
The TurboGrafx-16, known as the PC Engine outside North America, is a home video game console designed by Hudson Soft and sold by NEC Home Electronics. It was the first console marketed in the fourth generation, commonly known as the 16-bit era, though the console has an 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) coupled with a 16-bit graphics processor. It was released in Japan in 1987 and in North America in 1989. In Europe, the console is known as the PC Engine, after the Japanese model was imported and distributed in the United Kingdom and France from 1988. In Japan, the system was launched as a competitor to the Famicom, but the delayed United States release meant that it ended up competing with the Sega Genesis and later the Super NES.

Mystara is a campaign setting for the Dungeons & Dragons fantasy role playing game. It was the default setting for the "Basic" version of the game throughout the 1980s and 1990s. Most adventures published for the "Basic" edition of D&D take place in "The Known World", a central continent that includes a varied patchwork of both human and non-human realms. The human realms are based on various real-world historical cultures. In addition, unlike other D&D settings, Mystara had ascended immortal beings instead of gods.

Icewind Dale is a role-playing video game developed by Black Isle Studios and originally published by Interplay Entertainment for Windows in 2000 and by MacPlay for the Macintosh in 2002. The game takes place in the Dungeons & Dragons Forgotten Realms campaign setting and the region of Icewind Dale, and uses the 2nd edition ruleset. The story follows a different set of events than those of R. A. Salvatore's The Icewind Dale Trilogy novels: in the game, an adventuring party becomes enlisted as a caravan guard while in Icewind Dale, in the wake of strange events, and eventually discover a plot that threatens the Ten Towns of Icewind Dale and beyond.

Chill is an investigative and modern horror role-playing game originally published by Pacesetter Ltd in 1984 that captures the feel of 20th-century horror films.
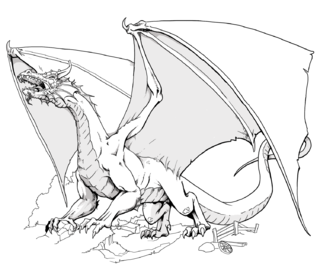
In the Dungeons & Dragons (D&D) fantasy role-playing game, dragons are an iconic type of monstrous creature. As a group, D&D dragons are loosely based on dragons from a wide range of fictional and mythological sources. Dungeons & Dragons allows players to fight the fictional dragons in the game and "slay their psychic dragons" as well. These dragons, specifically their "dungeon ecology", have implications for the literary theory of fantasy writing. D&D dragons also featured as targets of the moral panic surrounding the game.

Ravenloft is an adventure module for the Dungeons & Dragons (D&D) fantasy role-playing game. The American game publishing company TSR, Inc. released it as a standalone adventure booklet in 1983 for use with the first edition Advanced Dungeons & Dragons game. It was written by Tracy and Laura Hickman, and includes art by Clyde Caldwell with maps by David Sutherland III. The plot of Ravenloft focuses on the villain Strahd von Zarovich, a vampire who pines for his lost love. Various story elements, including Strahd's motivation and the locations of magical weapons, are randomly determined by drawing cards. The player characters attempt to defeat Strahd and, if successful, the adventure ends.
In the Dungeons & Dragons (D&D) fantasy role-playing game, alignment is a categorization of the ethical and moral perspective of player characters, non-player characters, and creatures.

Count Strahd von Zarovich is a fictional character originally appearing as the feature villain in the highly popular Advanced Dungeons and Dragons adventure module I6: Ravenloft. Later, this character and his world would be explored in follow-up modules, novels, and the Ravenloft campaign setting. Within this setting, Strahd is the first and best-known of Ravenloft's darklords. He is a powerful ancient vampire. He is also a master necromancer, a skilled warrior, and the unquestioned ruler of the domain of Barovia.

The TurboDuo is a fourth-generation video game console developed by NEC Home Electronics and Hudson Soft for the North American market. The TurboDuo was test-marketed in Los Angeles in October 1992, before a nationwide rollout in May 1993. It is the North American version of the Japanese PC Engine Duo game console which was released in September 1991.

Libris Mortis: The Book of Undead is a book which is an official supplement for the 3.5 edition of the Dungeons and Dragons role-playing game. The book covers the fictional undead within the D&D universe and comprises seven chapters, introducing new content for Dungeon Masters and players, as well as providing general information about undead.

The Temple of Elemental Evil is a 2003 role-playing video game by Troika Games. It is a remake of the classic Dungeons & Dragons adventure The Temple of Elemental Evil using the 3.5 edition rules. This is the only computer role-playing game to take place in the Greyhawk campaign setting, and the first video game to implement the 3.5 edition rule set. The game was published by Atari, who then held the interactive rights of the Dungeons & Dragons franchise.

Dungeon Explorer is an action role-playing video game developed by Atlus for the TurboGrafx-16 and originally published by Hudson Soft in Japan on March 4, 1989, and later in North America by NEC on November 15 of the same year. The first installment in the eponymous franchise, the game is set in the land of Oddesia, which has been overrun by an alien race and where players assume the role of one of eight main characters tasked with recovering the Ora stone to kill the alien king Natas. Co-directed by Kazutoshi Ueda and Yōsuke Niino, the title was created by most of the same team that would work on later several projects such as entries in the Megami Tensei series. Though it was initially launched for the TurboGrafx-16, it was later re-released through download services for various consoles.
The paladin is one of the standard playable character classes in most editions of the Dungeons & Dragons fantasy role-playing game. The paladin is a holy knight, crusading in the name of good and order, and is a divine spellcaster.
The cleric is one of the standard playable character class in the Dungeons & Dragons fantasy role-playing game. Clerics are versatile figures, both capable in combat and skilled in the use of divine magic (thaumaturgy). Clerics are powerful healers due to the large number of healing and curative magics available to them. With divinely-granted abilities over life or death, they are also able to repel or control undead creatures. Clerics also have specific 'domains' which usually align with the character's alignment and the god that cleric serves. Whether the cleric repels or controls undead is dependent on the cleric's alignment. It is the only class to be included in every edition of Dungeons & Dragons without a name change.

Dungeons and Dragons: Heroes is a hack and slash video game with RPG elements. It was published by Atari Interactive and developed by the subsidiary's Hunt Valley development studio, exclusively for Xbox in 2003. It is set in the Dungeons & Dragons universe and is playable solo or with up to four players. Players take on the role of four reincarnated heroes brought back to life to fight their former nemesis, a wizard named Kaedin.

In the Dungeons & Dragons fantasy role-playing game, a vampire is an undead creature. A humanoid or monstrous humanoid creature can become a vampire, and looks as it did in life, with pale skin, haunting red eyes, and a feral cast to its features. A new vampire is created when another vampire drains the life out of a living creature. Its depiction is related to those in the 1930s and 1940s Hollywood Dracula and monster movies. In writing vampires into the game, as with other creatures arising in folklore, the authors had to consider what elements arising in more recent popular culture should be incorporated into their description and characteristics.

Neutopia II is a 1991 action-adventure/action role-playing video game developed and published in Japan by Hudson Soft and in North America by Turbo Technologies for the TurboGrafx-16. It is the sequel to Neutopia, which was released earlier in 1989. In the game, the player takes control of Jazeta's son, who embarks on a quest to both save his father and defeat the returning evil demon Dirth.

Lords of Darkness is the name of two accessories for the fictional Forgotten Realms campaign setting for the Dungeons & Dragons fantasy role-playing game.
The Wand of Orcus is a fictional magical weapon described in various Dungeons & Dragons media. Because of the popularity of Orcus as a villain within the Dungeons & Dragons universe, many different authors have written materials describing artifacts created by or associated with the character. The Wand of Orcus is consistently the most important and most described of these artifacts. Screen Rant has noted that "[t]he weapon that Orcus wields in battle is almost as famous as the demon lord himself". Furthermore, the device has at times been employed in books, games, and other media within the franchise as a thing distinct from Orcus himself, such that adventurers may encounter the wand as a freestanding element of the game or story.

Dungeon Explorer II is an action role-playing video game developed and originally published by Hudson Soft for the TurboDuo in Japan on March 26, 1993, and in North America by Turbo Technologies in October of the same year. A sequel to 1989's Dungeon Explorer, it is the second installment in the eponymous franchise.















