
Discounts and allowances are reductions to a basic price of goods or services.
An application service provider (ASP) is a business providing computer-based services to customers over a network; such as access to a particular software application using a standard protocol.
Online banking, also known as internet banking, is an electronic payment system that enables customers of a bank or other financial institution to conduct a range of financial transactions through the financial institution's website. The online banking system will typically connect to or be part of the core banking system operated by a bank and is in contrast to branch banking which was the traditional way customers accessed banking services.
Medical billing is a payment practice within the United States health system. The process involves a healthcare provider submitting, following up on, and appealing claims with health insurance companies in order to receive payment for services rendered; such as testing, treatments, and procedures. The same process is used for most insurance companies, whether they are private companies or government sponsored programs: Medical coding reports what the diagnosis and treatment were, and prices are applied accordingly. Medical billers are encouraged, but not required by law, to become certified by taking an exam such as the CMRS Exam, RHIA Exam and others. Certification schools are intended to provide a theoretical grounding for students entering the medical billing field. Some community colleges in the United States offer certificates, or even associate degrees, in the field. Those seeking advancement may be cross-trained in medical coding or transcription or auditing, and may earn a bachelor's or graduate degree in medical information science and technology.
Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) is a communications protocol standard for securing credit card transactions over networks, specifically, the Internet. SET was not itself a payment system, but rather a set of security protocols and formats that enabled users to employ the existing credit card payment infrastructure on an open network in a secure fashion. However, it failed to gain attraction in the market. VISA now promotes the 3-D Secure scheme. Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) is a system for ensuring the security of financial transactions on the Internet. It was supported initially by Mastercard, Visa, Microsoft, Netscape, and others. With SET, a user is given an electronic wallet and a transaction is conducted and verified using a combination of digital certificates and digital signatures among the purchaser, a merchant, and the purchaser's bank in a way that ensures privacy and confidentiality

A prepaid mobile device is a mobile device such as a phone for which credit is purchased in advance of service use. The purchased credit is used to pay for telecommunications services at the point the service is accessed or consumed. If there is no credit, then access is denied by the cellular network/Intelligent Network. Users can top up their credit at any time using a variety of payment mechanisms.
A cold weather rule or cold weather law is a law or regulation that prohibits public utility companies from disconnecting customers who are unable to pay for the energy used to heat their homes during the winter. Such regulations may also require utility companies to reconnect customers during those periods. Several U.S. states have such rules, including Kansas, Minnesota, and Missouri. The protection provided by a cold weather rule may not be automatic, and poor customers may have to register with their service provider to indicate either a complete inability to pay or to set up a special payment plan.

A voucher is a bond of the redeemable transaction type which is worth a certain monetary value and which may be spent only for specific reasons or on specific goods. Examples include housing, travel, and food vouchers. The term voucher is also a synonym for receipt and is often used to refer to receipts used as evidence of, for example, the declaration that a service has been performed or that an expenditure has been made. Voucher is a tourist guide for using services with a guarantee of payment by the agency.
A late fee, also known as an overdue fine, late fine, or past due fee, is a charge fined against a client by a company or organization for not paying a bill or returning a rented or borrowed item by its due date. Its use is most commonly associated with businesses like creditors, video rental outlets and libraries. Late fees are generally calculated on a per day, per item basis.
A grace period is a period immediately after the deadline for an obligation during which a late fee, or other action that would have been taken as a result of failing to meet the deadline, is waived provided that the obligation is satisfied during the grace period. Grace periods can range from a number of minutes to a number of days or longer, and can apply in situations including arrival at a job, paying a bill, or meeting a government or legal requirement.
A payment gateway is a merchant service provided by an e-commerce application service provider that authorizes credit card or direct payments processing for e-businesses, online retailers, bricks and clicks, or traditional brick and mortar. The payment gateway may be provided by a bank to its customers, but can be provided by a specialised financial service provider as a separate service, such as a payment service provider.
Project finance is the long-term financing of infrastructure and industrial projects based upon the projected cash flows of the project rather than the balance sheets of its sponsors. Usually, a project financing structure involves a number of equity investors, known as 'sponsors', a 'syndicate' of banks or other lending institutions that provide loans to the operation. They are most commonly non-recourse loans, which are secured by the project assets and paid entirely from project cash flow, rather than from the general assets or creditworthiness of the project sponsors, a decision in part supported by financial modeling. The financing is typically secured by all of the project assets, including the revenue-producing contracts. Project lenders are given a lien on all of these assets and are able to assume control of a project if the project company has difficulties complying with the loan terms.
The Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP) is a United States federal social services program first established in 1981 and funded annually through Congressional appropriations. The mission of LIHEAP is to assist low income households, particularly those with the lowest incomes that pay a high proportion of household income for home energy, primarily in meeting their immediate home energy needs. The program, part of the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), is funded by grants appropriated from the federal government.

The Consumer Federation of California (CFC) was founded in 1960 as a nonprofit consumer advocacy organization. CFC campaigns for state and federal laws and appears at the California state legislature in support of consumer-focused regulations. The Consumer Federation of California is led by Executive Director Richard Holober and Board President James Gordon Jr.
Electronic billing or electronic bill payment and presentment, is when a seller such as company, organization, or group sends its bills or invoices over the internet, and customers pay the bills electronically. This replaces the traditional method where invoices were sent in paper form and payments were done by manual means such as sending cheques.
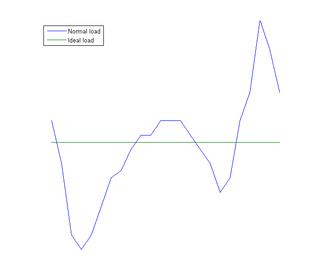
Load management, also known as demand side management (DSM), is the process of balancing the supply of electricity on the network with the electrical load by adjusting or controlling the load rather than the power station output. This can be achieved by direct intervention of the utility in real time, by the use of frequency sensitive relays triggering the circuit breakers, by time clocks, or by using special tariffs to influence consumer behavior. Load management allows utilities to reduce demand for electricity during peak usage times, which can, in turn, reduce costs by eliminating the need for peaking power plants. In addition, some peaking power plants can take more than an hour to bring on-line which makes load management even more critical should a plant go off-line unexpectedly for example. Load management can also help reduce harmful emissions, since peaking plants or backup generators are often dirtier and less efficient than base load power plants. New load-management technologies are constantly under development — both by private industry and public entities.
WAP billing is a mechanism for consumers to buy content from Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) sites that is charged directly to their mobile phone bill. It is an alternative payment mechanism to debit or credit cards and premium SMS for billing. Using WAP billing, consumers can buy mobile content without registering for a service or entering a username or password. The user clicks on a link and agrees to make a purchase, after which they can download content.
Fixed bill refers to an energy pricing program in which a consumer pays a predetermined amount for their total energy consumption for a given period. The price is independent of the amount of energy the customer uses or the unit price of the energy. Energy companies can offer this type of pricing by hedging the risks of fluctuating demand using weather derivatives.
A deposit account is a savings account, current account or any other type of bank account that allows money to be deposited and withdrawn by the account holder. These transactions are recorded on the bank's books, and the resulting balance is recorded as a liability for the bank and represents the amount owed by the bank to the customer. Some banks may charge a fee for this service, while others may pay the customer interest on the funds deposited.
Utility scams are fraudulent acts where a perpetrator calls or arrives unannounced at a utility customer's house in an attempt to take money or sell unnecessary energy accessories through misrepresentation. Often, the fraud involves telling the victim that he or she owes the utility company money and that their power, gas, or water will be shut off immediately unless payment is made.










