Related Research Articles
Keynesian economics are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand strongly influences economic output and inflation. In the Keynesian view, aggregate demand does not necessarily equal the productive capacity of the economy. It is influenced by a host of factors that sometimes behave erratically and impact production, employment, and inflation.

Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. This includes regional, national, and global economies. Macroeconomists study topics such as output/GDP and national income, unemployment, price indices and inflation, consumption, saving, investment, energy, international trade, and international finance.

The IS–LM model, or Hicks–Hansen model, is a two-dimensional macroeconomic model which is used as a pedagogical tool in macroeconomic teaching. The IS–LM model shows the relationship between interest rates and output in the short run in a closed economy. The intersection of the "investment–saving" (IS) and "liquidity preference–money supply" (LM) curves illustrates a "general equilibrium" where supposed simultaneous equilibria occur in both the goods and the money markets. The IS–LM model shows the importance of various demand shocks on output and consequently offers an explanation of changes in national income in the short run when prices are fixed or sticky. Hence, the model can be used as a tool to suggest potential levels for appropriate stabilisation policies. It is also used as a building block for the demand side of the economy in more comprehensive models like the AD–AS model.
This aims to be a complete article list of economics topics:

In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variables developed in reaction to the Great Depression of the 1930s, when the previous laissez-faire approach to economic management became unworkable. Fiscal policy is based on the theories of the British economist John Maynard Keynes, whose Keynesian economics theorised that government changes in the levels of taxation and government spending influence aggregate demand and the level of economic activity. Fiscal and monetary policy are the key strategies used by a country's government and central bank to advance its economic objectives. The combination of these policies enables these authorities to target inflation and to increase employment. In modern economies, inflation is conventionally considered "healthy" in the range of 2%–3%. Additionally, it is designed to try to keep GDP growth at 2%–3% percent and the unemployment rate near the natural unemployment rate of 4%–5%. This implies that fiscal policy is used to stabilise the economy over the course of the business cycle.

Nicholas Kaldor, Baron Kaldor, born Káldor Miklós, was a Cambridge economist in the post-war period. He developed the "compensation" criteria called Kaldor–Hicks efficiency for welfare comparisons (1939), derived the cobweb model, and argued for certain regularities observable in economic growth, which are called Kaldor's growth laws. Kaldor worked alongside Gunnar Myrdal to develop the key concept Circular Cumulative Causation, a multicausal approach where the core variables and their linkages are delineated. Both Myrdal and Kaldor examine circular relationships, where the interdependencies between factors are relatively strong, and where variables interlink in the determination of major processes. Gunnar Myrdal got the concept from Knut Wicksell and developed it alongside Nicholas Kaldor when they worked together at the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe. Myrdal concentrated on the social provisioning aspect of development, while Kaldor concentrated on demand-supply relationships to the manufacturing sector. Kaldor also coined the term "convenience yield" related to commodity markets and the so-called theory of storage, which was initially developed by Holbrook Working.
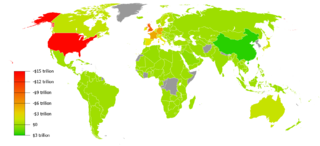
In international economics, the balance of payments of a country is the difference between all money flowing into the country in a particular period of time and the outflow of money to the rest of the world. In other words, it is economic transactions between countries during a period of time. These financial transactions are made by individuals, firms and government bodies to compare receipts and payments arising out of trade of goods and services.
In economics, effective demand (ED) in a market is the demand for a product or service which occurs when purchasers are constrained in a different market. It contrasts with notional demand, which is the demand that occurs when purchasers are not constrained in any other market. In the aggregated market for goods in general, demand, notional or effective, is referred to as aggregate demand. The concept of effective supply parallels the concept of effective demand. The concept of effective demand or supply becomes relevant when markets do not continuously maintain equilibrium prices.
Verdoorn's law is named after Dutch economist Petrus Johannes Verdoorn (1949). It states that in the long run productivity generally grows proportionally to the square root of output. In economics, this law pertains to the relationship between the growth of output and the growth of productivity. According to the law, faster growth in output increases productivity due to increasing returns. Verdoorn argued that "in the long run a change in the volume of production, say about 10 per cent, tends to be associated with an average increase in labor productivity of 4.5 per cent." The Verdoorn coefficient close to 0.5 (0.484) is also found in subsequent estimations of the law.

Export-oriented industrialization (EOI), sometimes called export substitution industrialization (ESI), export-led industrialization (ELI), or export-led growth, is a trade and economic policy aiming to speed up the industrialization process of a country by exporting goods for which the nation has a comparative advantage. Export-led growth implies opening domestic markets to foreign competition in exchange for market access in other countries.

Sho-Chieh Tsiang was a Chinese-American economist. He was born in China but resided primarily in the United States from 1949 until his death. He also resided in Taiwan in 1948 and in the 1980s.
The neoclassical synthesis (NCS), neoclassical–Keynesian synthesis, or just neo-Keynesianism was a neoclassical economics academic movement and paradigm in economics that worked towards reconciling the macroeconomic thought of John Maynard Keynes in his book The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (1936). It was formulated most notably by John Hicks (1937), Franco Modigliani (1944), and Paul Samuelson (1948), who dominated economics in the post-war period and formed the mainstream of macroeconomic thought in the 1950s, 60s, and 70s.

Anthony Philip Thirlwall was a British economist who was Professor of Applied Economics at the University of Kent. He made major contributions to regional economics; the analysis of unemployment and inflation; balance of payments theory, and to growth and development economics with particular reference to developing countries. He was the author of the bestselling textbook Economics of Development: Theory and Evidence now in its ninth edition. He was also the biographer and literary executor of the famous Cambridge economist Nicholas Kaldor. Perhaps his most notable contribution was to show that if long-run balance of payments equilibrium is a requirement for a country, its growth of national income can be approximated by the ratio of the growth of exports to the income elasticity of demand for imports.
The North–South model, developed largely by Columbia University economics professor Ronald Findlay, is a model in developmental economics that explains the growth of a less developed "South" or "periphery" economy that interacts through trade with a more developed "North" or "core" economy. The North–South model is used by dependencia theorists as a theoretical economic justification for dependency theory.
Disequilibrium macroeconomics is a tradition of research centered on the role of disequilibrium in economics. This approach is also known as non-Walrasian theory, equilibrium with rationing, the non-market clearing approach, and non-tâtonnement theory. Early work in the area was done by Don Patinkin, Robert W. Clower, and Axel Leijonhufvud. Their work was formalized into general disequilibrium models, which were very influential in the 1970s. American economists had mostly abandoned these models by the late 1970s, but French economists continued work in the tradition and developed fixprice models.
The Cambridge capital controversy, sometimes called "the capital controversy" or "the two Cambridges debate", was a dispute between proponents of two differing theoretical and mathematical positions in economics that started in the 1950s and lasted well into the 1960s. The debate concerned the nature and role of capital goods and a critique of the neoclassical vision of aggregate production and distribution. The name arises from the location of the principals involved in the controversy: the debate was largely between economists such as Joan Robinson and Piero Sraffa at the University of Cambridge in England and economists such as Paul Samuelson and Robert Solow at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States.
Stock-flow consistent models (SFC) are a family of macroeconomic models based on a rigorous accounting framework, that seeks to guarantee a correct and comprehensive integration of all the flows and the stocks of an economy. These models were first developed in the mid-20th century but have recently become popular, particularly within the post-Keynesian school of thought. Stock-flow consistent models are in contrast to dynamic stochastic general equilibrium models, which are used in mainstream economics.
This glossary of economics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in economics, its sub-disciplines, and related fields.
Robert A. Blecker is an American economist who is currently a Professor in the Department of Economics at American University in Washington, DC. He is also Affiliate Faculty of the American University School of International Service and Center for Latin American and Latino Studies, and a research associate at the Economic Policy Institute and Political Economy Research Institute. His research has made contributions to the fields of post-Keynesian and neo-Kaleckian macroeconomics, open economy macroeconomics, international trade theory and policy, global imbalances and the U.S. trade deficit, the North American Free Trade Agreement, the economy of Mexico, export-led growth, and the theory of balance-of-payments constrained growth.
Franklin Leon Peres Serrano is a Brazilian economist and professor at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro.
References
- Davidson, Paul (1991), A Post Keynesian Positive Contribution to "Theory", Journal of Post Keynesian Economics
- Harrod, R. (1933), International Economics (London; Macmillan).
- McCombie, J.S.L. (2011), Criticisms and defences of the balance-of-payments constrained growth model: some old, some new, PSL Quarterly Review, December.
- McCombie, J.S.L. and Thirlwall, A.P. (1994), Economic Growth and the Balance of Payments Constraint (London: Macmillan).
- McCombie, J.S.L. and Thirlwall, A.P. (2004), Essays on Balance of Payments Constrained Growth: Theory and Evidence (London: Routledge).
- O’Hara, P. A. (1999), Encyclopedia of Political Economy, Vol. 1. (London; Routledge).
- Setterfield, M. (2011), The remarkable durability of Thirlwall’s Law, PSL Quarterly Review, December.
- Thirlwall, A.P. (1979), The Balance of Payments Constraint as an Explanation of International Growth Rate Differences, Banca Nazionale del Lavoro Quarterly Review, March.
- Thirlwall, A.P. and M. Nureldin Hussain (1982), The Balance of Payments Constraint, Capital Flows and Growth Rate Differences Between Developing Countries, Oxford Economic Papers, November.
- Thirlwall, A.P. (2011), Balance of Payments Constrained Growth Models: History and Overview, PSL Quarterly Review, December.