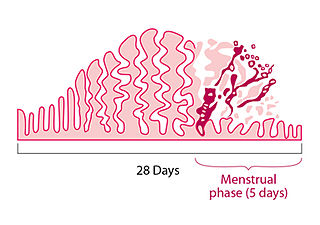
Menstruation is the regular discharge of blood and mucosal tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized by the rise and fall of hormones. Menstruation is triggered by falling progesterone levels and is a sign that pregnancy has not occurred.

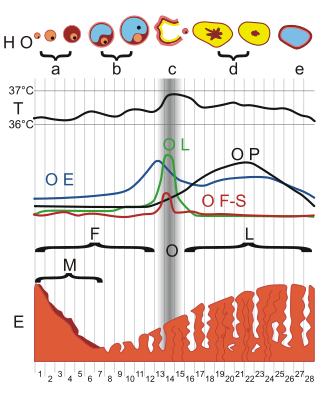
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs and the cyclic release of estrogen and progesterone. The uterine cycle governs the preparation and maintenance of the lining of the uterus (womb) to receive an embryo. These cycles are concurrent and coordinated, normally last between 21 and 35 days, with a median length of 28 days, and continue for about 30–45 years.

Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In women, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm. In addition, the uterine lining (endometrium) is thickened to be able to receive a fertilized egg. If no conception occurs, the uterine lining as well as the egg will be shed during menstruation.

Sexual attraction is attraction on the basis of sexual desire or the quality of arousing such interest. Sexual attractiveness or sex appeal is an individual's ability to attract other people sexually, and is a factor in sexual selection or mate choice. The attraction can be to the physical or other qualities or traits of a person, or to such qualities in the context where they appear. The attraction may be to a person's aesthetics, movements, voice, or smell, among other things. The attraction may be enhanced by a person's adornments, clothing, perfume or style. It can be influenced by individual genetic, psychological, or cultural factors, or to other, more amorphous qualities. Sexual attraction is also a response to another person that depends on a combination of the person possessing the traits and on the criteria of the person who is attracted.

Estradiol (E2), also spelled oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of the estrous and menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics such as the breasts, widening of the hips and a female-associated pattern of fat distribution. It is also important in the development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues such as the mammary glands, uterus and vagina during puberty, adulthood and pregnancy. It also has important effects in many other tissues including bone, fat, skin, liver, and the brain.
An antispasmodic is a pharmaceutical drug or other agent that suppresses muscle spasms.
Dysmenorrhea, also known as period pain, painful periods or menstrual cramps, is pain during menstruation. Its usual onset occurs around the time that menstruation begins. Symptoms typically last less than three days. The pain is usually in the pelvis or lower abdomen. Other symptoms may include back pain, diarrhea or nausea.

A menstrual cup is a menstrual hygiene device which is inserted into the vagina during menstruation. Its purpose is to collect menstrual fluid. Menstrual cups are usually made of flexible medical grade silicone, latex, or a thermoplastic isomer. They are shaped like a bell with a stem or a ring. The stem is used for insertion and removal, and the bell-shaped cup seals against the vaginal wall just below the cervix and collects menstrual fluid. This is unlike tampons and menstrual pads, which absorb the fluid instead.
Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB), previously known as menorrhagia or hypermenorrhea, is a menstrual period with excessively heavy flow. It is a type of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB).
Oligomenorrhea is infrequent menstruation. More strictly, it is menstrual periods occurring at intervals of greater than 35 days, with only four to nine periods in a year. Menstrual periods should have been regularly established before the development of infrequent flow. The duration of such events may vary.
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available. Such methods include adding 14 days to a known duration since fertilization, or by obstetric ultrasonography. The popularity of using this measure of pregnancy is due to the fact that menstrual periods are usually noticed, while there is generally no convenient way to discern when fertilization or implantation occurred. Gestational age is contrasted with fertilization age which takes the date of fertilization as the start date of gestation, and pregnancy which begins with implantation.
Menstrual synchrony, also called the McClintock effect, or the Wellesley effect, is a contested process whereby women who begin living together in close proximity would experience their menstrual cycle onsets becoming more synchronized together in time than when previously living apart. "For example, the distribution of onsets of seven female lifeguards was scattered at the beginning of the summer, but after 3 months spent together, the onset of all seven cycles fell within a 4-day period."
Peppermint extract is an herbal extract of peppermint made from the essential oils of peppermint leaves. Peppermint is a hybrid of water mint and spearmint and was indigenous to Europe and the Middle East before it became common in other regions, such as North America and Asia.

Emepronium is an anticholinergic drug used in urology as an antispasmodic. It can cause ulceration of esophagus, so it should be taken in orthostatic position with sufficient amounts of liquids.
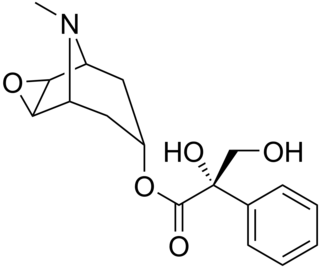
Anisodine, also known as daturamine and α-hydroxyscopolamine, is an antispasmodic and anticholinergic drug used in the treatment of acute circulatory shock in China. It is a tropane alkaloid and is found naturally in plants of the family Solanaceae like Scopolia tanguticus Anisodine acts as a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist.
Irregular menstruation is a menstrual disorder whose manifestations include irregular cycle lengths as well as metrorrhagia. The possible causes of irregular menstruation may vary. The common factors of it are related to lifestyle, such as stress, body weight, and smoking status. Several studies indicate that COVID-19 vaccine of any type may disrupt the menstrual cycle, although only momentarily. This side effect should resolve on its own in the following month.
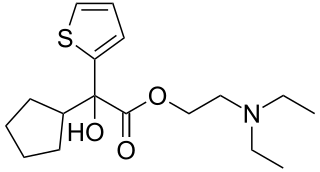
WIN-2299 is an anticholinergic drug. Human reactions to WIN-2299 include sedation, LSD-like reactions, and an acute delirious episode.

Menstrual hygiene management (MHM) or menstrual health and hygiene (MHH) refers to access to menstrual hygiene products to absorb or collect the flow of blood during menstruation, privacy to change the materials, and access to facilities to dispose of used menstrual management materials. It can also include the "broader systemic factors that link menstruation with health, well-being, gender equality, education, equity, empowerment, and rights". Menstrual hygiene management can be particularly challenging for girls and women in developing countries, where clean water and toilet facilities are often inadequate. Menstrual waste is largely ignored in schools in developing countries, despite it being a significant problem. Menstruation can be a barrier to education for many girls, as a lack of effective sanitary products restricts girls' involvement in educational and social activities.
Menstrual suppression refers to the practice of using hormonal management to stop or reduce menstrual bleeding. In contrast to surgical options for this purpose, such as hysterectomy or endometrial ablation, hormonal methods to manipulate menstruation are reversible.

Drofenine is an antimuscarinic antispasmodic drug used for relaxing smooth muscle, thereby treating conditions, such as: dysmenorrhea, and pain in the gastrointestinal tract, biliary passages, and urogenital tract. Drofenine is assumed to work by increasing the levels of the protein TRPV3.













