nationalist cultural and political movement proclaiming the need for close cooperation or political unification between people who are claimed by its supporters to be culturally, linguistically or ethnically related and to have Inner and Central Asian origin, such as the Turks, Mongols, Tungus, Hungarians, Finns, Estonians, and other smaller ethnic groups, for example, Japanese and Koreans, as a means of collaborating towards shared interests and opposing the cultural and political influences of the powers from Indo-Europeans of Europe and Southern Asian region and Sino-Tibetans of East Asia. It was born in the 19th century to counter the effects of pan-nationalist ideologies such as pan-Germanism and built upon the ideas of pan-Slavism.

Ural is a geographical region located around the Ural Mountains, between the East European and West Siberian plains. It is considered a part of Eurasian Steppe, extending approximately from the North to the South; from the Arctic Ocean to the end of the Ural River near Orsk city. The border between Europe and Asia runs along the Eastern side of the Ural Mountains. Ural mostly lies within Russia but also includes a small part of Northwestern Kazakhstan. This is historical, not an official entity, with borders overlapping its Western Volga and Eastern Siberia neighboring regions. At some point in the past, parts of the currently existing Ural region were considered a gateway to Siberia, or even Siberia itself, and were combined with the Volga administrative the divisions. Today, there are two official namesake entities: the Ural Federal District and the Ural economic region. While the latter follows the historical borders, the former is a political product; the District omits Western Ural and includes Western Siberia instead.
Turanian is a term that has been used in reference to diverse groups of people. It has had currency in Turanism, Pan-Turkism, and historic Turkish nationalism.

The Bolshoy Irgiz or Irgiz (Ирги́з) is a river in Samara and Saratov Oblast, Russia, a left tributary of the Volga, south of the Samara River. It is 675 km (419 mi) long and the area of its drainage basin is 24,000 km2 (9,266 sq mi). Its headwaters are at the Obshchy Syrt adjoining the Ural River basin. It flows west and joins the Volga south of Samara. Irgiz's meandering riverbed passes the steppes. The river has snow feeding. The town of Pugachyov is located along the Irgiz. The river flows to the Volgograd Reservoir of the Volga downstream Balakovo, near Volsk.
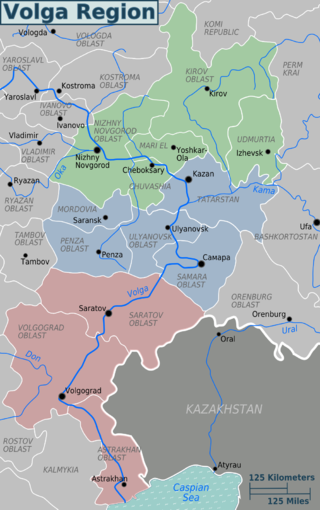
The Volga region is a historical region in Russia that encompasses the drainage basin of the Volga River, the longest river in Europe, in central and southern European Russia.
Obshchy Syrt is a highland ridge, or plateau (syrt), in the European part of Russia. It starts north of Orenburg as a branch of the Ural Mountains and runs in a southwesterly direction to the east bank of the Volga River. River Shagan, a tributary of the Ural, has its sources in the highlands.
Vritramimosaurus is an extinct genus of large early archosauromorph. Although originally placed in the family Prolacertidae, recent studies on archosauromorph relationships doubt the validity of the family, at least in its broadest sense. Fossils have been found from Early Triassic deposits of the Rassypnaya locality in Orenburg Oblast, Russia. Rassypnaya is located on the Obshchy Syrt, a plateau in the European part of Russia that extends southwest of the Urals toward the Volga River. Vritramimosaurus is similar to the later genus Malutinisuchus, also from Rassypnaya but present in Middle Triassic deposits.

Shaytan-Tau Nature Reserve is a Russian 'zapovednik' located along the Shaytantau ridge of the Southern Urals. The ridge contains limestone reefs which are of Cambrian age, almost 500 million years old. The main purpose of the reserve is to conserve representative Dubravnaya steppe and low-lying bog habitats of relict and endemic species of plants and animals. The area is the youngest federal reserve in the Urals, being set aside for protection on October 9, 2014. It is separated into four sectors, situated in both the Kuvandyksky District of Orenburg Oblast, and in Bashkortostan. It is about 220 km from the regional city of Orenburg.
This is a short History of the central steppe, an area roughly equivalent to modern Kazakhstan. Because the history is complex it is mainly an outline and index to the more detailed articles given in the links. It is a companion to History of the western steppe and History of the eastern steppe and is parallel to the History of Kazakhstan and the History of central Asia.

The Great Russian Regions are eight geomorphological areas in the Russian Federation displaying characteristic forms of relief. Seven of them are east of the Urals.

Nakas also known as Maly Nakas, is a mountain in the Southern Urals, Russian Federation. Its largest part is in Orenburg Oblast, with a small section in Bashkortostan.














