Related Research Articles

The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier which is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.

The International Bank Account Number (IBAN) is an internationally agreed system of identifying bank accounts across national borders to facilitate the communication and processing of cross border transactions with a reduced risk of transcription errors. An IBAN uniquely identifies the account of a customer at a financial institution. It was originally adopted by the European Committee for Banking Standards (ECBS) and later as an international standard under ISO 13616:1997. The current standard is ISO 13616:2020, which indicates SWIFT as the formal registrar. Initially developed to facilitate payments within the European Union, it has been implemented by most European countries and numerous countries in other parts of the world, mainly in the Middle East and the Caribbean. As of May 2020, 77 countries were using the IBAN numbering system.

ISO 4217 is a standard published by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individual currencies and their minor units. This data is published in three tables:

The Open Systems Interconnection model is a conceptual model that characterises and standardises the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology. Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard communication protocols.
The Common Management Information Service (CMIS) is the service interface specified in ITU-T Recommendation X.710, ISO/IEC International Standard 9595 that is employed by OSI network elements for network management. It defines the service interface that is implemented by the Common Management Information Protocol (CMIP) as specified in ITU-T Recommendation X.711, ISO/IEC International Standard 9596-1. CMIS is part of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) body of international network standards.
In telecommunication, a longitudinal redundancy check (LRC), or horizontal redundancy check, is a form of redundancy check that is applied independently to each of a parallel group of bit streams. The data must be divided into transmission blocks, to which the additional check data is added.
X.500 is a series of computer networking standards covering electronic directory services. The X.500 series was developed by the Telecommunication Standardization Sector of the International Telecommunications Union (ITU-T). ITU-T was formerly known as the Consultative Committee for International Telephony and Telegraphy (CCITT). X.500 was approved first in 1988. The directory services were developed to support requirements of X.400 electronic mail exchange and name lookup. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) was a partner in developing the standards, incorporating them into the Open Systems Interconnection suite of protocols. ISO/IEC 9594 is the corresponding ISO identification.

In computer networking, the transport layer is a conceptual division of methods in the layered architecture of protocols in the network stack in the Internet protocol suite and the OSI model. The protocols of this layer provide host-to-host communication services for applications. It provides services such as connection-oriented communication, reliability, flow control, and multiplexing.

A vehicle identification number (VIN) is a unique code, including a serial number, used by the automotive industry to identify individual motor vehicles, towed vehicles, motorcycles, scooters and mopeds, as defined in ISO 3779 and ISO 4030.
An application layer is an abstraction layer that specifies the shared communications protocols and interface methods used by hosts in a communications network. An application layer abstraction is specified in both the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) and the OSI model. Although both models use the same term for their respective highest-level layer, the detailed definitions and purposes are different.
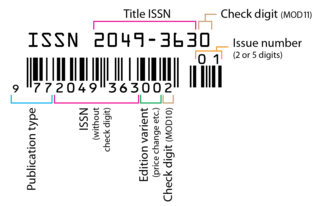
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit serial number used to uniquely identify a serial publication, such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSNs is used in ordering, cataloging, interlibrary loans, and other practices in connection with serial literature.
Magnetic ink character recognition code, known in short as MICR code, is a character recognition technology used mainly by the banking industry to streamline the processing and clearance of cheques and other documents. MICR encoding, called the MICR line, is at the bottom of cheques and other vouchers and typically includes the document-type indicator, bank code, bank account number, cheque number, cheque amount and a control indicator. The format for the bank code and bank account number is country-specific.
The Common Management Information Protocol (CMIP) is the OSI specified network management protocol.
ISO/IEC 7812Identification cards — Identification of issuers was first published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1989. It is the international standard specifies "a numbering system for the identification of the card issuers, the format of the issuer identification number (IIN) and the primary account number (PAN).", and procedures for registering IINs. ISO/IEC 7812 has two parts:

ISO 6346 is an international standard covering the coding, identification and marking of intermodal (shipping) containers used within containerized intermodal freight transport. The standard establishes a visual identification system for every container that includes a unique serial number, the owner, a country code, a size, type and equipment category as well as any operational marks. The standard is managed by the International Container Bureau (BIC).
The Open Systems Interconnection protocols are a family of information exchange standards developed jointly by the ISO and the ITU-T. The standardization process began in 1977.

Advanced Civil Speed Enforcement System (ACSES) is a positive train control cab signaling system developed by Alstom. The system is designed to prevent train-to-train collisions, protect against overspeed, and protect work crews with temporary speed restrictions. The information about permanent and temporary speed restrictions is transmitted to the train by transponders (Balises) lying in the track, coded track circuits and digital radio. It was installed beginning in 2000 on all of Amtrak's Northeast Corridor between Washington and Boston, and has been fully active since December 2015, a few months after the 2015 Philadelphia train derailment which it would have prevented.
The Universal Coded Character Set is a standard set of characters defined by the International Standard ISO/IEC 10646, Information technology — Universal Coded Character Set (UCS), which is the basis of many character encodings, improving as characters from previously unrepresented writing systems are added.
PDF/VT is an international standard published by ISO in August 2010 as ISO 16612-2. It defines the use of PDF as an exchange format optimized for variable and transactional printing. Built on top of PDF/X-4, it is the first variable-data printing (VDP) format which ensures modern International Color Consortium-based (ICC) color management through the use of ICC Output Intents. It adds the notion of encapsulated groups of graphic objects to support optimized efficient processing for repeating text, graphic or image content. Introducing the concept of document part metadata (DPM), it enables reliable and dynamic management of pages for High Volume Transactional Output (HVTO) print data, like record selection or postage optimization based on metadata.
The International Standard Link Identifier (ISLI), is an identifier standard. ISLI is a universal identifier for links between entities in the field of information and documentation. It was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and published on May 15, 2015. ISO/TC 46/SC 9 is responsible for the development of the ISLI standard.
References
- ITU Rec. X.227 (ISO 8650), X.217 (ISO 8649)