
Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta (PLEVA) is a disease of the immune system. It is the more severe version of pityriasis lichenoides chronica. The disease is characterized by rashes and small lesions on the skin. The disease is more common in males and usually occurs in young adulthood, although it has been seen in every age group and every race. It is possible for the disease to go into remission for short periods of time or forever.
Ocular rosacea is a manifestation of rosacea that affects the eyes and eyelids. Signs and symptoms generally consist of redness, irritation or burning of the eyes. Affected individuals may also feel that there is something, such as an eyelash, in the eye and frequently have redness of the nose and cheeks as well.
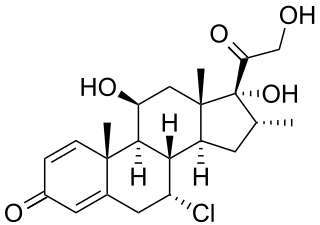
Alclometasone is a synthetic corticosteroid for topical dermatologic use, possessing anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, and vasoconstrictive properties.
ICD-10 is an international statistical classification used in health care and related industries.

Brimonidine is a medication used to treat open-angle glaucoma, ocular hypertension, and rosacea. In rosacea it improves the redness. It is used as eye drops or applied to the skin.

Rhinophyma is a condition causing development of a large, bulbous nose associated with granulomatous infiltration, commonly due to untreated rosacea.
Acne medicamentosa is acne that is caused or aggravated by medication. Because acne is generally a disorder of the pilosebaceous units caused by hormones, the medications that trigger acne medicamentosa most frequently are hormone analogs. It is also often caused by corticosteroids; in this case, it is referred to as steroid acne.
Acneiform eruptions are a group of dermatoses including acne vulgaris, rosacea, folliculitis, and perioral dermatitis. Restated, acneiform eruptions are follicular eruptions characterized by papules and pustules resembling acne. The hybrid term acneiform, literally, refers to an appearance similar to acne.

Steroid-induced rosacea is an iatrogenic condition from the use of either systemic steroid or topical steroids. It is nearly identical to steroid induced acne from the standpoint of etiology.
Steroid acne is an adverse reaction to corticosteroids, and presents as small, firm follicular papules on the forehead, cheeks, and chest. Steroid acne presents with monomorphous pink paupules, as well as comedones, which may be indistinguishable from those of acne vulgaris. Steroid acne is commonly associated with endogenous or exogenous sources of androgen, drug therapy, or diabetes and is less commonly associated with HIV infection or Hodgkin's disease.

Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei (LMDF), also known as acne agminata, is a disease with a similar appearance to acne vulgaris. The cause of LMDF is unknown.
Persistent edema of rosacea is a hard, nonpitting edema found on the areas involved, those mainly being the forehead, glabella, upper eyelids, nose, and/or cheeks.
Gnathophyma involves swelling of the chin. It is a type of lesion associated with rosacea, a common chronic inflammatory skin disorder of the sebaceous glands characterized by redness, swelling, and acne-like pustules.
Metophyma is cushion-like swellings on the forehead above the saddle of the nose.
Otophyma is a cauliflower-like swelling of one or both ears.
Blepharophyma is chronic swelling of eyelids, mainly due to sebaceous gland hyperplasia.
Haber syndrome is a cutaneous disorder of hyperpigmentation characterized by reticulated pigmentation of the person's skin. A rare genodermatosis, its key features include "rosacea-like facial eruption[,] reticulated hyperpigmentation of major flexures, comedones on the back and neck, and pitted facial scars."
Oculocerebrocutaneous syndrome is a condition characterized by orbital cysts, microphthalmia, porencephaly, agenesis of the corpus callosum, and facial skin tags.






