See also
- Burma, former name of Myanmar
Burm is an alternative spelling of berm, a landform.
Burm may also refer to:

Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. Around 1.4 billion people speak a Sino-Tibetan language. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Sinitic languages. Other Sino-Tibetan languages with large numbers of speakers include Burmese and the Tibetic languages. Other languages of the family are spoken in the Himalayas, the Southeast Asian Massif, and the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Most of these have small speech communities in remote mountain areas, and as such are poorly documented.
Mont may refer to:
Kachin or Kakhyen may refer to:

The country known in English as Burma, or Myanmar, has undergone changes in both its official and popular names worldwide. The choice of names stems from the existence of two different names for the country in Burmese, which are used in different contexts.

The Bamar are a Sino-Tibetan ethnic group native to Myanmar. With an estimated population of around 35 million people, they are the largest ethnic group in Myanmar, accounting for 68.78% of the country's total population.The geographic homeland of the Bamar is the Irrawaddy River basin. The Bamar speak the Burmese language which serves as the national language and lingua franca of Myanmar.
Burman is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:

The Anglo-Burmese people, also known as the Anglo-Burmans, are a community of Eurasians of Burmese and European descent, who emerged as a distinct community through mixed relationships between the British and other Europeans and Burmese people from 1826 until 1948 when Myanmar gained its independence from the British Empire. Those who could not adjust to the new way of life after independence and the ushering in of military dictatorship are dispersed throughout the world. How many stayed in Myanmar is not accurately known.
Varmā, Verma, Varman, or Burman are surnames found in India and Southeast Asia. These surnames are commonly used by people of different castes and ethnic groups across the region. The surname is used in North India by some of the groups among cluster of castes called Kayasthas. However, in the same region along with Central India, it can also be found among castes like Lodhi rajputs, Prajapats, Kurmis and Koeris.

Johannes Burman, was a Dutch botanist and physician. Burman specialized in plants from Ceylon, Amboina and Cape Colony. The name Pelargonium was introduced by Johannes Burman.

Nicolaas Laurens Burman was a Dutch botanist.
The Sal languages, also known as the Brahmaputran languages, are a branch of Tibeto-Burman languages spoken in northeast India, as well as parts of Bangladesh, Myanmar (Burma), and China.

The Lolo-Burmese languages of Burma and Southern China form a coherent branch of the Sino-Tibetan family.
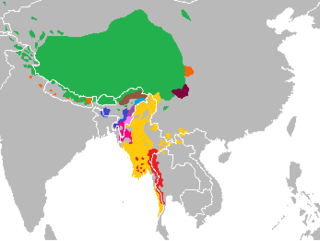
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The name derives from the most widely spoken of these languages, Burmese and the Tibetic languages, which also have extensive literary traditions, dating from the 12th and 7th centuries respectively. Most of the other languages are spoken by much smaller communities, and many of them have not been described in detail.
The Restored Hanthawaddy Kingdom, also known as the Neo-Ramanic State was the kingdom that ruled Lower Burma and parts of Upper Burma from 1740 to 1757. The kingdom grew out of a rebellion by the Mon led population of Pegu, who then rallied the other Mon as well as Delta Bama and Karens of Lower Burma, against the Toungoo Dynasty of Ava in Upper Burma. The rebellion succeeded in expelling Toungoo loyalists and restored the Mon-speaking Kingdom of Hanthawaddy which ruled Lower Burma from 1287 to 1539. The restored Hanthawady kingdom also claim heritage to Bayinaung's early Toungoo Empire whose capital was based in Pegu and guaranteed the loyalty of the non-Mon population of Lower Burma. Supported by the French, the upstart kingdom quickly carved out a space for itself in Lower Burma, and continued its push northward. In March 1752, its forces captured Ava, and ended the 266-year-old Toungoo dynasty.

Synaphea spinulosa is a species of small shrub in the flowering plant family Proteaceae. It is endemic to Western Australia. Together with Acacia truncata, it was the first Australian endemic to be scientifically described and named, and the specimen upon which that description is based is the oldest extant specimen of an Australian plant, and very likely among the first Australian plant specimens ever collected.

Cleretum bellidiforme, commonly called Livingstone daisy, Bokbaaivygie (Afrikaans), or Buck Bay vygie, is a species of flowering plant in the family Aizoaceae, native to the Cape Peninsula in South Africa. It is a low-growing succulent annual growing to 25 cm (10 in), and cultivated for its iridescent, many-petalled, daisy-like blooms in shades of white, yellow, orange, cream, pink and crimson. In temperate areas it is popularly grown as a half-hardy annual, and lends itself to mass plantings or as edging plants in summer bedding schemes in parks and gardens. It is still widely referenced under its former names, Mesembryanthemum criniflorum and Dorotheanthus bellidiformis.

Adiantum philippense,, also known as walking maidenhair fern, or black maidenhair, is a species of maidenhair fern (Adiantum) that is widely distributed through the southern hemisphere, notably Asia, Africa, and Madagascar.
Zaw is a Burmese name that may refer to

Mickelopteris is a genus of ferns in the subfamily Cheilanthoideae of the family Pteridaceae with a single species Mickelopteris cordata. Synonyms include Parahemionitis cordata and Hemionitis cordataRoxb. ex Hook. & Grev. The species is native to south-eastern Asia, from India to Taiwan and the Philippines.
Merr or MERR may refer to: