An acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their application in solving related problems; these are called the acid–base theories, for example, Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory.

In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances which react with acids as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century.

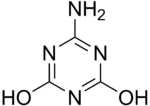
Melamine is an organic compound with the formula C3H6N6. This white solid is a trimer of cyanamide, with a 1,3,5-triazine skeleton. Like cyanamide, it contains 67% nitrogen by mass, and its derivatives have fire retardant properties due to its release of nitrogen gas when burned or charred. Melamine can be combined with formaldehyde and other agents to produce melamine resins. Such resins are characteristically durable thermosetting plastic used in high pressure decorative laminates such as Formica, melamine dinnerware, laminate flooring, and dry erase boards. Melamine foam is used as insulation, soundproofing material and in polymeric cleaning products, such as Magic Eraser.
In chemistry, a trimer is a molecule or an anion formed by combination or association of three molecules or ions of the same substance. In technical jargon, a trimer is a kind of oligomer derived from three identical precursors often in competition with polymerization.
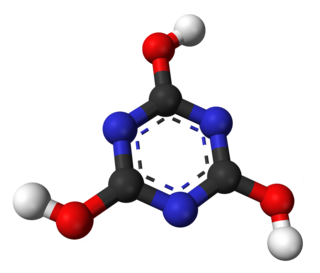
Cyanuric acid or 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triol is a chemical compound with the formula (CNOH)3. Like many industrially useful chemicals, this triazine has many synonyms. This white, odorless solid finds use as a precursor or a component of bleaches, disinfectants, and herbicides. In 1997, worldwide production was 160 million kilograms.

Triazines are a class of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. The parent molecules' molecular formula is C3H3N3. They exist in three isomeric forms, 1,3,5-triazines being common.

Cyanuric chloride is an organic compound with the formula (NCCl)3. This white solid is the chlorinated derivative of 1,3,5-triazine. It is the trimer of cyanogen chloride. Cyanuric chloride is the main precursor to the popular but controversial herbicide atrazine.

Beryllium nitride, Be3N2, is a nitride of beryllium. It can be prepared from the elements at high temperature (1100–1500 °C), unlike Beryllium azide or BeN6, it decomposes in vacuum into beryllium and nitrogen. It is readily hydrolysed forming beryllium hydroxide and ammonia. It has two polymorphic forms cubic α-Be3N2 with a defect anti-fluorite structure, and hexagonal β-Be3N2. It reacts with silicon nitride, Si3N4 in a stream of ammonia at 1800–1900 °C to form BeSiN2.

Sodium bisulfate, also known as sodium hydrogen sulfate, is the sodium salt of the bisulfate anion, with the molecular formula NaHSO4. Sodium bisulfate is an acid salt formed by partial neutralization of sulfuric acid by an equivalent of sodium base, typically in the form of either sodium hydroxide (lye) or sodium chloride (table salt). It is a dry granular product that can be safely shipped and stored. The anhydrous form is hygroscopic. Solutions of sodium bisulfate are acidic, with a 1M solution having a pH of around 1.
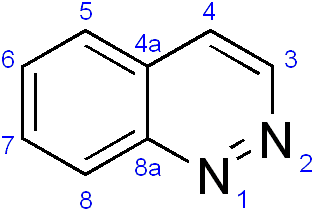
Cinnoline is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the formula C8H6N2. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinoxaline, phthalazine and quinazoline.
A Nitrate Test is a chemical test used to determine the presence of nitrate ion in solution. Testing for the presence of nitrate via wet chemistry is generally difficult compared with testing for other anions, as almost all nitrates are soluble in water. In contrast, many common ions give insoluble salts, e.g. halides precipitate with silver, and sulfate precipitate with barium.
The Kjeldahl method or Kjeldahl digestion (Danish pronunciation: [ˈkʰelˌtɛˀl]) in analytical chemistry is a method for the quantitative determination of nitrogen contained in organic substances plus the nitrogen contained in the inorganic compounds ammonia and ammonium (NH3/NH4+). Without modification, other forms of inorganic nitrogen, for instance nitrate, are not included in this measurement. Using an empirical relation between Kjeldahl nitrogen content and protein content it is an important method for analyzing proteins. This method was developed by Johan Kjeldahl in 1883.
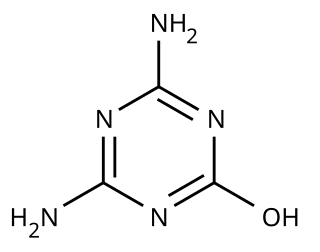
Ammeline (4,6-diamino-2-hydroxy-1,3,5-triazine) is a triazine derivative. It is the hydrolysis product of melamine.
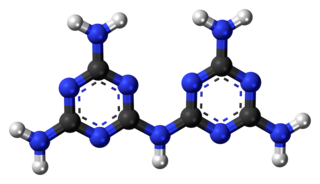
Melam is a condensation product of melamine.
Non-protein nitrogen is a term used in animal nutrition to refer collectively to components such as urea, biuret, and ammonia, which are not proteins but can be converted into proteins by microbes in the ruminant stomach. Due to their lower cost compared to plant and animal proteins their inclusion in a diet can result in economic gain, but at too high levels cause a depression in growth and possible ammonia toxicity NPN can also be used to artificially raise crude protein values, which are measured based on nitrogen content, as protein is about 16% nitrogen, but, for example, urea is 47% nitrogen. The source of NPN is typically a chemical feed additive, or sometimes chicken waste and cattle manure.
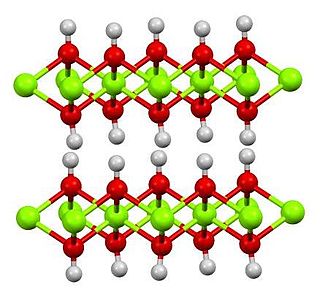
Cadmium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd(OH)2. It is a white crystalline ionic compound that is a key component of nickel–cadmium battery.

Ammonium thiocyanate is an inorganic compound with the formula NH4SCN. It is the salt of the ammonium cation and the thiocyanate anion.

Ammonium sulfite is the ammonium salt of sulfurous acid with the chemical formula (NH4)2SO3.

Cyanuric bromide is a heterocyclic compound with formula C3N3Br3. It contains a six-membered ring of alternating nitrogen and carbon atoms, with a bromine atom attached to each carbon. It is formed by the spontaneous trimerisation of cyanogen bromide.