Data integrity is the maintenance of, and the assurance of, data accuracy and consistency over its entire life-cycle. It is a critical aspect to the design, implementation, and usage of any system that stores, processes, or retrieves data. The term is broad in scope and may have widely different meanings depending on the specific context even under the same general umbrella of computing. It is at times used as a proxy term for data quality, while data validation is a prerequisite for data integrity.
In software engineering, version control is a class of systems responsible for managing changes to computer programs, documents, large web sites, or other collections of information. Version control is a component of software configuration management.
Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1) is a standard interface description language (IDL) for defining data structures that can be serialized and deserialized in a cross-platform way. It is broadly used in telecommunications and computer networking, and especially in cryptography.
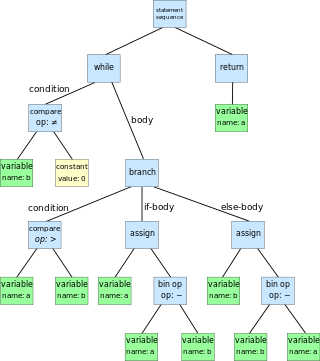
An abstract syntax tree (AST) is a data structure used in computer science to represent the structure of a program or code snippet. It is a tree representation of the abstract syntactic structure of text written in a formal language. Each node of the tree denotes a construct occurring in the text. It is sometimes called just a syntax tree.
In software development, Make is a build automation tool that builds executable programs and libraries from source code by reading files called makefiles which specify how to derive the target program. Though integrated development environments and language-specific compiler features can also be used to manage a build process, Make remains widely used, especially in Unix and Unix-like operating systems.
Code review is a software quality assurance activity in which one or more people check a program, mainly by viewing and reading parts of its source code, either after implementation or as an interruption of implementation. At least one of the persons must not have authored the code. The persons performing the checking, excluding the author, are called "reviewers".
Netfilter is a framework provided by the Linux kernel that allows various networking-related operations to be implemented in the form of customized handlers. Netfilter offers various functions and operations for packet filtering, network address translation, and port translation, which provide the functionality required for directing packets through a network and prohibiting packets from reaching sensitive locations within a network.
Automated code review software checks source code for compliance with a predefined set of rules or best practices. The use of analytical methods to inspect and review source code to detect bugs or security issues has been a standard development practice in both Open Source and commercial software domains. This process can be accomplished both manually and in an automated fashion. With automation, software tools provide assistance with the code review and inspection process. The review program or tool typically displays a list of warnings. A review program can also provide an automated or a programmer-assisted way to correct the issues found. This is a component for mastering easily software. This is contributing to the Software Intelligence practice. This process is usually called "linting" since one of the first tools for static code analysis was called Lint.
Attempto Controlled English (ACE) is a controlled natural language, i.e. a subset of standard English with a restricted syntax and restricted semantics described by a small set of construction and interpretation rules. It has been under development at the University of Zurich since 1995. In 2013, ACE version 6.7 was announced.
MISRA C is a set of software development guidelines for the C programming language developed by The MISRA Consortium. Its aims are to facilitate code safety, security, portability and reliability in the context of embedded systems, specifically those systems programmed in ISO C / C90 / C99.
Coding conventions are a set of guidelines for a specific programming language that recommend programming style, practices, and methods for each aspect of a program written in that language. These conventions usually cover file organization, indentation, comments, declarations, statements, white space, naming conventions, programming practices, programming principles, programming rules of thumb, architectural best practices, etc. These are guidelines for software structural quality. Software programmers are highly recommended to follow these guidelines to help improve the readability of their source code and make software maintenance easier. Coding conventions are only applicable to the human maintainers and peer reviewers of a software project. Conventions may be formalized in a documented set of rules that an entire team or company follows, or may be as informal as the habitual coding practices of an individual. Coding conventions are not enforced by compilers.
Azure DevOps Server, formerly known as Team Foundation Server (TFS) and Visual Studio Team System (VSTS), is a Microsoft product that provides version control, reporting, requirements management, project management, automated builds, testing and release management capabilities. It covers the entire application lifecycle and enables DevOps capabilities. Azure DevOps can be used as a back-end to numerous integrated development environments (IDEs) but is tailored for Microsoft Visual Studio and Eclipse on all platforms.
Protel stands for "Procedure Oriented Type Enforcing Language". It is a programming language created by Nortel Networks and used on telecommunications switching systems such as the DMS-100. Protel-2 is the object-oriented version of Protel.
Checkstyle is a static code analysis tool used in software development for checking if Java source code is compliant with specified coding rules.
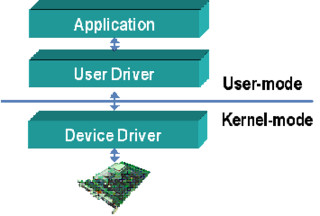
Device drivers are programs which allow software or higher-level computer programs to interact with a hardware device. These software components act as a link between the devices and the operating systems, communicating with each of these systems and executing commands. They provide an abstraction layer for the software above and also mediate the communication between the operating system kernel and the devices below.
Software construction is a software engineering discipline. It is the detailed creation of working meaningful software through a combination of coding, verification, unit testing, integration testing, and debugging. It is linked to all the other software engineering disciplines, most strongly to software design and software testing.
JArchitect is a static analysis tool for Java code. This tool supports a large number of code metrics, allows for visualization of dependencies using directed graphs and dependency matrix. The tools also performs code base snapshots comparison, and validation of architectural and quality rules. User-defined rules can be written using LINQ queries. This possibility is named CQLinq. The tool also comes with a large number of predefined CQLinq code rules.

SDC Verifier is a commercial finite element analysis post-processor software with a calculation core for checking structures according to different standards, either predefined or self programmed, and final report generation with all checks. The goal is to automate routine work and speed up a verification of the engineering projects. It works as an addon for popular FEA software Ansys, Femap and Simcenter 3D.
CppDepend is a static analysis tool for C/C++ code. This tool supports a large number of code metrics, allows for visualization of dependencies using directed graphs and dependency matrix. The tools also performs code base snapshots comparison, and validation of architectural and quality rules. User-defined rules can be written using LINQ queries. This possibility is named CQLinq. The tool also comes with a large number of predefined CQLinq code rules.


