
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in southern Central Europe. Slovenia is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short coastline within the Adriatic Sea to the southwest. Slovenia is mostly mountainous and forested, covers 20,271 square kilometres (7,827 sq mi), and has a population of approximately 2.1 million. Slovene, a South Slavic language, is the official language. Slovenia has a predominantly temperate continental climate, with the exception of the Slovene Littoral and the Julian Alps. A sub-mediterranean climate reaches to the northern extensions of the Dinaric Alps that traverse the country in a northwest–southeast direction. The Julian Alps in the northwest have an alpine climate. Toward the northeastern Pannonian Basin, a continental climate is more pronounced. Ljubljana, the capital and largest city of Slovenia, is geographically situated near the centre of the country.
The history of Slovenia chronicles the period of the Slovenian territory from the 5th century BC to the present. In the Early Bronze Age, Proto-Illyrian tribes settled an area stretching from present-day Albania to the city of Trieste. The Slovenian territory was part of the Roman Empire, and it was devastated by the Migration Period's incursions during late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. The main route from the Pannonian plain to Italy ran through present-day Slovenia. Alpine Slavs, ancestors of modern-day Slovenians, settled the area in the late 6th Century AD. The Holy Roman Empire controlled the land for nearly 1,000 years, and between the mid-14th century and 1918 most of Slovenia was under Habsburg rule. In 1918, most Slovene territory became part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, and in 1929 the Drava Banovina was created within the Kingdom of Yugoslavia with its capital in Ljubljana, corresponding to Slovenian-majority territories within the state. The Socialist Republic of Slovenia was created in 1945 as part of federal Yugoslavia. Slovenia gained its independence from Yugoslavia in June 1991, and today it is a member of the European Union and NATO.

Janez Drnovšek was a Slovenian liberal politician, President of the Presidency of Yugoslavia (1989–1990), Prime Minister of Slovenia and President of Slovenia (2002–2007).

Dimitrij Rupel is a Slovenian politician.

Ivan Janša, baptized and best known as Janez Janša, is a Slovenian politician who served three times as a prime minister of Slovenia, a position he had held from 2004 to 2008, from 2012 to 2013, and from 2020 to 2022. Since 1993, Janša has led the Slovenian Democratic Party, which has emerged as the pre-eminent Slovenian conservative party. Janša lost his fourth bid for prime minister in April 2022, his party defeated by the Freedom Movement party.

Alojz "Lojze" Peterle is a Slovenian politician. He is a member of New Slovenia, part of the European People's Party. He served as Prime Minister of Slovenia from 1990 to 1992, Leader of the Christian Democrats from the founding of the party in 1990 until it merged with the Slovenian People's Party in 2000, and was Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1993 to 1994 and again in 2000. He was a Member of the National Assembly from 1996 to 2004, and a Member of the European Parliament from 2004 to 2019.
The Slovenian Intelligence and Security Agency is the main civilian intelligence service of Slovenia and as a government agency is subordinated directly to the Prime Minister of Slovenia. The mission of SOVA as the central intelligence and security service in the Republic of Slovenia is to provide national security. The agency's headquarters are located at Stegne Street in Dravlje, northwest of Ljubljana's centre.
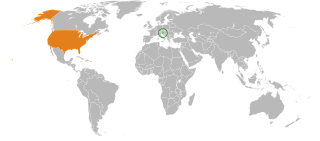
The United States has maintained an official presence in Slovenia since the early 1970s, when the United States Information Agency (USIS) opened a library and American press and cultural center in Ljubljana. From its opening through 1992, the American Center worked to develop closer grassroots relations between the United States and the people of the then-Socialist Republic of Slovenia, a constituent republic of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. On December 23, 1990, the Slovene people voted in a plebiscite to separate from greater Yugoslavia. On June 25, 1991, the new Republic of Slovenia officially declared its independence from the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. A 10-day war commenced, during which Slovenian territorial troops fought off incursions by the Yugoslav People's Army. The United States formally recognized the new republic on April 7, 1992. To develop U.S. diplomatic relations with the new state, the United States opened a new Embassy in Ljubljana in August 1992. From the departure of Yousif Ghafari in January 2009 till November 2010, the U.S. Ambassador position was vacant. From November 2010 to 2015 it was held by Joseph A. Mussomeli. The Ambassador position is currently held by Jamie Harpootlian.

Russia–Slovenia relations are foreign relations between Russia and Slovenia. Both countries established diplomatic relations on May 25, 1992. Russia has an embassy in Ljubljana. Slovenia has an embassy in Moscow and two honorary consulates. Until 2022, Russia had five honorary consuls in Slovenia, but Slovenia withdrew its consent to the appointments due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine.

Matjaž Šinkovec is a Slovenian diplomat, politician, translator, journalist and science fiction writer. He was one of the co-founders of the Slovenian Democratic Party.

Samuel Žbogar is a Slovenian diplomat and politician who is the EU Special Representative in North Macedonia. He served as Minister of Foreign Affairs of Slovenia from 2008 to 2012. He is currently acting Minister for Development Cooperation.

Bulgaria–Uzbekistan relations are foreign relations between Bulgaria and Uzbekistan. Both countries established diplomatic relations on September 12, 1992. Bulgaria has an embassy in Tashkent. Uzbekistan is represented in Bulgaria through a non resident ambassador based in Tashkent Both countries are full members of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe.

Moldova–Slovenia relations are the bilateral relations between Moldova and Slovenia. Moldova recognized the Republic of Slovenia under an unknown date. Diplomatic relations were established on October 27, 1993. Both countries are represented in each other through their embassies in Budapest (Hungary). Slovenia is a member of the European Union, which Moldova applied for in 2022. Both countries are full members of Council of Europe.
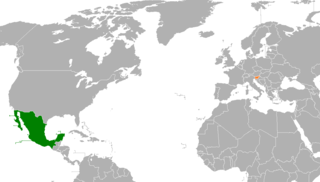
The nations of Mexico and Slovenia established diplomatic relations in 1992. Both nations are members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and the United Nations.
The Government of the Republic of Slovenia exercises executive authority in Slovenia pursuant to the Constitution and the laws of Slovenia. It is also the highest administrative authority in Slovenia.

Egypt–Greece relations refer to bilateral relations between Egypt and Greece. Due to the strong cultural and historical ties between the two nations, Egypt and Greece today enjoy friendly relations. Modern diplomatic relations between the two countries were established after Greece gained its independence in 1830, and are today regarded as cordial. Both countries are members and partners in several international organizations such as the UN, IMF, OSCE, and the Union for the Mediterranean.

Albania and Egypt have cordial and cooperative relations. Albania has an embassy in Cairo, and Egypt has an embassy in Tirana. Diplomatic relations between Albania and Egypt were established in 1958. Both countries are members of Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.

India–Slovenia relations are the bilateral relations between India and Slovenia.

Slovenia–Spain relations are the bilateral relations between Slovenia and Spain. Slovenia has an embassy in Madrid and three consulates in Barcelona, San Sebastián and Seville. Spain has an embassy in Ljubljana. The Spanish representation in Slovenia is exercised through the Embassy, which has the support of two Aggregators: Defense and Interior; two departments: Tourism and Economy and Commerce, all of them with residence in surrounding countries, although the Economic and Commercial Office has an Antenna in Ljubljana. There is a Cervantes Classroom under the Instituto Cervantes of Vienna. The relations of these two countries are mainly defined by their membership in both the European Union and the NATO.

Georgia–Slovenia relations are the bilateral relations between Georgia and Slovenia, two European nations with a communist past that established their bilateral ties in 1993. Their relations have been highly represented with a close diplomatic partnership, with Slovenia being one of the staunch supporters of Georgia's territorial integrity and pro-Western path. Both nations are members of the Council of Europe.




















