Related Research Articles

The Book of Joshua is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Israel from the conquest of Canaan to the Babylonian exile. It tells of the campaigns of the Israelites in central, southern and northern Canaan, the destruction of their enemies, and the division of the land among the Twelve Tribes, framed by two set-piece speeches, the first by God commanding the conquest of the land, and, at the end, the second by Joshua warning of the need for faithful observance of the Law (torah) revealed to Moses.
The Book of Exodus is the second religious book of the Bible. It is a narrative of the Exodus, the origin myth of the Israelites leaving slavery in Biblical Egypt through the strength of their deity named Yahweh, who according to the story chose them as his people. The Israelites then journey with the legendary prophet Moses to Mount Sinai, where Yahweh gives the 10 commandments and they enter into a covenant with Yahweh, who promises to make them a "holy nation, and a kingdom of priests" on condition of their faithfulness. He gives them their laws and instructions to build the Tabernacle, the means by which he will come from heaven and dwell with them and lead them in a holy war to conquer Canaan, which has earlier, according to the myth of Genesis, been promised to the "seed" of Abraham, the legendary patriarch of the Israelites.

The history of ancient Israel and Judah begins in the Southern Levant region of Western Asia during the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age. The earliest known reference to "Israel" as a people or tribal confederation is in the Merneptah Stele, an inscription from ancient Egypt that dates to about 1208 BCE, but the people group may be older. According to modern archaeology, ancient Israelite culture developed as an outgrowth from the pre-existing Canaanite civilization. Two related Israelite polities known as the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria) and the Kingdom of Judah had emerged in the region by Iron Age II.

Joshua, also known as Yehoshua or Josue, functioned as Moses' assistant in the books of Exodus and Numbers, and later succeeded Moses as leader of the Israelite tribes in the Book of Joshua of the Hebrew Bible. His name was Hoshea the son of Nun, of the tribe of Ephraim, but Moses called him "Yehoshua", the name by which he is commonly known in English. According to the Bible, he was born in Egypt prior to the Exodus.

The Torah is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is known as the Pentateuch or the Five Books of Moses by Christians. It is also known as the Written Torah in Jewish tradition. If meant for liturgic purposes, it takes the form of a Torah scroll. If in bound book form, it is called Chumash, and is usually printed with the rabbinic commentaries.

Yahweh was an ancient Levantine deity, and national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah. Though no consensus exists regarding the deity's origins, scholars generally contend that Yahweh emerged as a "divine warrior" associated first with Seir, Edom, Paran and Teman, and later with Canaan. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age, if not somewhat earlier.

The Israelites were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The historicity of the Bible is the question of the Bible's relationship to history—covering not just the Bible's acceptability as history but also the ability to understand the literary forms of biblical narrative. One can extend biblical historicity to the evaluation of whether or not the Christian New Testament is an accurate record of the historical Jesus and of the Apostolic Age. This tends to vary depending upon the opinion of the scholar.
Idolatry in Judaism is prohibited. Judaism holds that idolatry is not limited to the worship of an idol itself, but also worship involving any artistic representations of God. The prohibition is epitomized by the first two "words" of the decalogue: I am the Lord thy God, Thou shalt have no other gods before me, and Thou shalt not make unto thee any graven image or any image in the sky, on earth or in the sea. These prohibitions are re-emphasized repeatedly by the later prophets, suggesting the ongoing appeal of Canaanite religion and syncretic assimilation to the ancient Israelites.

The Exodus is the founding myth of the Israelites whose narrative is spread over four of the five books of the Pentateuch.

The Bible Unearthed: Archaeology's New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Its Sacred Texts, a book by Israel Finkelstein, Professor of Archaeology at Tel Aviv University, and Neil Asher Silberman, an archaeologist, historian and contributing editor to Archaeology Magazine published in 2001 by Simon & Schuster using its imprint The Free Press and reprinted in 2002 using its Touchstone imprint, discusses the archaeology of Israel and its relationship to the origins and content of the Hebrew Bible.
William Gwinn Dever is an American archaeologist, scholar, historian, semiticist, and theologian. He is an active scholar of the Old Testament, and historian, specialized in the history of the Ancient Near East and the ancient kingdoms of Israel and Judah in biblical times. He was Professor of Near Eastern Archaeology and Anthropology at the University of Arizona in Tucson from 1975 to 2002. He is a Distinguished Professor of Near Eastern Archaeology at Lycoming College in Pennsylvania.

Mosaic authorship is the Judeo-Christian tradition that the Torah, the first five books of the Hebrew Bible/Old Testament, were dictated by God to Moses. The tradition probably began with the legalistic code of the Book of Deuteronomy and was then gradually extended until Moses, as the central character, came to be regarded not just as the mediator of law but as author of both laws and narrative.
Did God Have a Wife?: Archaeology and Folk Religion in Ancient Israel is a book by Syro-Palestinian archaeologist William G. Dever, Professor Emeritus of Near Eastern Archeology and Anthropology at the University of Arizona. Did God Have a Wife? was intended as a popular work making available to the general public the evidence long known to archaeologists regarding ancient Israelite religion: namely that the Israelite God of antiquity, Yahweh, had a consort, that her name was Asherah, and that she was part of the Canaanite pantheon.

The origins of Judaism lie in Bronze Age polytheistic Canaanite religion. Judaism also syncretized elements of other Semitic religions such as Babylonian religion, which is reflected in the early prophetic books of the Hebrew Bible.

The Kenite hypothesis proposes that the origins of Yahweh, and by extension Yahwism, do not lie in Canaan as the Hebrew Bible describes, but instead originated in the area immediately south of the Levant, possibly extending far into the northwest Arabian Peninsula, on the east shore of the Gulf of Aqaba on the Red Sea, in the area the Tanakh calls "Midian". The theory states that Yahweh originally was a Midianite deity, who made his way up north to the proto-Israelites.
The earliest known precursor to Hebrew, an inscription in the Paleo-Hebrew alphabet, is the Khirbet Qeiyafa Inscription, if it can be considered Hebrew at that early a stage.
The Exodus is the founding myth of the Israelites. The scholarly consensus is that the Exodus, as described in the Torah, is not historical, even though there may be a historical core behind the Biblical narrative.
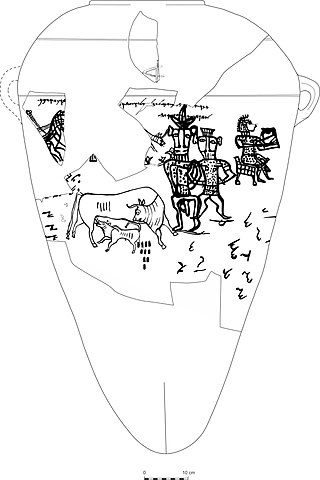
Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel and Judah. Yahwism was essentially polytheistic, with a pantheon of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah, and second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, each of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees.
War in the Hebrew Bible concerns any military engagement narrated or discussed in the Hebrew Bible, also known as the Tanakh or Old Testament of the Bible. Texts about war in the Hebrew Bible are part of the broader topic of The Bible and violence. They cover a wide range of topics from detailed battle reports including weapons and tactics used, numbers of combatants involved, and casualties experienced, to discussions of motives and justifications for war, the sacred and secular aspects of war, descriptions and considerations of what in modern times would be considered war crimes such as genocide or wartime sexual violence, and reflections on wars that have happened, or predictions, visions or imaginations of wars that are yet to come.
References
- ↑ Bible's Buried Secrets (three-part 2011 BBC series) on IMDb
- ↑ Boedeker, Hal, "'Bible's Buried Secrets' from PBS's 'Nova' Likely to Stir Controversy with its Look at Good Book's Authorship", Orlando Sentinel , July 14, 2008
- ↑ Bible gets a reality check, Cosmic Blog: MSNBC, Alan Boyle
- ↑ The Biblical Archaeology Review
- ↑ Rabbi Wesley Gardenswartz. "NOVA | The Bible's Buried Secrets | Rabbi Wesley Gardenswartz". PBS. Retrieved 2012-09-06.
- ↑ Reverend Kenneth Himes. "NOVA | The Bible's Buried Secrets | Reverend Kenneth Himes". PBS. Retrieved 2012-09-06.
- ↑ New PBS program says Bible isn't true, stories made up Archived 2013-02-21 at archive.today , AFA Action Alert, American Family Association
- ↑ Josh Kimball. 'Bible's Buried Secrets' Trailer Hits YouTube, Christian post
- ↑ Dewayne Bryant. The Bible's Buried Secrets Apologetics Press
- ↑ "New PBS program says Bible isn't true, stories made up - Associates for Biblical Research". biblearchaeology.org. Retrieved 2021-04-25.