
Tharsis is a vast volcanic plateau centered near the equator in the western hemisphere of Mars. The region is home to the largest volcanoes in the Solar System, including the three enormous shield volcanoes Arsia Mons, Pavonis Mons, and Ascraeus Mons, which are collectively known as the Tharsis Montes. The tallest volcano on the planet, Olympus Mons, is often associated with the Tharsis region but is actually located off the western edge of the plateau. The name Tharsis is the Greco-Latin transliteration of the biblical Tarshish, the land at the western extremity of the known world.

Ascraeus Mons is a large shield volcano located in the Tharsis region of the planet Mars. It is the northernmost and tallest of three shield volcanoes collectively known as the Tharsis Montes.
In planetary nomenclature, a fossa is a long, narrow depression (trough) on the surface of an extraterrestrial body, such as a planet or moon. The term, which means "ditch" or "trench" in Latin, is not a geological term as such but a descriptor term used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the International Astronomical Union (IAU) for topographic features whose geology or geomorphology is uncertain due to lack of data or knowledge of the exact processes that formed them. Fossae are believed to be the result of a number of geological processes, such as faulting or subsidence. Many fossae on Mars are probably graben.

Alba Mons is a volcano located in the northern Tharsis region of the planet Mars. It is the biggest volcano on Mars in terms of surface area, with volcanic flow fields that extend for at least 1,350 km (840 mi) from its summit. Although the volcano has a span comparable to that of the United States, it reaches an elevation of only 6.8 km (22,000 ft) at its highest point. This is about one-third the height of Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano on the planet. The flanks of Alba Mons have very gentle slopes. The average slope along the volcano's northern flank is 0.5°, which is over five times lower than the slopes on the other large Tharsis volcanoes. In broad profile, Alba Mons resembles a vast but barely raised welt on the planet's surface. It is a unique volcanic structure with no counterpart on Earth or elsewhere on Mars.

Amazonis Planitia is one of the smoothest plains on Mars. It is located between the Tharsis and Elysium volcanic provinces, to the west of Olympus Mons, in the Amazonis and Memnonia quadrangles, centered at 24.8°N 196.0°E. The plain's topography exhibits extremely smooth features at several different lengths of scale. A large part of the Medusae Fossae Formation lies in Amazonis Planitia.

Elysium, located in the Elysium and Cebrenia quadrangles, is the second largest volcanic region on Mars, after Tharsis. The region includes the volcanoes Hecates Tholus, Elysium Mons and Albor Tholus. The province is centered roughly on Elysium Mons at 24.7°N 150°E. Elysium Planitia is a broad plain to the south of Elysium, centered at 3.0°N 154.7°E. Another large volcano, Apollinaris Mons, lies south of Elysium Planitia and is not part of the province. Besides having large volcanoes, Elysium has several areas with long trenches, called fossa or fossae (plural) on Mars. They include the Cerberus Fossae, Elysium Fossae, Galaxias Fossae, Hephaestus Fossae, Hyblaeus Fossae, Stygis Fossae and Zephyrus Fossae.

The Cerberus Fossae are a series of semi-parallel fissures on Mars formed by faults which pulled the crust apart in the Cerberus region. They are 1235 km across and centered at 11.28 °N and 166.37 °E. Their northernmost latitude is 16.16 °N and their southernmost latitude 6.23 °N. Their easternmost and westernmost longitudes are 174.72 °E and 154.43 °E, respectively. They can be seen in the Elysium quadrangle.
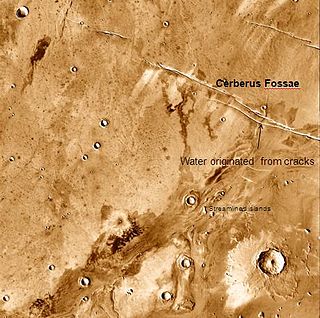
The Athabasca Valles are a late Amazonian-period outflow channel system in the central Elysium Planitia region of Mars, located to the south of the Elysium Rise. They are part of a network of outflow channels in this region that are understood to emanate from large fissures in the Martian surface rather than the chaos terrains that source the circum-Chryse outflow channels. The Athabasca Valles in particular emanate from one of the Cerberus Fossae fissures and flow downstream to the southwest, constrained to the south by a wrinkle ridge for over 100 km, before debouching into the Cerberus Palus volcanic plain. The Athabasca Valles are widely understood to be the youngest outflow channel system on the planet.
Volcanic activity, or volcanism, has played a significant role in the geologic evolution of Mars. Scientists have known since the Mariner 9 mission in 1972 that volcanic features cover large portions of the Martian surface. These features include extensive lava flows, vast lava plains, and the largest known volcanoes in the Solar System. Martian volcanic features range in age from Noachian to late Amazonian, indicating that the planet has been volcanically active throughout its history, and some speculate it probably still is so today. Both Earth and Mars are large, differentiated planets built from similar chondritic materials. Many of the same magmatic processes that occur on Earth also occurred on Mars, and both planets are similar enough compositionally that the same names can be applied to their igneous rocks and minerals.

The Medusae Fossae Formation is a large geological formation of probable volcanic origin on the planet Mars. It is named for the Medusa of Greek mythology. "Fossae" is Latin for "trenches". The formation is a collection of soft, easily eroded deposits that extends discontinuously for more than 5,000 km along the equator of Mars. Its roughly-shaped regions extend from just south of Olympus Mons to Apollinaris Patera, with a smaller additional region closer to Gale Crater.

Tharsis Tholus is an intermediate-sized shield volcano located in the eastern Tharsis region of the planet Mars. The volcano was discovered by the Mariner 9 spacecraft in 1972 and originally given the informal name Volcano 7. In 1973, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) officially designated it Tharsis Tholus. In planetary geology, tholus is the term for a small domical mountain, usually a volcano.

The Diacria quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northwestern portion of Mars' western hemisphere and covers 180° to 240° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Diacria quadrangle is also referred to as MC-2. The Diacria quadrangle covers parts of Arcadia Planitia and Amazonis Planitia.

The Elysium quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Elysium quadrangle is also referred to as MC-15.

The Amazonis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Amazonis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-8.

The Tharsis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Tharsis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-9 . The name Tharsis refers to a land mentioned in the Bible. It may be at the location of the old town of Tartessus at the mouth of Guadalquivir.

The Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle is also referred to as MC-17. Parts of Daedalia Planum, Sinai Planum, and Solis Planum are found in this quadrangle. Phoenicis Lacus is named after the phoenix which according to myth burns itself up every 500 years and then is reborn.
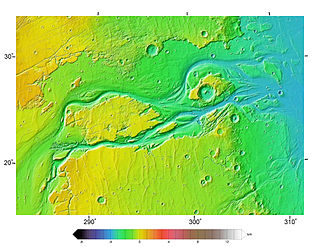
Outflow channels are extremely long, wide swathes of scoured ground on Mars. They extend many hundreds of kilometers in length and are typically greater than one kilometer in width. They are thought to have been carved by huge outburst floods.
Mars may contain ores that would be very useful to potential colonists. The abundance of volcanic features together with widespread cratering are strong evidence for a variety of ores. While nothing may be found on Mars that would justify the high cost of transport to Earth, the more ores that future colonists can obtain from Mars, the easier it would be to build colonies there.
The common surface features of Mars include dark slope streaks, dust devil tracks, sand dunes, Medusae Fossae Formation, fretted terrain, layers, gullies, glaciers, scalloped topography, chaos terrain, possible ancient rivers, pedestal craters, brain terrain, and ring mold craters.

Elysium Planitia, located in the Elysium and Aeolis quadrangles, is a broad plain that straddles the equator of Mars, centered at 3.0°N 154.7°E. It lies to the south of the volcanic province of Elysium, the second largest volcanic region on the planet, after Tharsis. Elysium contains the major volcanoes Elysium Mons, Albor Tholus and Hecates Tholus. Another more ancient shield volcano, Apollinaris Mons, is situated just to the south of eastern Elysium Planitia. Within the plains, Cerberus Fossae is the only Mars location with recent volcanic eruptions. Lava flows dated no older than 0.2 million years from the present have been found, and evidence has been found that volcanic activity may have occurred as recently as 53,000 years ago. Such activity could have provided the environment, in terms of energy and chemicals, needed to support life forms.

















