 | |
Belarus | Serbia |
|---|---|
On December 31, 1991, SFR Yugoslavia recognized Belarus by the decision on the recognition of the former republics of the USSR.
Contents
Belarus has an embassy in Belgrade. Serbia has an embassy in Minsk.
 | |
Belarus | Serbia |
|---|---|
On December 31, 1991, SFR Yugoslavia recognized Belarus by the decision on the recognition of the former republics of the USSR.
Belarus has an embassy in Belgrade. Serbia has an embassy in Minsk.
The important stimulus for closer economic and cultural cooperation, and also for the development of tourism, is the visa-free regime which has been in force between Belarus and Serbia since 2000. Serbian artists regularly take part in the Slavianski Bazaar in Vitebsk and have won several awards over the years.


The contract-legal basis of cooperation of Belarus and Serbia includes 20 signed agreements which cover almost all areas of bilateral interests.
I know Serbia wonderfully. I was there more than once. I know the history and sentiments of the people of Serbia. After all, Serbia originated in Kosovo. In Kosovo, there are Serbian sacred sites.
Following the 2020 Belarusian presidential election, Serbia signed the Declaration initiated by the European Union rejecting the election results and criticizing crackdown against those protesting. [2]
Serbian businessman Dragomir Karić is the honorary consul of the Republic of Belarus in Belgrade. [3]
In 2006, Belarusian exports to Serbia were tractors, potash fertilizers, salt, ferrous metal, twisted wires and cotton fabric. Serbian exports to Belarus were pipes, rubber hoses and sleeves, synthetic polymer paints and varnishes, rough-grinding machine tools, honing machines, and modular machines for metal processing. Belarus and Serbia signed a free trade agreement in 2009. [4] [5]
| Period | Belarusian export | Serbian export |
|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 16.4 million USD | 7.6 million USD |
| 2003 | 17.2 | 4.8 |
| 2004 | 27.4 | 7.7 |
| 2005 | 35.1 | 12.3 |
| 2006 | 16.6 | 20.9 |
| 2007 | 32.7 | 21.2 |
| 2008 | 41.4 | 23.4 |

The Byelorussian SSR was one of only two Soviet republics to be separate members of the United Nations. Both republics and the Soviet Union joined the UN when the organization was founded in 1945.
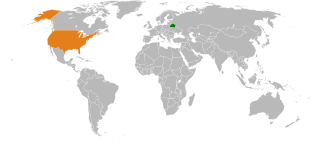
Interstate relations between the United States and Belarus began in 1991 upon the dissolution of the Soviet Union, of which Belarus had been a part. However, the relations have turned sour due to accusations by the United States that Belarus has been violating human rights. Belarus, in turn, has accused the United States of interfering in its internal affairs.

Mutual relations between the Republic of Belarus and the European Union (EU) were initially established after the European Economic Community recognised Belarusian independence in 1991.
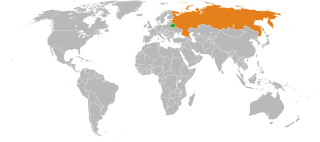
Belarus and Russia share a land border and constitute the supranational Union State. Several treaties have been concluded between the two nations bilaterally. Russia is Belarus' largest and most important economic and political partner. Both are members of various international organizations, including the Commonwealth of Independent States, the Eurasian Economic Union, the Collective Security Treaty Organization, and the United Nations.

Serbia–Ukraine relations are foreign relations between Serbia and Ukraine. Serbia, as a direct successor to the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, recognized Ukraine on 15 April 1994. Diplomatic relations between Ukraine and the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia were established on 15 April 1994.

Diplomatic relations between the Republic of Serbia and the Republic of San Marino were established by the exchange of Notes on 14 February 2002.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Belarus is the Belarusian government ministry which oversees the foreign relations of Belarus.

Belarus and Ukraine are both are full members of the Baku Initiative and Central European Initiative. In 2020, during the Belarusian protests against president Lukashenko, the relationship between Ukraine and Belarus began to deteriorate, after the Ukrainian government criticized Belarusian president Alexander Lukashenko. In the waning days of 2021, the relationship between both countries rapidly deteriorated, culminating in a full-scale invasion on 24 February 2022. Belarus has allowed the stationing of Russian troops and equipment in its territory and its use as a springboard for offensives into northern Ukraine but has denied the presence of Belarusian troops in Ukraine. Even though part of the Russian invasion was launched from Belarus, Ukraine did not break off diplomatic relations with Belarus, but remain frozen.

Currently, Belarus has an embassy in Riga, while Latvia has an embassy in Minsk. The countries share 161 km as it relates to their common border. In May 2021 the relations were de facto terminated as both countries were expelling each other's diplomats of the corresponding embassy, Latvia was insisting to use an inaccurate opposition flag as a representation for Belarus in the Ice Hockey World Championship in Riga over the Ryanair Flight 4978 diplomatic row. Belarusian Foreign Minister Vladimir Makei called Latvia's move 'an act of international vandalism' and called for an apology and return the legal green, red and white flag to its original place. The Belarusian government reacted with expelling every Latvian diplomat including the Ambassador inside the country, with Latvia following with the same response. The Zurich-based International Ice Hockey Federation sided with Belarus and asked the mayor of Riga to urgently take down the IIHF flags to protest to what the body called a political gesture.

French-Serbian relations are foreign relations between France and Serbia. Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1839, between the Kingdom of France and the Principality of Serbia.

Bilateral relations exist between Armenia and Serbia. Diplomatic relations between Armenia and the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia were established on 14 January 1993; Serbia is the legal successor to this country. Both countries are represented through their embassies in Athens, Greece, and both have established honorary consulates, which serve as the only diplomatic representatives between the two countries.

Relations between Azerbaijan and Belarus are at very high level that Belarusian president Alexander Lukashenko describes Azerbaijan as a "saver" of independence and sovereignty of Belarus and adds that "there's not anything close" in Azerbaijani-Belarusian relations. Both countries were part of the Russian Empire until 1918 and before 1991, they were part of the Soviet Union. Azerbaijan has an embassy in Minsk and Belarus has an embassy in Baku. Both countries are full members of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). Azerbaijan is a full member of the Council of Europe, Belarus is a candidate. Both Azerbaijan and Belarus are full members of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM). There are more than 6,000 Azerbaijanis living in Belarus.
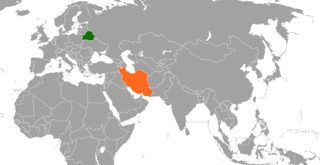
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic recognized de facto the Islamic Republic of Iran in February 1979, and Belarus and Iran established de jure diplomatic relations in 1992. Belarus has an embassy in Tehran. Iran has an embassy in Minsk.

The Republic of Poland and the Republic of Belarus established diplomatic relations on 2 March 1992. Poland was one of the first countries to recognise Belarusian independence. Both countries share a border and have shared histories, for they have been part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and later, the Russian Empire. They joined the United Nations together in October 1945 as original members. The two countries are currently engaged in a border crisis.

The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic recognized Bangladesh's independence on 24 January 1972. Official diplomatic relations between Bangladesh and Belarus were established in 1992. Neither country has a resident ambassador.

Belarus does not have an embassy in Baghdad, but it does maintain a consulate in Erbil. Iraq has an embassy in Minsk. The last Ambassador of Iraq to Belarus was Haidar Hadi who served from July 2010 to November 2015. Since his post expired, there has been no Iraqi Ambassador in Belarus. Both are members of the Non-Aligned Movement.

Kazakhstan–Serbia relations refer to bilateral relations between Kazakhstan and Serbia. Serbia opened an embassy in Astana in June 2011, and Kazakhstan opened a consulate in Belgrade in June 2015.

Dragomir "Dragan" Karić is an entrepreneur and politician in Serbia. A close ally of his younger brother Bogoljub Karić, he has been a prominent figure in Serbia's business community since the 1980s. He has served in the National Assembly of Serbia since 2012 as a member of the Strength of Serbia Movement.

The Embassy of Ukraine in the Republic of Serbia is a diplomatic mission of Ukraine in Serbia, located in the capital city Belgrade.