| Abbreviation | FWIC |
|---|---|
| Formation | 1919 |
| Type | Organizations based in Canada with royal patronage |
| Legal status | active |
| Purpose | advocate and public voice, educator and network |
| Headquarters | St. George, Ontario, Canada |
| Location |
|
Region served | Canada |
Membership | 13,000 members |
Official language | English, French |
President | Margaret Byl |
| Website | http://fwic.ca/ |
The Federated Women's Institutes of Canada is an umbrella organization for Women's Institutes in Canada.
"The idea to form a national group was first considered in 1912. In 1914, however, when the war began the idea was abandoned. At the war's end, it was Miss Mary MacIssac, Superintendent of Alberta Women's Institute, who revived the idea. She realized the importance of organizing the rural women of Canada so they might speak as one voice for needed reforms, and the value of co-ordinating provincial groups for a more consistent organization. In February 1919, representatives of the provinces met in Winnipeg, Manitoba, to form the Federated Women's Institutes of Canada." - History of FWIC

Victoria University is a federated university, which forms part of the wider University of Toronto. The school was founded in 1836 by the Wesleyan Methodist Church of Canada as a nonsectarian literary institution. From 1841 to 1890, Victoria operated as an independent degree-granting university, before federating the University of Toronto in 1890, relocating from Cobourg to Toronto.
Corps is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was first named as such in 1805. The size of a corps varies greatly, but two to five divisions and anywhere from 40,000 to 80,000 are the numbers stated by the US Department of Defense.

The Canadian Armed Forces are the unified military forces of Canada, including land, sea, and air commands referred to as the Canadian Army, Royal Canadian Navy, and the Royal Canadian Air Force. The CAF also operates several other commands, including the Canadian Forces Intelligence Command, the Canadian Joint Operations Command, and the Canadian Special Operations Forces Command.
The Women's Institute (WI) is a community-based organization for women in the United Kingdom, Canada, South Africa and New Zealand. The movement was founded in Stoney Creek, Ontario, Canada, by Erland and Janet Lee with Adelaide Hoodless being the first speaker in 1897. It was based on the British concept of Women's Guilds, created by Rev Archibald Charteris in 1887 and originally confined to the Church of Scotland. From Canada the organization spread back to the motherland, throughout the British Empire and Commonwealth, and thence to other countries. Many WIs belong to the Associated Country Women of the World organization.

The Communist Party of Canada is a federal political party in Canada. Founded in 1921 under conditions of illegality, it is the second oldest active political party in Canada, after the Liberal Party of Canada. Although it does not currently have any parliamentary representation, the party's candidates have previously been elected to the House of Commons, the Ontario legislature, the Manitoba legislature, and various municipal governments across the country.

The Senate is one of the two chambers of the bicameral Federal Parliament of Belgium, the other being the Chamber of Representatives. It is considered to be the "upper house" of the Federal Parliament. Created in 1831 as a chamber fully equal to the Chamber of Representatives, it has undergone several reforms in the past, most notably in 1993 and 2014. The 2014 elections were the first without a direct election of senators. Instead, the new Senate is composed of members of community and regional parliaments and co-opted members. It is a chamber of the communities and regions and serves as a platform for discussion and reflection about matters between these federated entities. The Senate today plays a minor role in the federal legislative process. However, the Senate, together with the Chamber, has full competence for the Constitution and legislation on the organization and functioning of the Federal State and the federated entities. Since the reform of 2014, it holds about ten plenary sessions a year.
The women's liberation movement (WLM) was a political alignment of women and feminist intellectualism that emerged in the late 1960s and continued into the 1980s primarily in the industrialized nations of the Western world, which effected great change throughout the world. The WLM branch of radical feminism, based in contemporary philosophy, comprised women of racially and culturally diverse backgrounds who proposed that economic, psychological, and social freedom were necessary for women to progress from being second-class citizens in their societies.
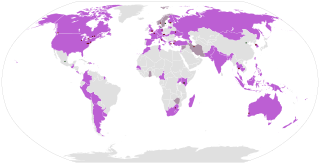
The International Council of Women (ICW) is a women's organization working across national boundaries for the common cause of advocating human rights for women. In March and April 1888, women leaders came together in Washington D.C., with 80 speakers and 49 delegates representing 53 women's organizations from 9 countries: Canada, the United States, Ireland, India, United Kingdom, Finland, Denmark, France and Norway. Women from professional organizations, trade unions, arts groups and benevolent societies participate. National councils are affiliated to the ICW and thus make themselves heard at the international level. The ICW enjoys consultative status with the United Nations and its Permanent Representatives to ECOSOC, ILO, FAO, WHO, UNDP, UNEP, UNESCO, UNICEF, UNCTAD, and UNIDO.

The Royal Architectural Institute of Canada (RAIC) is a not-for-profit, national organization that has represented architects and architecture for over 100 years, in existence since 1907. The RAIC is the leading voice for excellence in the built environment in Canada, demonstrating how design enhances the quality of life, while addressing important issues of society through responsible architecture. The RAIC’s mission is to promote excellence in the built environment and to advocate for responsible architecture. The organization national office is based in Ottawa with a growing federated chapter model. Current chapters and networks are based in British Columbia, Alberta and Nova Scotia.

The Catholic Women's League (CWL) is a Roman Catholic lay organisation founded in 1906 by Margaret Fletcher. Originally intended to bring together Catholic women in England, the organization has grown, and may be found in numerous Commonwealth countries. It is especially flourishing in Canada, Australia, New Zealand and Hong Kong. Membership consists mainly of women who are members of the Roman Catholic Church, and who work together to promote Catholic values and to carry out volunteer and charitable work.
The history of feminism in Canada has been a gradual struggle aimed at establishing equal rights. The history of Canadian feminism, like modern Western feminism in other countries, has been divided by scholars into four "waves", each describing a period of intense activism and social change. The use of "waves" has been critiqued for its failure to include feminist activism of Aboriginal and Québécois women who organized for changes in their own communities as well as for larger social change.

A peace movement is a social movement which seeks to achieve ideals such as the ending of a particular war or minimizing inter-human violence in a particular place or situation. They are often linked to the goal of achieving world peace. Some of the methods used to achieve these goals include advocacy of pacifism, nonviolent resistance, diplomacy, boycotts, peace camps, ethical consumerism, supporting anti-war political candidates, supporting legislation to remove profits from government contracts to the military–industrial complex, banning guns, creating tools for open government and transparency, direct democracy, supporting whistleblowers who expose war crimes or conspiracies to create wars, demonstrations, and political lobbying. The political cooperative is an example of an organization which seeks to merge all peace-movement and green organizations; they may have diverse goals, but have the common ideal of peace and humane sustainability. A concern of some peace activists is the challenge of attaining peace when those against peace often use violence as their means of communication and empowerment.

Erland Lee was a Canadian farmer, teacher, and government employee from Stoney Creek, Ontario. He was a co-founder of the Women's Institutes, an international organization originally formed to promote the education of isolated rural women.

Janet Robertson (Chisholm) Lee (1862–1940) was an important figure in the Niagara Region of Canada, best known for her role in the formation of the Women's Institutes in 1897, and for pioneering the Kindergarten program in Hamilton, Ontario.

The Communist Party of Quebec is a provincial political party in Quebec. It is affiliated with, but officially independent from, the Communist Party of Canada (CPC). The PCQ-PCC publishes the newspaper Clarté.

Margaret Robertson Watt was a Canadian writer, editor and activist. She was a woman of great energy and drive who believed strongly in the power exerted by women working together. She is known to members of Women's Institutes in the United Kingdom for introducing the concepts and practices of the Canadian Women's Institute movement to Britain in 1914. She is remembered internationally as one of the founding members of the Associated Country Women of the World (ACWW) in 1933.

The Federated Women's Institutes of Ontario (FWIO) is a not-for-profit charitable organization with affiliations around the world, working with and for women in Ontario.
Pratima "Tima" Bansal is a Canadian economist and management professor. She is a professor of strategy at the Ivey Business School and director of Ivey's Centre on Building Sustainable Value. She is the founder and executive director of the Network for Business Sustainability, a vehicle aimed at sharing academic research on business sustainability with managers. In April 2020, she was appointed to chair the expert panel on the circular economy by the Council of Canadian Academies.