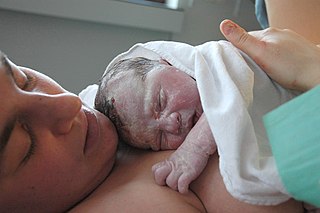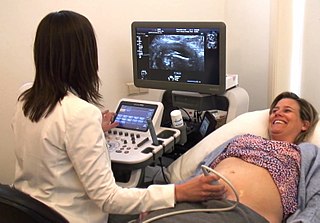
Midwifery is the health science and health profession that deals with pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period, in addition to the sexual and reproductive health of women throughout their lives. In many countries, midwifery is a medical profession. A professional in midwifery is known as a midwife.

Obstetric fistula is a medical condition in which a hole develops in the birth canal as a result of childbirth. This can be between the vagina and rectum, ureter, or bladder. It can result in incontinence of urine or feces. Complications may include depression, infertility, and social isolation.
A birthing center or centre is a healthcare facility, staffed by nurse-midwives, midwives and/or obstetricians, for mothers in labor, who may be assisted by doulas and coaches. By attending the laboring mother, the doulas can assist the midwives and make the birth easier. The midwives monitor the labor, and well-being of the mother and fetus during birth. Should additional medical assistance be required the mother can be transferred to a hospital. Some hospitals are now adding birth centers to their facilities as an alternative to the high tech maternity wards commonly found at most hospitals.

A postpartum period begins immediately after the birth of a child as the mother's body, including hormone levels and uterus size, returns to a non-pregnant state. The terms puerperium or puerperal period, or immediate postpartum period are commonly used to refer to the first six weeks following childbirth. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes the postnatal period as the most critical and yet the most neglected phase in the lives of mothers and babies; most maternal and newborn deaths occur during the postnatal period. In scientific literature, the term is commonly abbreviated to Px, where x is a number; for example, "day P5" should be read as "the fifth day after birth". This is not to be confused with the medical nomenclature that uses G P to stand for number and outcomes of pregnancy.

In the United States, a certified nurse-midwife (CNM) is a midwife who exceeds the International Confederation of Midwives essential competencies for a midwife and is also an advanced practice registered nurse having completed registered nursing and midwifery education. CNMs provide care of women across their lifespan, including pregnancy and the postpartum period, and well woman care and birth control. Certified nurse midwives are exceptionally recognized by the International Confederation of Midwives as a type of midwives in the United States.
In 1982, The Midwives Alliance of North America (MANA) was established as a professional organization for midwives. Its stated goal is to unify and strengthen the profession of midwifery, thereby improving the quality of health care for women, babies, and communities.
A birth attendant, also known as skilled birth attendant, is a health professional who provides basic and emergency care to women and their newborns during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. A birth attendant, who may be a midwife, physician, obstetrician, or nurse, is trained to be present at ("attend") childbirth, whether the delivery takes place in a health care institution or at home, to recognize and respond appropriately to medical complications, and to implement interventions to help prevent them in the first place, including through prenatal care. Different birth attendants are able to provide different levels of care.
Deficient sanitation systems, poor nutrition, and inadequate health services have pushed Haiti to the bottom of the World Bank’s rankings of health indicators. According to the United Nations World Food Programme, 80 percent of Haiti’s population lives below the poverty line. In fact, 75% of the Haitian population lives off of $2.50 per day. Consequently, malnutrition is a significant problem. Half the population can be categorized as "food insecure," and half of all Haitian children are undersized as a result of malnutrition. Less than half the population has access to clean drinking water, a rate that compares poorly even with other less-developed nations. Haiti’s healthy life expectancy at birth is 63 years. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that only 43 percent of the target population receives the recommended immunizations.

Community health agent is the title of a specific lay health care worker developed in Brazil by way of PACS in 1991 as part of the construction of the Brazilian Unified Health System established by Constitutional rule in 1988.
The International Assistance Mission (IAM) is a non-profit Christian development non-governmental organization (NGO) working in Afghanistan since 1966. IAM runs projects in eye care, health, education and community development. IAM is registered in Geneva, Switzerland, and is the longest continuously serving NGO in Afghanistan, and only works in Afghanistan.
Childbirth in rural Appalachia has long been a subject of concern. Infant mortality rates are higher in Appalachia than in other parts of the United States. Additionally, poor health in utero, at birth, and in childhood can contribute to poor health throughout life. The region's low income, geographic isolation, and low levels of educational attainment reduce both access to and utilization of modern medical care. Traditional medical practices, including lay midwifery, persisted longer in Appalachia than in other U.S. regions.

Addis Ababa Fistula Hospital and its regional Hamlin Fistula Centres provide comprehensive care for women who suffer from incontinence, physical impairment, shame and marginalisation as a result of an obstetric fistula. The hospital was created by the Australian obstetrician and gynaecologists Catherine Hamlin and her husband Reginald Hamlin to care for women with childbirth injuries and has been in operation since 1974. It is in Addis Ababa, the capital of Ethiopia. It is the only hospital of its kind in the world dedicated exclusively to women with obstetric fistula, and it treats all patients free of charge. Patients undergo surgical repair by Ethiopian and expatriate surgeons trained at the hospital's main facility in Addis Ababa. Around 93% of these patients are repaired successfully.

Comfort Iyabo Amah Momoh, is a British midwife who specializes in the treatment of female genital mutilation (FGM). Born in Nigeria, Momoh is a member of the British FGM national clinical group, established in 2007 to train health professionals in how to deal with the practice. Until 2017 she served as a public-health specialist at Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust in London. She is the editor of Female Genital Mutilation (2005).

Nasrin Oryakhil (1964) is an Afghani minister, gynecologist and obstetrician. She won awards for her work and in 2015 she was made a minister.
Abortion in Afghanistan is affected by the religious constraints from the national religion, Islam, and by the extremely high birthrates. Afghanistan has one of the highest fertility rates, but its levels are decreasing since the fall of the Taliban, as aid workers can now enter the country to help with fertility and decrease mortality rates. Afghan law is influenced by Islamic law, which comes from the Qur’an. These laws state that abortion is only legal if it is performed to save the life of the mother or if the child is going to be born with a severe disability. This interpretation of Islamic law is based in Islamic medicine, as Muslims cherish the sanctity of human life and believe God does not cause harm or illnesses that are incurable. Due to these constraints, women choose either to pursue an abortion illegally or be shunned by society due to a pregnancy outside of the socially accepted norms. Contraception is approved by Islam when it prevents the formation of the zygote and prevents implantation in the uterus.

Victoria Joyce Ely was an American nurse who served in World War I in the Army Nurse Corps and then provided nursing services in the Florida Panhandle in affiliation with the American Red Cross. To address the high infant and maternal death rates in Florida in the 1920s, she lectured and worked at the state health office. Due to her work, training improved for birth attendants and death rates dropped. After 15 years in the state's service, she opened a rural health clinic in Ruskin, Florida, providing both basic nursing services and midwife care. The facility was renamed the Joyce Ely Health Center in her honor in 1954. In 1983, she was inducted into Florida Public Health Association's Hall of Memory and in 2002 was inducted into the Florida Women's Hall of Fame.
A death midwife, or death doula, is a person who assists in the dying process, much like a midwife or doula does with the birthing process. It is often a community based role, aiming to help families cope with death through recognizing it as a natural and important part of life. The role can supplement and go beyond hospice. Practitioners perform a large variety of service, including but not limited to creating death plans, and providing spiritual, psychological, and social support before and just after death. Their role can also include more logistical activities, helping with services, planning funerals and memorial services, and guiding mourners in their rights and responsibilities.
Circle of Health International, known as COHI for short, is a US based non-governmental organization founded in 2004 with the mission to work with women and their communities with a community based approach in times of crisis. As of 2016, COHI has responded to eighteen humanitarian emergencies and served over three million women globally. COHI has worked with midwives and public health professionals in Sri Lanka, Louisiana, Tibet, Tanzania, Israel, the Philippines, Palestine, Jordan, Syria, Oklahoma, Nicaragua, Sudan, Haiti, and Afghanistan.