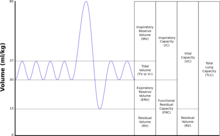
Spirometry is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is helpful in assessing breathing patterns that identify conditions such as asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and COPD. It is also helpful as part of a system of health surveillance, in which breathing patterns are measured over time.
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the alveoli of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process is disrupted, and the tissue around the air sacs becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The disease presents itself with the following symptoms: shortness of breath, nonproductive coughing, fatigue, and weight loss, which tend to develop slowly, over several months. The average rate of survival for someone with this disease is between three and five years. The term ILD is used to distinguish these diseases from obstructive airways diseases.

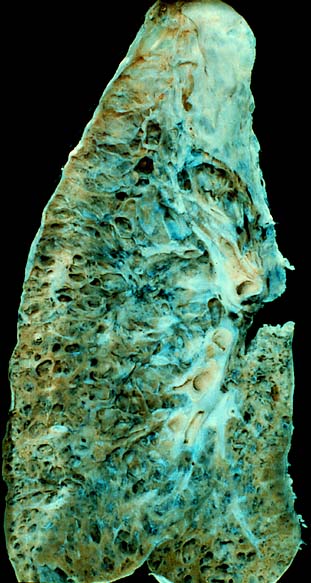
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory failure, pneumothorax, and lung cancer.
Airway obstruction is a blockage of respiration in the airway that hinders the free flow of air. It can be broadly classified into being either in the upper airway (UPA) or lower airway (LOA).

Bronchiolitis obliterans (BO), also known as obliterative bronchiolitis, constrictive bronchiolitis and popcorn lung, is a disease that results in obstruction of the smallest airways of the lungs (bronchioles) due to inflammation. Symptoms include a dry cough, shortness of breath, wheezing and feeling tired. These symptoms generally get worse over weeks to months. It is not related to cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, previously known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia.
DLCO or TLCO is the extent to which oxygen passes from the air sacs of the lungs into the blood. Commonly, it refers to the test used to determine this parameter. It was introduced in 1909.
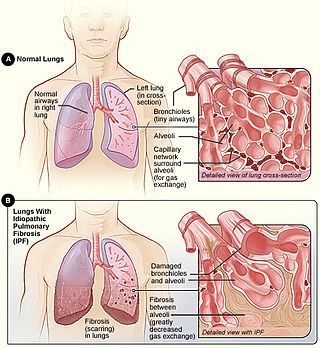
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), or (formerly) fibrosing alveolitis, is a rare, progressive illness of the respiratory system, characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissue, associated with the formation of scar tissue. It is a type of chronic scarring lung disease characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in lung function. The tissue in the lungs becomes thick and stiff, which affects the tissue that surrounds the air sacs in the lungs. Symptoms typically include gradual onset of shortness of breath and a dry cough. Other changes may include feeling tired, and abnormally large and dome shaped finger and toenails. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, pneumonia or pulmonary embolism.
A bronchial challenge test is a medical test used to assist in the diagnosis of asthma. The patient breathes in nebulized methacholine or histamine. Thus the test may also be called a methacholine challenge test or histamine challenge test respectively. Both drugs provoke bronchoconstriction, or narrowing of the airways. Whereas histamine causes nasal and bronchial mucus secretion and bronchoconstriction via the H1 receptor, methacholine utilizes the M3 receptor for bronchoconstriction. The degree of narrowing can then be quantified by spirometry. People with pre-existing airway hyperreactivity, such as asthmatics, will react to lower doses of drug.

Obstructive lung disease is a category of respiratory disease characterized by airway obstruction. Many obstructive diseases of the lung result from narrowing (obstruction) of the smaller bronchi and larger bronchioles, often because of excessive contraction of the smooth muscle itself. It is generally characterized by inflamed and easily collapsible airways, obstruction to airflow, problems exhaling, and frequent medical clinic visits and hospitalizations. Types of obstructive lung disease include; asthma, bronchiectasis, bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Although COPD shares similar characteristics with all other obstructive lung diseases, such as the signs of coughing and wheezing, they are distinct conditions in terms of disease onset, frequency of symptoms, and reversibility of airway obstruction. Cystic fibrosis is also sometimes included in obstructive pulmonary disease.
Restrictive lung diseases are a category of extrapulmonary, pleural, or parenchymal respiratory diseases that restrict lung expansion, resulting in a decreased lung volume, an increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or oxygenation. Pulmonary function test demonstrates a decrease in the forced vital capacity.

Pulmonary function testing (PFT) is a complete evaluation of the respiratory system including patient history, physical examinations, and tests of pulmonary function. The primary purpose of pulmonary function testing is to identify the severity of pulmonary impairment. Pulmonary function testing has diagnostic and therapeutic roles and helps clinicians answer some general questions about patients with lung disease. PFTs are normally performed by a pulmonary function technician, respiratory therapist, respiratory physiologist, physiotherapist, pulmonologist, or general practitioner.
Pulmonary rehabilitation, also known as respiratory rehabilitation, is an important part of the management and health maintenance of people with chronic respiratory disease who remain symptomatic or continue to have decreased function despite standard medical treatment. It is a broad therapeutic concept. It is defined by the American Thoracic Society and the European Respiratory Society as an evidence-based, multidisciplinary, and comprehensive intervention for patients with chronic respiratory diseases who are symptomatic and often have decreased daily life activities. In general, pulmonary rehabilitation refers to a series of services that are administered to patients of respiratory disease and their families, typically to attempt to improve the quality of life for the patient. Pulmonary rehabilitation may be carried out in a variety of settings, depending on the patient's needs, and may or may not include pharmacologic intervention.

An acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis (AECB), is a sudden worsening of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) symptoms including shortness of breath, quantity and color of phlegm that typically lasts for several days.
The BODE index, for Body-mass index, airflow Obstruction, Dyspnea, and Exercise, is a multidimensional scoring system and capacity index used to test patients who have been diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and to predict long-term outcomes for them. The index uses the four factors to predict risk of death from the disease.

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms of COPD include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce mucus. COPD progressively worsens, with everyday activities such as walking or dressing becoming difficult. While COPD is incurable, it is preventable and treatable. The two most common types of COPD are emphysema and chronic bronchitis and have been the two classic COPD phenotypes. Emphysema is defined as enlarged airspaces (alveoli) whose walls have broken down resulting in permanent damage to the lung tissue. Chronic bronchitis is defined as a productive cough that is present for at least three months each year for two years. Both of these conditions can exist without airflow limitation when they are not classed as COPD. Emphysema is just one of the structural abnormalities that can limit airflow and can exist without airflow limitation in a significant number of people. Chronic bronchitis does not always result in airflow limitation but in young adults who smoke the risk of developing COPD is high. Many definitions of COPD in the past included emphysema and chronic bronchitis, but these have never been included in GOLD report definitions. Emphysema and chronic bronchitis remain the predominant phenotypes of COPD but there is often overlap between them and a number of other phenotypes have also been described. COPD and asthma may coexist and converge in some individuals. COPD is associated with low-grade systemic inflammation.
The post bronchodilator test, also commonly referred to as a reversibility test, is a test that utilizes spirometry to assess possible reversibility of bronchoconstriction in diseases such as asthma.
Physiotherapists treating patients following uncomplicated coronary artery bypass surgery surgery continue to use interventions such as deep breathing exercises that are not supported by best available evidence. Standardised guidelines may be required to better match clinical practice with current literature.
Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia (DIPNECH) is a diffuse parenchymal lung disease which often presents with symptoms of cough and shortness of breath. The pathological definition published by the World Health Organization is “a generalized proliferation of scattered single cells, small nodules, or linear proliferations of pulmonary neuroendocrine (PNE) cells that may be confined to the bronchial and bronchiolar epithelium.” The true prevalence of this disease is not known. To date, just under 200 cases have been reported in the literature. However, with an increase in recognition of this disease by radiologists and pulmonologists, the number of cases has been increasing. DIPNECH predominantly affects middle-aged women with slowly progressive lung obstruction. DIPNECH is usually discovered in one of two ways: 1) as an unexpected finding following a lung surgery; or 2) by evaluation of a patient in a pulmonary clinic with longstanding, unexplained symptoms.

Emphysema is any air-filled enlargement in the body's tissues. Most commonly emphysema refers to the enlargement of air spaces (alveoli) in the lungs, and is also known as pulmonary emphysema.
Asthma-Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Overlap (ACO), also known as Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome (ACOS) is a chronic inflammatory, obstructive airway disease in which features of both asthma and COPD predominate. Asthma and COPD were once thought of as distinct entities, however in some, there are clinical features of both asthma and COPD with significant overlap in pathophysiology and symptom profile. It is unclear whether ACO is a separate disease entity or a clinical subtype of asthma and COPD. The pathogenesis of ACO is poorly understood, but it is thought to involve both type 2 inflammation as well as type 1 inflammation. The incidence and prevalence of ACO are not well known. The risk factors for ACO are also incompletely understood, but tobacco smoke is known to be a major risk factor.