Webcam software allows users to take pictures and video and save them to their computer.
Webcam software allows users to take pictures and video and save them to their computer.
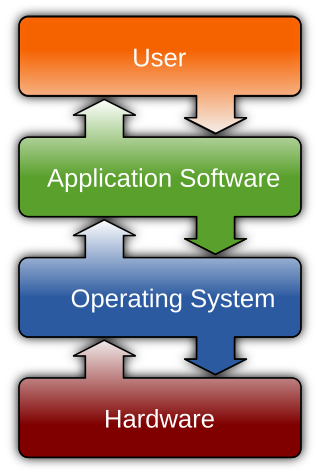
Software is a collection of programs and data that tell a computer how to perform specific tasks. Software often includes associated software documentation. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.

Free software, libre software, or libreware is computer software distributed under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, and distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program. Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices.

Oracle Corporation is an American multinational computer technology company headquartered in Austin, Texas, United States. In 2020, Oracle was the third-largest software company in the world by revenue and market capitalization. In 2023, the company’s seat in Forbes Global 2000 was 80. The company sells database software and cloud computing. Oracle's core application software is a suite of enterprise software products, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, human capital management (HCM) software, customer relationship management (CRM) software, enterprise performance management (EPM) software, Customer Experience Commerce and supply chain management (SCM) software.

A programmer, computer programmer or coder is an author of computer source code – someone with skill in computer programming.
Software engineering is an engineering approach to software development. A practitioner, a software engineer, applies the engineering design process to develop software.

Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations.

A wiki is a form of online hypertext publication that is collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience directly through a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base.

The software release life cycle is the process of developing, testing, and distributing a software product. It typically consists of several stages, such as pre-alpha, alpha, beta, and release candidate, before the final version, or "gold", is released to the public.
Software development is the process used to create software. Programming and maintaining the source code is the central step of this process, but it also includes conceiving the project, evaluating its feasibility, analyzing the business requirements, software design, testing, to release. Software engineering, in addition to development, also includes project management, employee management, and other overhead functions. Software development may be sequential, in which each step is complete before the next begins, but iterative development methods where multiple steps can be executed at once and earlier steps can be revisited have also been devised to improve flexibility, efficiency, and scheduling.

SAP SE is a German multinational software company based in Walldorf, Baden-Württemberg. It develops enterprise software to manage business operations and customer relations. The company is the world's leading enterprise resource planning (ERP) software vendor. Apart from ERP software, the company also sells database software and technology, cloud-engineered systems, and other ERP software products, such as human capital management (HCM) software, customer relationship management (CRM) software, enterprise performance management (EPM) software, product lifecycle management (PLM) software, supplier relationship management (SRM) software, supply chain management (SCM) software, business technology platform (BTP) software and programming environment SAP AppGyver for business.

Open-source software (OSS) is computer software that is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and distribute the software and its source code to anyone and for any purpose. Open-source software may be developed in a collaborative, public manner. Open-source software is a prominent example of open collaboration, meaning any capable user is able to participate online in development, making the number of possible contributors indefinite. The ability to examine the code facilitates public trust in the software.
An application program is a computer program designed to carry out a specific task other than one relating to the operation of the computer itself, typically to be used by end-users. Word processors, media players, and accounting software are examples. The collective noun "application software" refers to all applications collectively. The other principal classifications of software are system software, relating to the operation of the computer, and utility software ("utilities").

Ubuntu is a Linux distribution derived from Debian and composed mostly of free and open-source software. Ubuntu is officially released in multiple editions: Desktop, Server, and Core for Internet of things devices and robots. The operating system is developed by the British company Canonical, and a community of other developers, under a meritocratic governance model. As of April 2024, the most-recent long-term support release is 24.04.

Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software that is available under a license that grants the right to use, modify, and distribute the software, modified or not, to everyone free of charge. The public availability of the source code is, therefore, a necessary but not sufficient condition. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term for free software and open-source software. FOSS is in contrast to proprietary software, where the software is under restrictive copyright or licensing and the source code is hidden from the users.
Software as a service is a form of cloud computing in which the provider offers the use of application software to a client and manages all the physical and software resources used by the application. The distinguishing feature of SaaS compared to other software delivery models is that it separates "the possession and ownership of software from its use". SaaS began around the turn of the twenty-first century and became the main form of software application deployment by 2023.

Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses and recommends the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the use and importance of GNU software in many distributions, causing some controversy.

Free content, libre content, libre information, or free information is any kind of functional work, work of art, or other creative content that meets the definition of a free cultural work, meaning "works or expressions which can be freely studied, applied, copied and/or modified, by anyone, for any purpose." Free content encompasses all works in the public domain and also those copyrighted works whose licenses honor and uphold the definition of free cultural work.
Proprietary software is software that grants its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner a legal monopoly by modern copyright and intellectual property law to exclude the recipient from freely sharing the software or modifying it, and—in some cases, as is the case with some patent-encumbered and EULA-bound software—from making use of the software on their own, thereby restricting their freedoms.

The GNU General Public License is a series of widely used free software licenses, or copyleft, that guarantee end users the four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The license was the first copyleft for general use, and was originally written by Richard Stallman, the founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project. The license grants the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The licenses in the GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. It is more restrictive than the Lesser General Public License, and even further distinct from the more widely-used permissive software licenses BSD, MIT, and Apache.
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985, to support the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed under copyleft terms, such as with its own GNU General Public License. The FSF was incorporated in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, where it is also based.