Related Research Articles

In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine from the human end, while the machine simultaneously feeds back information that aids the operators' decision-making process. Examples of this broad concept of user interfaces include the interactive aspects of computer operating systems, hand tools, heavy machinery operator controls and process controls. The design considerations applicable when creating user interfaces are related to, or involve such disciplines as, ergonomics and psychology.
In software and systems engineering, the phrase use case is a polyseme with two senses:
- A usage scenario for a piece of software; often used in the plural to suggest situations where a piece of software may be useful.
- A potential scenario in which a system receives an external request and responds to it.

In computing, a visual programming language or block coding is a programming language that lets users create programs by manipulating program elements graphically rather than by specifying them textually. A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations.
Extensible Application Markup Language is a declarative XML-based language developed by Microsoft for initializing structured values and objects. It is available under Microsoft's Open Specification Promise.
A user interface markup language is a markup language that renders and describes graphical user interfaces and controls. Many of these markup languages are dialects of XML and are dependent upon a pre-existing scripting language engine, usually a JavaScript engine, for rendering of controls and extra scriptability.
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) is a free and open-source graphical subsystem originally developed by Microsoft for rendering user interfaces in Windows-based applications. WPF, previously known as "Avalon", was initially released as part of .NET Framework 3.0 in 2006. WPF uses DirectX and attempts to provide a consistent programming model for building applications. It separates the user interface from business logic, and resembles similar XML-oriented object models, such as those implemented in XUL and SVG.
Domain-specific modeling (DSM) is a software engineering methodology for designing and developing systems, such as computer software. It involves systematic use of a domain-specific language to represent the various facets of a system.
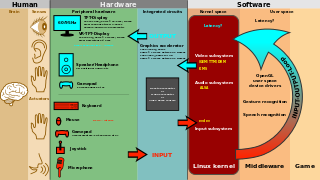
User interface (UI) design or user interface engineering is the design of user interfaces for machines and software, such as computers, home appliances, mobile devices, and other electronic devices, with the focus on maximizing usability and the user experience. In computer or software design, user interface (UI) design primarily focuses on information architecture. It is the process of building interfaces that clearly communicates to the user what's important. UI design refers to graphical user interfaces and other forms of interface design. The goal of user interface design is to make the user's interaction as simple and efficient as possible, in terms of accomplishing user goals.
Object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD) is a technical approach for analyzing and designing an application, system, or business by applying object-oriented programming, as well as using visual modeling throughout the software development process to guide stakeholder communication and product quality.
WebML is a visual notation and a methodology for designing complex data-intensive Web applications. It provides graphical, yet formal, specifications, embodied in a complete design process, which can be assisted by visual design tools.
Object-oriented design (OOD) is the process of planning a system of interacting objects for the purpose of solving a software problem. It is one approach to software design.
The DASL Programming Language is a high-level, strongly typed programming language originally developed at Sun Microsystems Laboratories between 1999 and 2003 as part of the Ace Project. The goals of the project were to enable rapid development of web-based applications based on Sun's J2EE architecture, and to eliminate the steep learning curve of platform-specific details.
Adobe Flash Catalyst is a designers' tool for creating the user interface for rich web applications.
A single-page application (SPA) is a web application or website that interacts with the user by dynamically rewriting the current web page with new data from the web server, instead of the default method of a web browser loading entire new pages. The goal is faster transitions that make the website feel more like a native app.
ZK is an open-source Ajax Web application framework, written in Java, that enables creation of graphical user interfaces for Web applications with little required programming knowledge.
MARIA is a universal, declarative, multiple abstraction level, XML-based user interface markup language for modelling interactive applications in ubiquitous environments.
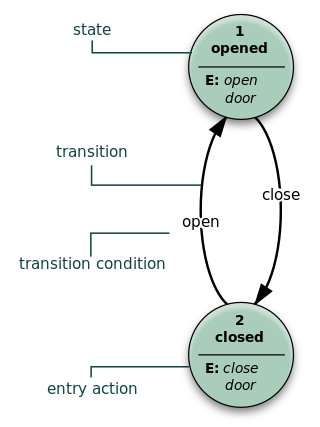
UML is a modeling language used by software developers. UML can be used to develop diagrams and provide users (programmers) with ready-to-use, expressive modeling examples. Some UML tools generate program language code from UML. UML can be used for modeling a system independent of a platform language. UML is a graphical language for visualizing, specifying, constructing, and documenting information about software-intensive systems. UML gives a standard way to write a system model, covering conceptual ideas. With an understanding of modeling, the use and application of UML can make the software development process more efficient.
The Unified Modeling Language for Interactive Systems (UMLi) is a conservative extension of the Unified Modeling Language for user interface design. UMLi was developed in the period between 1998 and 2002 as part of Paulo Pinheiro's Ph.D. Thesis at the University of Manchester. UMLi is based on model-based user interface development environments (MB-UIDEs), which provide the capability to design and implement user interfaces in a declarative and systematic way.

The Interaction Flow Modeling Language (IFML) is a standardized modeling language in the field of software engineering. IFML includes a set of graphic notations to create visual models of user interactions and front-end behavior in software systems.

Sparx Systems Enterprise Architect is a visual modeling and design tool based on the OMG UML. The platform supports: the design and construction of software systems; modeling business processes; and modeling industry based domains. It is used by businesses and organizations to not only model the architecture of their systems, but to process the implementation of these models across the full application development life-cycle.
References
- [Paternò 2005] – F Paternò, Model-based tools for pervasive usability, Interacting with Computers 17 (3), 291-315
- [Trætteberg2002] – H. Trætteberg, Model-based User Interface Design, Doctoral thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2002
- [SilvaPaton2003] – P. Pinheiro da Silva, N. W. Paton, User Interface Modeling in UMLi, Stanford University / University of Manchester, 2003
- [Markopoulos1997] – P. Markopoulos, A compositional model for the formal specification of user interface software, Doctoral thesis, Queen Mary and Westfield College University of London, 1997
- [Trevisan2003] – D. Trevisan, J. Vanderdonck, B. Macq, Model-Based Approach and Augmented Reality Systems, Université catholique de Louvain, 1348 Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2003
- [wwwUMLi] – The Unified Modeling Language for Interactive Applications
- [Cerny2013] – Černý, T. - Čemus, K. - Donahoo, M.J. - Song, M.J.: Aspect-driven, Data-reflective and Context-aware User Interfaces Design (page 53). In: ACM SIGAPP Applied Computing Review [online, 2013, vol. 13, no. 4, p. 53-65, ISSN 1559-6915.
- [Cerny2013a] – Černý, T. - Donahoo, M.J. - Song, E.: Towards Effective Adaptive User Interfaces Design, Proceedings of the 2013 Research in Applied Computation Symposium (RACS 2013), Montreal: ACM, 2013, ISBN 978-1-4503-2348-2.
- [AspectFaces] – "AspectFaces". Coding Crayons s.r.o. Archived from the original on 2 Feb 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - [Cerny2012] – T. Cerny and E. Song. Model-driven Rich Form Generation. Information: An International Interdisciplinary Journal, 15(7, SI):2695–2714, JUL 2012.
- [Generative programming] – Krzysztof Czarnecki and Ulrich W. Eisenecker. 2000. Generative Programming: Methods, Tools, and Applications. ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publ. Co., New York, NY, USA.