
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus Gossypium in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds.

Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufactured sewing threads may be finished with wax or other lubricants to withstand the stresses involved in sewing. Embroidery threads are yarns specifically designed for needlework. Yarn can be made of a number of natural or synthetic materials, and comes in a variety of colors and thicknesses. Although yarn may be dyed different colours, most yarns are solid coloured with a uniform hue.

A diaper /ˈdaɪpə(r)/ or a nappy is a type of underwear that allows the wearer to urinate or defecate without using a toilet, by absorbing or containing waste products to prevent soiling of outer clothing or the external environment. When diapers become wet or soiled, they require changing, generally by a second person such as a parent or caregiver. Failure to change a diaper on a sufficiently regular basis can result in skin problems around the area covered by the diaper.
Samwise Gamgee is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth. A hobbit, Samwise is the chief supporting character of The Lord of the Rings, serving as the sidekick of the protagonist Frodo Baggins. Sam is a member of the Fellowship of the Ring, the group of nine charged with destroying the One Ring to prevent the Dark Lord Sauron from taking over the world.

A tampon is a menstrual product designed to absorb blood and vaginal secretions by insertion into the vagina during menstruation. Unlike a pad, it is placed internally, inside of the vaginal canal. Once inserted correctly, a tampon is held in place by the vagina and expands as it soaks up menstrual blood. However, in addition to menstrual blood, the tampon also absorbs the vagina's natural lubrication and bacteria, which can change the normal pH, increasing the risk of infections from the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, which can lead to toxic shock syndrome (TSS). TSS is a rare but life-threatening infection that requires immediate medical attention.

Lyocell is a semi-synthetic fiber used to make textiles for clothing and other purposes. It is a form of regenerated cellulose made by dissolving pulp and dry jet-wet spinning. Unlike rayon made by some of the more common viscose processes, Lyocell production does not use carbon disulfide, which is toxic to workers and the environment. Lyocell was originally trademarked as Tencel in 1982.

Ramie is a flowering plant in the nettle family Urticaceae, native to eastern Asia. It is a herbaceous perennial growing to 1.0–2.5 m tall; the leaves are heart-shaped, 7–15 cm (2.8–5.9 in) long and 6–12 cm (2.4–4.7 in) broad, and white on the underside with dense, small hairs—this gives it a silvery appearance; unlike stinging nettles, the hairs do not sting. The true ramie or China grass is also called Chinese plant or white ramie.

Dr Joseph Sampson Gamgee, MRCS, FRSE was a surgeon at the Queen's Hospital in Birmingham, England. He pioneered aseptic surgery, and, in 1880 invented Gamgee Tissue, an absorbent cotton wool and gauze surgical dressing.
Gamgee Tissue is a surgical dressing invented by Dr. Joseph Sampson Gamgee in Birmingham, England, in 1880.

A bathrobe, also known as a housecoat or a dressing gown, is a loose-fitting outer garment worn by people, often after washing the body or around a pool. A bathrobe is considered to be very informal clothing, and is not worn with everyday clothes.

Cotton pads are pads made of cotton which are used for medical or cosmetic purposes. For medical purposes, cotton pads are used to stop or prevent bleeding from minor punctures such as injections or venipuncture. They may be secured in place with tape. Cotton pads are also used in the application and the removal of makeup. Cotton pads are soft enough that they can be used to clean babies. Cotton balls have much of the same applications as cotton pads, and can be used interchangeably.

Textile Manufacturing or Textile Engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods such as clothing, household items, upholstery and various industrial products.

Natural fibers or natural fibres are fibers that are produced by geological processes, or from the bodies of plants or animals. They can be used as a component of composite materials, where the orientation of fibers impacts the properties. Natural fibers can also be matted into sheets to make paper or felt.
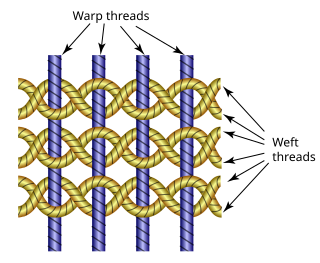
Gauze is a thin, translucent fabric with a loose open weave. In technical terms "gauze" is a weave structure in which the weft yarns are arranged in pairs and are crossed before and after each warp yarn keeping the weft firmly in place. This weave structure is used to add stability to fabric, which is important when using fine yarns loosely spaced. However, this weave structure can be used with any weight of yarn, and can be seen in some rustic textiles made from coarse hand-spun plant fiber yarns. Gauze is widely used for medical dressings.

A cloth diaper or a cloth nappy or real nappy or a reusable nappy is a reusable diaper made from natural fibers, man-made materials, or a combination of both. They are often made from industrial cotton which may be bleached white or left the fiber’s natural color. Other natural fiber cloth materials include wool, bamboo, and unbleached hemp. Man-made materials such as an internal absorbent layer of microfiber toweling or an external waterproof layer of polyurethane laminate (PUL) may be used. Polyester fabrics microfleece or suedecloth are often used inside cloth diapers as a "stay-dry" wicking liner because of the non-absorbent properties of those synthetic fibers.
The manufacture of textiles is one of the oldest of human technologies. To make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fiber from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving, which turns yarn into cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. For decoration, the process of colouring yarn or the finished material is dyeing. For more information of the various steps, see textile manufacturing.
The United Nations General Assembly declared 2009 as the International Year of Natural Fibres (IYNF), as well as the International Year of Astronomy.

Eri silk is the product of the domesticated silkworm Samia ricini, found mainly in North East India and some part of China and Japan. It was imported to Thailand in 1974. The name "eri" is derived from the Assamese word "era", which means "castor", as the silkworm feeds on castor plants. Another type of eri silk is "Ailanthus silk moth", refers to the host plant, Borkesseu, Ailanthus excelsa, practiced in China. Eri silk is also known as endi or errandi in India. The woolly white silk is often referred to as the fabric of peace when it is processed without killing the silkworm. This process results in a silk called Ahimsa silk. Moths leave the cocoon and then the cocoons are harvested to be spun. The eri silkworm is the only completely domesticated silkworm other than Bombyx mori.

Charles Walker Cathcart, CBE, MB CM, FRCSEd, FRCSE was a Scottish surgeon who worked for most of his career at the Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh (RIE). As a young man he had represented Scotland at rugby on three occasions. During the First World War he jointly published an account of the value of sphagnum moss as a wound dressing which led to its widespread use by the British Army for that purpose.

Robinson and Sons Ltd was founded in 1839 by John Bradbury Robinson in Chesterfield, Derbyshire. The company started making pill boxes and grew to become a major packaging and healthcare business.
















