Related Research Articles
Windows Server 2003, codenamed "Whistler Server", is the second version of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft. It is part of the Windows NT family of operating systems and was released to manufacturing on March 28, 2003 and generally available on April 24, 2003. Windows Server 2003 is the successor to the Server editions of Windows 2000 and the predecessor to Windows Server 2008. An updated version, Windows Server 2003 R2, was released to manufacturing on December 6, 2005. Windows Server 2003 is based on the consumer operating system, Windows XP.
In computing, the superuser is a special user account used for system administration. Depending on the operating system (OS), the actual name of this account might be root, administrator, admin or supervisor. In some cases, the actual name of the account is not the determining factor; on Unix-like systems, for example, the user with a user identifier (UID) of zero is the superuser, regardless of the name of that account; and in systems which implement a role based security model, any user with the role of superuser can carry out all actions of the superuser account. The principle of least privilege recommends that most users and applications run under an ordinary account to perform their work, as a superuser account is capable of making unrestricted, potentially adverse, system-wide changes.
NTLDR is the boot loader for all releases of Windows NT operating system from 1993 with the release of Windows NT 3.1 up until Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. From Windows Vista onwards it was replaced by the BOOTMGR bootloader. NTLDR is typically run from the primary storage device, but it can also run from portable storage devices such as a CD-ROM, USB flash drive, or floppy disk. NTLDR can also load a non NT-based operating system given the appropriate boot sector in a file.
Fast user switching is a feature of a multi-user operating system which allows users to switch between user accounts without quitting applications and logging out.
The Encrypting File System (EFS) on Microsoft Windows is a feature introduced in version 3.0 of NTFS that provides filesystem-level encryption. The technology enables files to be transparently encrypted to protect confidential data from attackers with physical access to the computer.
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft Corporation which provides a user with a graphical interface to connect to another computer over a network connection. The user employs RDP client software for this purpose, while the other computer must run RDP server software.

Windows Console is the infrastructure for console applications in Microsoft Windows. An instance of a Windows Console has a screen buffer and an input buffer. It allows console apps to run inside a window or in hardware text mode. The user can switch between the two using the Alt+↵ Enter key combination. The text mode is unavailable in Windows Vista and later. Starting with Windows 10, however, a native full-screen mode is available.
Command Prompt, also known as cmd.exe or cmd, is the default command-line interpreter for the OS/2, eComStation, ArcaOS, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS operating systems. On Windows CE .NET 4.2, Windows CE 5.0 and Windows Embedded CE 6.0 it is referred to as the Command Processor Shell. Its implementations differ between operating systems, but the behavior and basic set of commands are consistent. cmd.exe is the counterpart of COMMAND.COM in DOS and Windows 9x systems, and analogous to the Unix shells used on Unix-like systems. The initial version of cmd.exe for Windows NT was developed by Therese Stowell. Windows CE 2.11 was the first embedded Windows release to support a console and a Windows CE version of cmd.exe. The ReactOS implementation of cmd.exe is derived from FreeCOM, the FreeDOS command line interpreter.
AutoRun and the companion feature AutoPlay are components of the Microsoft Windows operating system that dictate what actions the system takes when a drive is mounted.
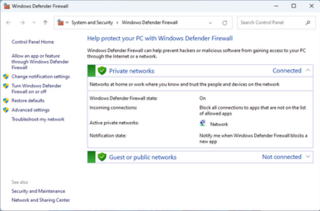
Windows Firewall is a firewall component of Microsoft Windows. It was first included in Windows XP SP2 and Windows Server 2003 SP1. Before the release of Windows XP Service Pack 2, it was known as the "Internet Connection Firewall."
As the next version of Windows NT after Windows 2000, as well as the successor to Windows Me, Windows XP introduced many new features but it also removed some others.
The booting process of Windows NT is the process run to start Windows NT. The process has been changed between releases, with the biggest changes being made with Windows Vista. In versions before Vista, the booting process begins when the BIOS loads the Windows NT bootloader, NTLDR. Starting with Vista, the booting process begins with either the BIOS or UEFI load the Windows Boot Manager, which replaces NTLDR as the bootloader. Next, the bootloader starts the kernel, which starts the session manager, which begins the login process. Once the user is logged in, File Explorer, the graphical user interface used by Windows NT, is started.
In computing, bootcfg is a command on Microsoft Windows NT-based operating systems which acts as a wrapper for editing the boot.ini file.

User Account Control (UAC) is a mandatory access control enforcement feature introduced with Microsoft's Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 operating systems, with a more relaxed version also present in Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows 10, and Windows 11. It aims to improve the security of Microsoft Windows by limiting application software to standard user privileges until an administrator authorises an increase or elevation. In this way, only applications trusted by the user may receive administrative privileges and malware are kept from compromising the operating system. In other words, a user account may have administrator privileges assigned to it, but applications that the user runs do not inherit those privileges unless they are approved beforehand or the user explicitly authorises it.
Windows Vista introduced a number of new I/O functions to the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems. They are intended to shorten the time taken to boot the system, improve the responsiveness of the system, and improve the reliability of data storage.
The NTFS file system defines various ways to redirect files and folders, e.g., to make a file point to another file or its contents without making a copy of it. The object being pointed to is called the target. Such file is called a hard or symbolic link depending on a way it's stored on the filesystem.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of both the Windows Setup and the Windows startup processes, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools such as random access memory diagnostic program, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, a completely new Task Scheduler, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista. Subsystem for UNIX Applications, which provides a POSIX-compatible environment is also introduced.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS), known as Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008 and earlier, is one of the components of Microsoft Windows that allow a user to initiate and control an interactive session on a remote computer or virtual machine over a network connection. RDS was first released in 1998 as Terminal Server in Windows NT 4.0 Terminal Server Edition, a stand-alone edition of Windows NT 4.0 Server that allowed users to log in remotely. Starting with Windows 2000, it was integrated under the name of Terminal Services as an optional component in the server editions of the Windows NT family of operating systems, receiving updates and improvements with each version of Windows. Terminal Services were then renamed to Remote Desktop Services with Windows Server 2008 R2 in 2009.
Control-Alt-Delete is a computer keyboard command on IBM PC compatible computers, invoked by pressing the Delete key while holding the Control and Alt keys: Ctrl+Alt+Delete. The function of the key combination differs depending on the context but it generally interrupts or facilitates interrupting a function. For instance, in pre-boot environment or in MS-DOS, Windows 3.0 and earlier versions of Windows or OS/2, the key combination reboots the computer. Starting with Windows 95, the key combination invokes a task manager or security related component that facilitates ending a Windows session or killing a frozen application.
References
- IBM Redbooks Technote Enabling Serial Over LAN for a Remote Windows Text Console using OSA SMBridge
- Egan Ford: xCAT Windows NT/2000/XP HOWTO March 2005