Related Research Articles

An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the power of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.

Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter; with frequencies between 300 MHz (1 m) and 300 GHz (1 mm). Different sources define different frequency ranges as microwaves; the above broad definition includes both UHF and EHF bands. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz. In all cases, microwaves include the entire SHF band at minimum. Frequencies in the microwave range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations.
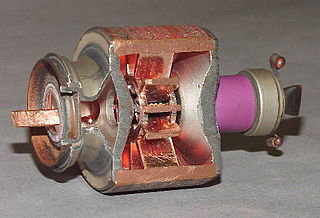
The cavity magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube that generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field while moving past a series of open metal cavities. Electrons pass by the openings to these cavities and cause microwaves to oscillate within, similar to the way a whistle produces a tone when excited by an air stream blown past its opening. The frequency of the microwaves produced, the resonant frequency, is determined by the cavities' physical dimensions. Unlike other vacuum tubes such as a klystron or a traveling-wave tube (TWT), the magnetron cannot function as an amplifier in order to increase the intensity of an applied microwave signal; the magnetron serves solely as an oscillator, generating a microwave signal from direct current electricity supplied to the vacuum tube.

An optical amplifier is a device that amplifies an optical signal directly, without the need to first convert it to an electrical signal. An optical amplifier may be thought of as a laser without an optical cavity, or one in which feedback from the cavity is suppressed. Optical amplifiers are important in optical communication and laser physics. They are used as optical repeaters in the long distance fiberoptic cables which carry much of the world's telecommunication links.

A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube, invented in 1937 by American electrical engineers Russell and Sigurd Varian, which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequencies, from UHF up into the microwave range. Low-power klystrons are used as oscillators in terrestrial microwave relay communications links, while high-power klystrons are used as output tubes in UHF television transmitters, satellite communication, radar transmitters, and to generate the drive power for modern particle accelerators.

A valve amplifier or tube amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that uses vacuum tubes to increase the amplitude or power of a signal. Low to medium power valve amplifiers for frequencies below the microwaves were largely replaced by solid state amplifiers in the 1960s and 1970s. Valve amplifiers can be used for applications such as guitar amplifiers, satellite transponders such as DirecTV and GPS, high quality stereo amplifiers, military applications and very high power radio and UHF television transmitters.

A traveling-wave tube or traveling-wave tube amplifier is a specialized vacuum tube that is used in electronics to amplify radio frequency (RF) signals in the microwave range. The TWT belongs to a category of "linear beam" tubes, such as the klystron, in which the radio wave is amplified by absorbing power from a beam of electrons as it passes down the tube. Although there are various types of TWT, two major categories are:
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a resonator can be either electromagnetic or mechanical. Resonators are used to either generate waves of specific frequencies or to select specific frequencies from a signal. Musical instruments use acoustic resonators that produce sound waves of specific tones. Another example is quartz crystals used in electronic devices such as radio transmitters and quartz watches to produce oscillations of very precise frequency.

A gyrotron is a class of high-power linear-beam vacuum tubes which generates millimeter-wave electromagnetic waves by the cyclotron resonance of electrons in a strong magnetic field. Output frequencies range from about 20 to 527 GHz, covering wavelengths from microwave to the edge of the terahertz gap. Typical output powers range from tens of kilowatts to 1–2 megawatts. Gyrotrons can be designed for pulsed or continuous operation. The gyrotron was invented by soviet scientists at NIRFI, based in Nizhny Novgorod, Russia.

A crossed-field amplifier (CFA) is a specialized vacuum tube, first introduced in the mid-1950s and frequently used as a microwave amplifier in very-high-power transmitters.

A backward wave oscillator (BWO), also called carcinotron or backward wave tube, is a vacuum tube that is used to generate microwaves up to the terahertz range. Belonging to the traveling-wave tube family, it is an oscillator with a wide electronic tuning range.

A single-ended triode (SET) is a vacuum tube electronic amplifier that uses a single triode to produce an output, in contrast to a push-pull amplifier which uses a pair of devices with antiphase inputs to generate an output with the wanted signals added and the distortion components subtracted. Single-ended amplifiers normally operate in Class A; push-pull amplifiers can also operate in Classes AB or B without excessive net distortion, due to cancellation.

A valve RF amplifier or tube amplifier (U.S.), is a device for electrically amplifying the power of an electrical radio frequency signal.
The inductive output tube (IOT) or klystrode is a variety of linear-beam vacuum tube, similar to a klystron, used as a power amplifier for high frequency radio waves. It evolved in the 1980s to meet increasing efficiency requirements for high-power RF amplifiers in radio transmitters. The primary commercial use of IOTs is in UHF television transmitters, where they have mostly replaced klystrons because of their higher efficiencies and smaller size. IOTs are also used in particle accelerators. They are capable of producing power output up to about 30 kW continuous and 7 MW pulsed and gains of 20–23 dB at frequencies up to about a gigahertz.
A Microwave Power Module (MPM) is a microwave device used to amplify radio frequency signals to high power levels. It is a hybrid combination of solid-state and vacuum tube electronics, which encloses a solid-state driver amplifier (SSPA), traveling wave tube amplifier (TWTA) and electronic power conditioning (EPC) modules into a single unit. Their average output power capability falls between that of solid-state power amplifiers (SSPAs) and dedicated Traveling Wave Tube (TWT) amplifiers. They may be applied wherever high power microwave amplification is required, and space is at a premium. They are available in various frequency ranges, from S band up to W band. Typical output power at Ku band ranges from 20W to 1 kW.

The Barkhausen–Kurz tube, also called the retarding-field tube, reflex triode, B–K oscillator, and Barkhausen oscillator was a high frequency vacuum tube electronic oscillator invented in 1920 by German physicists Heinrich Georg Barkhausen and Karl Kurz. It was the first oscillator that could produce radio power in the ultra-high frequency (UHF) portion of the radio spectrum, above 300 MHz. It was also the first oscillator to exploit electron transit time effects. It was used as a source of high frequency radio waves in research laboratories, and in a few UHF radio transmitters through World War 2. Its output power was low which limited its applications. However it inspired research that led to other more successful transit time tubes such as the klystron, which made the low power Barkhausen-Kurz tube obsolete.
COHO, short for Coherent Oscillator, is a technique used with radar systems based on the cavity magnetron to allow them to implement a moving target indicator display. Because the signals are only coherent when received, not transmitted, the concept is also sometimes known as coherent on receive. Due to the way the signal is processed, radars using this technique are known as pseudo-coherent radar.
Sir John Turton Randall, was an English physicist and biophysicist, credited with radical improvement of the cavity magnetron, an essential component of centimetric wavelength radar, which was one of the keys to the Allied victory in the Second World War. It is also the key component of microwave ovens.

A Sutton tube, or reflex klystron, is a type of vacuum tube used to generate microwaves. It is a low-power device used primarily for two purposes; one is to provide a tuneable low-power frequency source for the local oscillators in receiver circuits, and the other, with minor modifications, as a switch that could turn on and off another microwave source. The second use, sometimes known as a soft Sutton tube or rhumbatron switch, was a key component in the development of microwave radar by Britain during World War II. Microwave switches of all designs, including these, are more generally known as T/R tubes or T/R cells.
Linearizers are electronic circuits which improve the non-linear behaviour of amplifiers to increase efficiency and maximum output power.
References
- Wolff, Christian. "Twystron". Radartutorial.
- La Rue, Albert; Rubert, Rodney (31 October 1964). Multi-megawatt hybrid TWT's at S-band and C-band. 1964 International Electron Devices Meeting. doi:10.1109/IEDM.1964.187444.