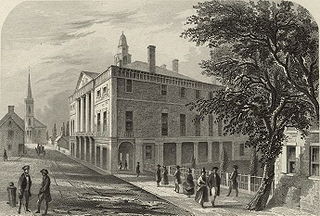Up is the y-axis relative vertical direction opposed to down.

Congresses are formal meetings of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter during battle, from the Latin congressus.
Union commonly refers to:
An electoral college is a set of electors who are selected to elect a candidate to particular offices. Often these represent different organizations, political parties or entities, with each organization, political party or entity represented by a particular number of electors or with votes weighted in a particular way.
In government, unicameralism is the practice of having a single legislative or parliamentary chamber. Thus, a unicameral parliament or unicameral legislature is a legislature which consists of a single chamber or house.
Deputy is one empowered to act for another. Depute is the historical form of "deputy" and is still used in the Scottish legal system.
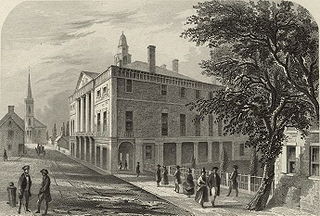
The 1st United States Congress, comprising the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives, met from March 4, 1789, to March 4, 1791, during the first two years of George Washington's presidency, first at Federal Hall in New York City and later at Congress Hall in Philadelphia. With the initial meeting of the First Congress, the United States federal government officially began operations under the new frame of government established by the 1787 Constitution. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the provisions of Article I, Section 2, Clause 3 of the Constitution. Both chambers had a Pro-Administration majority. Twelve articles of amendment to the Constitution were passed by this Congress and sent to the states for ratification; the ten ratified as additions to the Constitution on December 15, 1791, are collectively known as the Bill of Rights, with an additional amendment ratified more than two centuries later to become the Twenty-seventh Amendment to the United States Constitution.

The speaker of a deliberative assembly, especially a legislative body, is its presiding officer, or the chair. The title was first used in 1377 in England.
National Congress is a term used in the names of various political parties and legislatures.

The Ohio Republican Party is the Ohio affiliate of the Republican Party. It was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1854.
The Indian Union Muslim League or I. U. M. L. is an Indian political party primarily based in the Indian states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu. It is recognized by the Election Commission of India as a State Party in Kerala.

The Government of Kerala, formally and commonly referred to as Kerala Government is the state government of the Indian state of Kerala. The government is led by the chief minister, who selects all the other ministers. The chief minister and their most senior ministers belong to the supreme decision-making committee, known as the cabinet.

Kerala is an Indian state, where federal legislative power is vested in the unicameral Kerala Legislative Assembly. The multilateral system has, since 1956, been dominated by the several pre-poll and post-poll alliances.
Cop or Cops commonly refers to:
Socialist Party is the name of many different political parties around the world. The list of parties using the exact name "Socialist Party" is to be found in the Socialist Party article.
The Federal government of Mexico is the national government of the United Mexican States, the central government established by its constitution to share sovereignty over the republic with the governments of the 31 individual Mexican states, and to represent such governments before international bodies such as the United Nations. The Mexican federal government has three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial and functions per the Constitution of the United Mexican States, as enacted in 1917, and as amended. The executive power is exercised by the executive branch, which is headed by the president and his Cabinet, which, together, are independent of the legislature. Legislative power is vested upon the Congress of the Union, a bicameral legislature comprising the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Judicial power is exercised by the judiciary, consisting of the Supreme Court of Justice of the Nation, the Council of the Federal Judiciary, and the collegiate, unitary, and district courts.

The United States Senate elections of 1858 and 1859 were elections which had the Republican Party gain five additional seats in the United States Senate, but the Democrats retained their majority. That majority would erode in 1860 with the secession of the southern states leading up to the Civil War. In Illinois, incumbent Stephen A. Douglas (D) and challenger Abraham Lincoln (R) held a series of seven debates, known as the "Lincoln–Douglas debates."

Mundakkal Mathew Jacob, alias M. M. Jacob, was an Indian politician, working in Indian National Congress. He married Achamma Kunnuthara from Tiruvalla, Kerala and had four daughters. He was appointed Governor of Meghalaya in 1995 and again in 2000 for a second term. He also discharged the function of the Governor of Arunachal Pradesh as well for some time in 1996. He is longest serving governor of any Indian state. He served for more than 11 years.
United Front, known till 1971 as Mini Front (1970–1971) and as Maxi Front (1971–1979) thereafter, was a coalition of political parties in Kerala state, India, which was the ruling combine in the state from 1970 to 1979. The coalition was formed by five political parties immediately before the 1970 Kerala Legislative Assembly election. It saw the inclusion a few other parties in the following years.