External links
- eb/arp tables website
- download site
- git tree
- arptables(8) - Linux man page
- arptables, and ARP poisoning
| This network-related software article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
The arptables computer software utility is a network administrator's tool for maintaining the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) packet filter rules in the Linux kernel firewall modules.
The tools may be used to create, update, and view the tables that contain the filtering rules, similarly to the iptables program from which it was developed. A popular application is the creation of filter configurations to prevent ARP spoofing.
Linux kernel 2.4 only offers two ARP filtering chains, INPUT and OUTPUT, and Linux kernel 2.6 adds the third, FORWARD, applied when bridging packets.
| This network-related software article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a communication protocol used for discovering the link layer address, such as a MAC address, associated with a given internet layer address, typically an IPv4 address. This mapping is a critical function in the Internet protocol suite. ARP was defined in 1982 by RFC 826, which is Internet Standard STD 37.
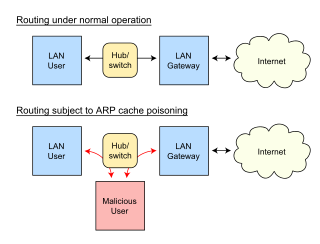
In computer networking, ARP spoofing, ARP cache poisoning, or ARP poison routing, is a technique by which an attacker sends (spoofed) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages onto a local area network. Generally, the aim is to associate the attacker's MAC address with the IP address of another host, such as the default gateway, causing any traffic meant for that IP address to be sent to the attacker instead.
A Martian packet is an IP packet seen on the public Internet that contains a source or destination address that is reserved for special-use by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). On the public Internet, such a packet either has a spoofed source address, and it cannot actually originate as claimed, or the packet cannot be delivered. The requirement to do this is found in RFC 1812, Section 5.2.3.
iptables is a user-space utility program that allows a system administrator to configure the IP packet filter rules of the Linux kernel firewall, implemented as different Netfilter modules. The filters are organized in different tables, which contain chains of rules for how to treat network traffic packets. Different kernel modules and programs are currently used for different protocols; iptables applies to IPv4, ip6tables to IPv6, arptables to ARP, and ebtables to Ethernet frames.
Netfilter is a framework provided by the Linux kernel that allows various networking-related operations to be implemented in the form of customized handlers. Netfilter offers various functions and operations for packet filtering, network address translation, and port translation, which provide the functionality required for directing packets through a network and prohibiting packets from reaching sensitive locations within a network.
A default gateway is the node in a computer network using the internet protocol suite that serves as the forwarding host (router) to other networks when no other route specification matches the destination IP address of a packet.
dsniff is a set of password sniffing and network traffic analysis tools written by security researcher and startup founder Dug Song to parse different application protocols and extract relevant information. dsniff, filesnarf, mailsnarf, msgsnarf, urlsnarf, and webspy passively monitor a network for interesting data. arpspoof, dnsspoof, and macof facilitate the interception of network traffic normally unavailable to an attacker. sshmitm and webmitm implement active man-in-the-middle attacks against redirected SSH and HTTPS sessions by exploiting weak bindings in ad-hoc PKI.
The Common Address Redundancy Protocol or CARP is a computer networking protocol which allows multiple hosts on the same local area network to share a set of IP addresses. Its primary purpose is to provide failover redundancy, especially when used with firewalls and routers. In some configurations, CARP can also provide load balancing functionality. CARP provides functionality similar to VRRP and to Cisco Systems' HSRP. It is implemented in several BSD-based operating systems and has been ported to Linux (ucarp).
Ettercap is a free and open source network security tool for man-in-the-middle attacks on LAN. It can be used for computer network protocol analysis and security auditing. It runs on various Unix-like operating systems including Linux, Mac OS X, BSD and Solaris, and on Microsoft Windows. It is capable of intercepting traffic on a network segment, capturing passwords, and conducting active eavesdropping against a number of common protocols. Its original developers later founded Hacking Team.
Linux IP Firewalling Chains, normally called ipchains, is free software to control the packet filter or firewall capabilities in the 2.2 series of Linux kernels. It superseded ipfirewall, but was replaced by iptables in the 2.4 series. Unlike iptables, ipchains is stateless.
In Linux, the System.map file is a symbol table used by the kernel.
Reverse-path forwarding (RPF) is a technique used in modern routers for the purposes of ensuring loop-free forwarding of multicast packets in multicast routing and to help prevent IP address spoofing in unicast routing.
seccomp is a computer security facility in the Linux kernel. seccomp allows a process to make a one-way transition into a "secure" state where it cannot make any system calls except exit , sigreturn , read and write to already-open file descriptors. Should it attempt any other system calls, the kernel will terminate the process with SIGKILL or SIGSYS. In this sense, it does not virtualize the system's resources but isolates the process from them entirely.

ipfirewall or ipfw is a FreeBSD IP, stateful firewall, packet filter and traffic accounting facility. Its ruleset logic is similar to many other packet filters except IPFilter. ipfw is authored and maintained by FreeBSD volunteer staff members. Its syntax enables use of sophisticated filtering capabilities and thus enables users to satisfy advanced requirements. It can either be used as a loadable kernel module or incorporated into the kernel; use as a loadable kernel module where possible is highly recommended. ipfw was the built-in firewall of Mac OS X until Mac OS X 10.7 Lion in 2011 when it was replaced with the OpenBSD project's PF. Like FreeBSD, ipfw is open source. It is used in many FreeBSD-based firewall products, including m0n0wall and FreeNAS. A port of an early version of IPFW was used since Linux 1.1 as the first implementation of firewall available for Linux, until it was replaced by ipchains. A modern port of ipfw and the dummynet traffic shaper is available for Linux and Microsoft Windows. wipfw is a Windows port of an old (2001) version of ipfw.
The Netlink socket family is a Linux kernel interface used for inter-process communication (IPC) between both the kernel and userspace processes, and between different userspace processes, in a way similar to the Unix domain sockets. Similarly to the Unix domain sockets, and unlike INET sockets, Netlink communication cannot traverse host boundaries. However, while the Unix domain sockets use the file system namespace, Netlink processes are usually addressed by process identifiers (PIDs).
The Berkeley Packet Filter (BPF) is a technology used in certain computer operating systems for programs that need to, among other things, analyze network traffic. It provides a raw interface to data link layers, permitting raw link-layer packets to be sent and received. It is available on most Unix-like operating systems. In addition, if the driver for the network interface supports promiscuous mode, it allows the interface to be put into that mode so that all packets on the network can be received, even those destined to other hosts.

nftables is a subsystem of the Linux kernel providing filtering and classification of network packets/datagrams/frames. It has been available since Linux kernel 3.13 released on 19 January 2014.

ngrep is a network packet analyzer written by Jordan Ritter. It has a command-line interface, and relies upon the pcap library and the GNU regex library.

netsniff-ng is a free Linux network analyzer and networking toolkit originally written by Daniel Borkmann. Its gain of performance is reached by zero-copy mechanisms for network packets, so that the Linux kernel does not need to copy packets from kernel space to user space via system calls such as recvmsg. libpcap, starting with release 1.0.0, also supports the zero-copy mechanism on Linux for capturing (RX_RING), so programs using libpcap also use that mechanism on Linux.
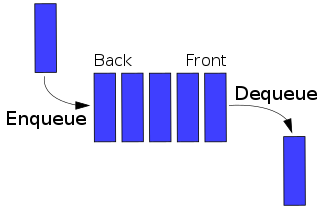
A network scheduler, also called packet scheduler, queueing discipline, qdisc or queueing algorithm, is an arbiter on a node in packet switching communication network. It manages the sequence of network packets in the transmit and receive queues of the network interface controller. There are several network schedulers available for the different operating systems, that implement many of the existing network scheduling algorithms.