Related Research Articles

Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels.

The Vanguard class is a class of nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs) in service with the Royal Navy. The class was introduced in 1994 as part of the Trident nuclear programme, and comprises four vessels: Vanguard, Victorious, Vigilant and Vengeance, built between 1986 and 1999 at Barrow-in-Furness by Vickers Shipbuilding and Engineering, now owned by BAE Systems. All four boats are based at HM Naval Base Clyde , 40 km (25 mi) west of Glasgow, Scotland.

The Tang-class submarines were the first submarines designed and built by the United States Navy after WWII. They incorporated the best features of the high-speed German Type XXI U-boat and the venerable U.S. Navy fleet submarine. The Tang-class, with the fleet submarines converted under the Greater Underwater Propulsion Power (GUPPY) program, had much higher submerged performance than their predecessors, but were quickly surpassed by the nuclear-propelled submarines that entered service beginning in 1954. Six units in total were built.

Type 53 is the common name for a family of 53 cm torpedoes manufactured in Russia, starting with the 53-27 torpedo and continuing to the modern UGST (Fizik-1), which is being replaced by the Futlyar.

A sonobuoy is a relatively small buoy – typically 13 cm (5 in) diameter and 91 cm (3 ft) long – expendable sonar system that is dropped/ejected from aircraft or ships conducting anti-submarine warfare or underwater acoustic research.

An anti-submarine weapon (ASW) is any one of a number of devices that are intended to act against a submarine and its crew, to destroy (sink) the vessel or reduce its capability as a weapon of war. In its simplest sense, an anti-submarine weapon is usually a projectile, missile or bomb that is optimized to destroy submarines.
Sonar 2087 is a towed array sonar designed and manufactured by Thales Underwater Systems at sites in the UK and in France (Brest). Sonar 2087 replaces the older Sonar 2031 in the Royal Navy and equips eight Type 23 frigates. The system is also expected to equip the Royal Navy's future Type 26 Global Combat Ship starting around 2020.

An acoustic torpedo is a torpedo that aims itself by listening for characteristic sounds of its target or by searching for it using sonar. Acoustic torpedoes are usually designed for medium-range use, and often fired from a submarine.

The Mark 24 mine is an air-dropped anti-submarine warfare weapon (ASW) incorporating passive acoustic homing system and torpedo integration. It was used by the United States, the British and Canadian forces during the Second World War and entered service in March 1943 and remained in use with the US Navy until 1948. Approximately 4,000 torpedoes were produced, with 340 ultimately being deployed during the war. Two-hundred and four torpedoes were launched against submarine targets, with 37 Axis submarines being sunk and a further 18 damaged. The deceptive name of "Mark 24 mine" was deliberately chosen for security purposes, to conceal the true nature of the weapon.

Anti-submarine warfare is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations are typically carried out to protect friendly shipping and coastal facilities from submarine attacks and to overcome blockades.
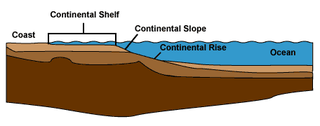
A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margin consists of three different features: the continental rise, the continental slope, and the continental shelf. The continental shelf is the relatively shallow water area found in proximity to continents. Continental margins constitute about 28% of the oceanic area.

The Mark 37 torpedo is a torpedo with electrical propulsion, developed for the US Navy after World War II. It entered service with the US Navy in the early 1950s, with over 3,300 produced. It was phased out of service key with the US Navy during the 1970s, and the stockpiles were sold to foreign navies.

The Type 039 submarine is a class of diesel-electric submarines of the People's Liberation Army Navy. The class is the first diesel-electric submarine to be fully developed within China and also the first Chinese diesel-electric submarine to use the teardrop hull shape.
The Department of Defence Production of the Ministry of Defence is responsible for the indigenous production of equipment used by the Indian Navy and the other armed forces. It comprises the 41 Indian Ordnance Factories under control of the Ordnance Factories Board and eight Defence PSUs: HAL, BEL, BEML, BDL, MDL, GSL, GRSE and Midhani. The present weapon systems of the Indian Navy are:
The term acoustic signature is used to describe a combination of acoustic emissions of sound emitters, such as those of ships and submarines. In addition, aircraft, machinery, and living animals can be described as having their own characteristic acoustic signatures or sound attributes, which can be used to study their condition, behavior, and physical location.

The AN/UQQ-2 Surveillance Towed Array Sensor System (SURTASS), colloquially referred to as the ship's "Tail", is a towed array sonar system of the United States Navy.

Passive Underwater Fire Control Feasibility System (PUFFS) was a passive sonar system for submarines. It was designated AN/BQG-4 and was primarily installed on United States Navy conventional submarines built in the 1950s beginning with the Tang class, and also those converted to GUPPY III or otherwise modernized in the 1960s. It was also equipped on the nuclear-powered USS Tullibee (SSN-597). It was also installed on the USS Thomas Edison (SSBN-610) but never achieved operational status. Its transducers can be seen on pictures of the vessel. A version known as "Micropuffs" was fitted on Oberon-class submarines for the Royal Australian Navy, and as Type 2041 on the Upholder-class for the British Royal Navy. This class still serves in the Royal Canadian Navy as the Victoria class, where Micropuffs is known as BQG-501. The system was notable for three tall, fin-like domes topside, except on Micropuffs installations. The system was retained on several submarines transferred by the US to foreign navies. It was associated with long-range passive detection of targets for the Mark 45 nuclear torpedo and other weapons. Most submarines backfitted with it were also lengthened 12–16 feet to accommodate additional electronics and plotting rooms. It was also planned for Thresher and Sturgeon class nuclear submarines, but was not fitted on them except Micropuffs experimentally on Barb and Haddock. With the exception of the four Canadian Victoria-class submarines, all PUFFS-equipped submarines have been disposed of or preserved as museum ships.
Geophysical MASINT is a branch of Measurement and Signature Intelligence (MASINT) that involves phenomena transmitted through the earth and manmade structures including emitted or reflected sounds, pressure waves, vibrations, and magnetic field or ionosphere disturbances.
Sonar 2076 is a submarine sonar detection system designed by Thales for the Royal Navy.
The Type 035 submarine is a class of diesel-electric submarines of the People's Liberation Army Navy. The Type 035 is a heavily improved redesign of the older Type 033 submarines, which were built in China from 1962 to 1984.
References
- ↑ Steel Boats, Iron Men: History of the U.S. Submarine Force, Mike H. Rindskopf, page 60